- Преподавателю
- Иностранные языки
- Методическая разработка урока по английскому языку Types and composition of frozen desserts
Методическая разработка урока по английскому языку Types and composition of frozen desserts
| Раздел | Иностранные языки |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Другие методич. материалы |
| Автор | Карибаева Г.И. |
| Дата | 13.12.2015 |
| Формат | doc |
| Изображения | Есть |
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып Тема
Types and composition of frozen desserts.
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of writing skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about frozen desserts.?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
Types and composition of frozen desserts.
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate: Types and composition of frozen desserts
By varying quantities of main ingredients, numerous types of frozen dairy desserts can be produced Ice cream and ice milk. Major components of ice cream are known to be milk fat, nonfat milk solids, sugar, stabilizer, and flavouring. There exist a wide range for producers to vary content of both milk fat and nonfat milk solids, the quantity of one component being increased, thequantity of the other being decreased. Ice cream has the highest fat content, ranging from 10 to 20 percent.
Frozen custard, or French ice cream, is basically the same formula as ice cream except that in finished form it must contain at least 1.4 percent egg yolk2 solids.
Plain ice creams contain colouring and flavouring ingredients (such as vanilla, coffee and maple syrup) no more than 5 percent of their unfrozen volume Ice milk may be more commonly called "light" or "reduced-fat"4 ice cream. It contains between 2 and 7 percent milk fat and at least 11 percent total milk solids.
The first step in ice cream making is formulating a suitable mix, the latter being composed of a combination of dairy ingredients, such as fresh milk and cream, frozen cream, condensed or dried skim, buttermilk, dairy whey, or whey protein concentrate. Sugars may include sucrose, corn syrup, honey, and other syrups. Stabilizers and emulsifiers are added in small amounts to help prevent formation of ice crystals, particularly during temperature fluctuations in storage.
The ice cream mix is pasteurized at no less than 79°C for 25 seconds. The heated mix is typically homogenized in order to assure a smoother body and texture.
After homogenization, the hot mix is quickly cooled to 4.4°C. The mix must age at this temperature for at least four hours to allow the fat to solidify and fat globules to clump1. This ageing process results in quicker freezing and a smoother product.
Semifrozen ice cream leaving the freezer at a temperature between -9° and -5°C is placed in a suitable container and conveyed to a blast freezer4, where temperatures are in the range of -29° to -34°C. Rapid freezing at this stage prevents the formation of large ice crystals and favours a smooth body and texture.
Much of the appeal of ice cream comes from the variety of standard mixes and flavours available throughout the year. Most ice cream manufacturers make a standard mix consisting of milk, cream, sugars, and stabilizers, to which flavours may be added just prior to freezing. There exist various types of flavours, such as high-volume flavours (vanilla, chocolate, strawberry), with large particles (fruit, nuts, cookies, or candy parts), so they are added at different stages of the process.Being kept below -23° C and protected from temperature fluctuations, ice cream and other frozen desserts require no preservatives and have long shelf lives. Airtight6 packaging materials have made it possible to store frozen products for six months or longer without loss of flavour or body and texture.
Sherbets. They are characterized by a sweet but tart flavour and a low content of total milk solids (usually 3 to 5 percent).) Most standards require between 1 and 2 percent milk fat and between 2 and 5 percent total milk solids. Sherbet contains considerably more sugar and less air than ice cream (the target overrun is 30 to 40 percent), and therefore it is heavier and often contains more calories per serving.Ices. Being similar to sherbet, but containing no milk solids, water ices are usually composed of sugar (30 percent), fruit juice (20 percent), flavouring, colour, stabilizer (0.2 to 0.6 percent), citric acid, and water.
Overrun in ices should be approximately 30 percent.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогыРефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Answer the questions:
1) How does condensed milk differ from evaporated milk in the percentage of total milk solids and milk fat?
2) Which type of milk product (condensed/evaporated/dried) can be stored longer?
3) What kinds of dairy products can be dried?
4) What are the most desirable characteristics of frozen dessert?
5) What is the difference between plain and bulky ice creams.
6) What are the characteristics of sherbets?
7) What are ices composed of?
8) What are the steps of ice cream manufacture process?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Read and translate: Types and composition of frozen desserts
By varying quantities of main ingredients, numerous types of frozen dairy desserts can be produced Ice cream and ice milk. Major components of ice cream are known to be milk fat, nonfat milk solids, sugar, stabilizer, and flavouring. There exist a wide range for producers to vary content of both milk fat and nonfat milk solids, the quantity of one component being increased, thequantity of the other being decreased. Ice cream has the highest fat content, ranging from 10 to 20 percent.
Frozen custard, or French ice cream, is basically the same formula as ice cream except that in finished form it must contain at least 1.4 percent egg yolk2 solids.
Plain ice creams contain colouring and flavouring ingredients (such as vanilla, coffee and maple syrup) no more than 5 percent of their unfrozen volume Ice milk may be more commonly called "light" or "reduced-fat"4 ice cream. It contains between 2 and 7 percent milk fat and at least 11 percent total milk solids.
The first step in ice cream making is formulating a suitable mix, the latter being composed of a combination of dairy ingredients, such as fresh milk and cream, frozen cream, condensed or dried skim, buttermilk, dairy whey, or whey protein concentrate. Sugars may include sucrose, corn syrup, honey, and other syrups. Stabilizers and emulsifiers are added in small amounts to help prevent formation of ice crystals, particularly during temperature fluctuations in storage.
The ice cream mix is pasteurized at no less than 79°C for 25 seconds. The heated mix is typically homogenized in order to assure a smoother body and texture.
After homogenization, the hot mix is quickly cooled to 4.4°C. The mix must age at this temperature for at least four hours to allow the fat to solidify and fat globules to clump1. This ageing process results in quicker freezing and a smoother product.
Semifrozen ice cream leaving the freezer at a temperature between -9° and -5°C is placed in a suitable container and conveyed to a blast freezer4, where temperatures are in the range of -29° to -34°C. Rapid freezing at this stage prevents the formation of large ice crystals and favours a smooth body and texture.
Much of the appeal of ice cream comes from the variety of standard mixes and flavours available throughout the year. Most ice cream manufacturers make a standard mix consisting of milk, cream, sugars, and stabilizers, to which flavours may be added just prior to freezing. There exist various types of flavours, such as high-volume flavours (vanilla, chocolate, strawberry), with large particles (fruit, nuts, cookies, or candy parts), so they are added at different stages of the process.Being kept below -23° C and protected from temperature fluctuations, ice cream and other frozen desserts require no preservatives and have long shelf lives. Airtight6 packaging materials have made it possible to store frozen products for six months or longer without loss of flavour or body and texture.
Sherbets. They are characterized by a sweet but tart flavour and a low content of total milk solids (usually 3 to 5 percent).) Most standards require between 1 and 2 percent milk fat and between 2 and 5 percent total milk solids. Sherbet contains considerably more sugar and less air than ice cream (the target overrun is 30 to 40 percent), and therefore it is heavier and often contains more calories per serving.Ices. Being similar to sherbet, but containing no milk solids, water ices are usually composed of sugar (30 percent), fruit juice (20 percent), flavouring, colour, stabilizer (0.2 to 0.6 percent), citric acid, and water.
Overrun in ices should be approximately 30 percent.
Answer the questions:
1) How does condensed milk differ from evaporated milk in the percentage of total milk solids and milk fat?2) Which type of milk product (condensed/evaporated/dried) can be stored longer?
3) What kinds of dairy products can be dried?4) What are the most desirable characteristics of frozen dessert?5) What is the difference between plain and bulky ice creams.6) What are the characteristics of sherbets?7) What are ices composed of?8) What are the steps of ice cream manufacture process?
Types of Frozen Desserts
Ice cream and frozen desserts come in many flavors and types with numerous delicious choices. Whether the flavor is vanilla, chocolate, cookie dough or chocolate chip, ice cream and its related products share certain basic characteristics that are often unknown or misunderstood by us.
Frozen desserts come in many forms. Each of the following types has its own definition, and many are standardized by federal regulations:
Ice Cream
Ice Cream consists of a mixture of dairy ingredients such as milk and nonfat milk, and ingredients for sweetening and flavoring, such as extracts, fruits, nuts and chocolate chips. Functional ingredients, such as stabilizers and emulsifiers, are often included to promote proper texture and enhance the eating experience. By federal law, ice cream must contain at least 10 percent milkfat, before the addition of bulky ingredients, and must weigh a minimum of 4.5 pounds to the gallon.
Frozen Custard or French Ice Cream
Frozen Custard or French Ice Cream must also contain a minimum of 10 percent milkfat, as well as at least 1.4 percent egg yolk solids.
Sherbets
Sherbets have a milkfat content of between 1 and 2 percent, and a slightly higher sweetener content than ice cream. Sherbet weighs a minimum of 6 pounds to the gallon and is flavored either with fruit or other similar ingredients.
Gelato
Gelato has an intense flavor and is served in a semi-frozen state that is similar to "soft serve" ice cream. Italian-style gelato is more dense than ice cream, since it has less air. Typically, gelato has more milk than cream, if any, and also contains sweeteners, egg yolks and flavoring.
Sorbet and Water Ices
Sorbet and Water Ices are similar to sherbets, but contain no dairy ingredients.
Quiescently Frozen Confection
A Quiescently Frozen Confection is a frozen novelty such as a water ice novelty on a stick (e.g. Popsicles).
Frozen Yogurt
Frozen Yogurt consists of a mixture of dairy ingredients such as milk and nonfat milk which have been cultured, as well as ingredients for sweetening and flavoring.
Novelties
Novelties are separately packaged single servings of a frozen dessert (e.g. ice cream sandwiches, fudge sticks and juice bars) that may or may not contain dairy ingredients.
July is National Ice Cream Month
July was designation as National Ice Cream Month by President Ronald Reagan in 1984 and the third Sunday of the month as National Ice Cream Day. President Reagan recognized America's appeal for ice cream -- ice cream is enjoyed by ninety percent of our nation's population -- when making this designation. He stated that these two events should be observed with "appropriate ceremonies and activities."
The United States ice cream industry generates more than 21 billion dollars in annual sales and provides thousands of jobs for our citizens. About 9 percent of all the milk produced by United States dairy farmers is used to produce ice cream, contributing significantly to the economic well-being of the nation's dairy industry.
From Karen's Kitchen has a wonderful selection of recipes for Ice Cream Desserts, Ice Cream Cakes,Ice Cream Pies and Milkshakes to celebrate these two events.
Popular Ice Cream Trends
Popular flavors
Vanilla continues to be America's favorite flavor in ice cream and novelties. This flavor is the most versatile, mixing well with toppings, drinks and bakery desserts. America's top five favorite individual flavors are vanilla, chocolate, butter pecan, strawberry and chocolate chip mint.
Manufacturers, scoop shops and chefs constantly are creating new and exciting flavors for their customers. To keep us looking to see what's next in the freezer case, individual processors often release limited time "seasonal" flavors, such as gingerbread, peppermint or caramel ice cream for the November/December holidays.
Healthy alternatives
While the majority of ice cream products have long been regular-fat products, processors continue to diversify their lines of frozen desserts in order to fit into various lifestyles -- often called "better for you" products. There are now an array of frozen desserts to fit specific dietary needs or wants, such as reduced-fat, fat-free, low-carb, "no sugar added," added calcium or other nutrients, or lactose-free ice cream. Novelty/single-serving products are also an important part of this trend, as some of us prefer the pre-packaged portion when counting calories, carbs or fat grams.
However, most of us are looking for an indulgence when eating ice cream. Therefore, ice cream manufacturers make sure to offer a full selection of premium and superpremium products in innovative flavors and with such mix-ins as cookies, brownies, candies and cake.
Popular brand ingredients added to ice cream
Another important trend for ice cream is the continuing popularity of popular companion products being added to ice cream. There has been an increase in the number of new ice cream products that use ingredients from well-known candy, cookie, fruit and flavoring manufacturers. In particular, novelty manufacturers have placed a strong emphasis on adding popular candy flavors. And, some ice cream manufacturers have teamed up in recent years with popular coffee and chocolate brands to create "ultrapremium" products. Signs indicate that this trend will continue in the future.
Storing And Handling Ice Cream
Ice cream is a perishable product and should be treated carefully. When frozen desserts are exposed to temperatures above 10°F (-12°C), the ice cream's body, texture and flavor are subject to adverse changes. Although homemade and individual manufacturers' recipes yield ice cream of varying consistency and flavor, all ice cream will be affected if improperly handled or stored.
Because of the fluctuating temperatures in most home freezers, if you follow these tips, you will be able to enjoy your ice cream within a month of making at home or purchasing from the supermarket.
The following suggestions on the proper handling and storage of ice cream and frozen desserts will help you enjoy America's favorite treat to the fullest.
At the store
-
Make the ice cream aisle your last stop during your trip to the supermarket.
-
Check the temperature of your grocer's freezer case. it should not be above -20°F (-29°C). If kept at a proper temperature, ice cream will be thoroughly frozen and will feel hard to the touch. If the ice cream is soft, you should bring it to the attention of the store manager.
-
In an open top freezer case, always select ice cream and frozen treats stored below the freezer line.
-
Put ice cream products in the separate section of your grocery cart, or place on top of other groceries.
-
Insulate ice cream products for the ride home. When your groceries are packed, request a freezer bag or additional brown paper bag to insulate your ice cream. Some store are now selling insulated grocery bags for reuse. Use these type of bags for all of your frozen groceries to keep them all frozen.
-
Make the grocery store or ice cream parlor your last errand before going home. This will avoid your ice cream from sitting in a warm car while you are making other stops.
At home
-
Do not allow ice cream to repeatedly soften and re-freeze. When the small ice crystals in ice cream melt and re-freeze, they can eventually turn into large, unpalatable lumps.
-
Your freezer should be set at between -5°F and 0°F (-21°C and -18°C). The ideal serving range is between 6°F and 10°F (-14°C and -12°C).
-
Store ice cream in the main compartment of the freezer. Since the door of your freezer is repeatedly open and shut, do not store ice cream in the freezer door, where ice cream can be subject to more fluctuating temperatures.
-
Keep the ice cream container lid tightly closed when storing in the freezer and make sure the ice cream is covered with plastic wrap or the ice cream carton's protective covering before closing the lid.
-
Don't store ice cream alongside uncovered foods; odors may penetrate the ice cream and affect its flavor. If this cannot be prevented, place ice cream or ice cream carton in a plastic container with a tight lid.
By following these simple suggestions, you can help keep your ice cream and other frozen dessert treats stay as they were when first made -- attractive and delicious!
Tips for Successful Homemade Ice Cream
 Ice Cream is enjoyed by people all over the world. While it is sometimes easier and less-expensive to purchase ice cream from your local supermarket, there is just something extra-special about making homemade ice cream that you can't get from the supermarket.
Ice Cream is enjoyed by people all over the world. While it is sometimes easier and less-expensive to purchase ice cream from your local supermarket, there is just something extra-special about making homemade ice cream that you can't get from the supermarket.
With just a few ingredients -- cream, milk, eggs, sugar, and flavorings -- you can make this fabulous treat at home. Here are some helpful tips to make your homemade ice cream successful.
Make your ice cream the day before serving.
If possible, make your ice cream the day before you plan on serving it. This will allow plenty of time for the ice cream to harden in the freezer, resulting in a smoother and creamier ice cream.
Pre-freeze ice maker bowls
Since the bowls of most ice cream makers take at least 24 hours to freeze, keep them tightly wrapped in a plastic bag in the freezer. Then they will always be ready when you want to make ice cream.
Use only 3 to 4 tablespoons of hot liquid when tempering egg yolks
Regardless of the recipe's instructions, when tempering egg yolks for custard-based ice creams, only pour 3 or 4 tablespoons of hot cream into the yolks before slowly adding them back into the ice cream mixture to avoid the eggs from scrambling.
Use alcohol in moderation in your ice cream mixture
Only use up to 1/4 cup of alcohol per 1 quart of ice cream. Any more will interfere with the ice cream's ability to freeze. To prevent loss of flavor, add the alcohol after the ice cream mixture has cooled.
Add in your extracts when ice cream has cooled
For the best flavor, add the extracts or flavoring oils (vanilla, almond, maple, orange, peppermint, etc.) after the ice cream mixture has cooled.
Strain custard-based mixture before processing
When making egg-based or custard-style ice cream, strain the completed mixture before chilling to remove small chunks of egg that may have scrambled during cooking.
Keep the ice cream mixture cold
Always, place your ice cream mixture in a container and chill it in the refrigerator for 8 hours or overnight. The ice cream mixture freezes quicker and better if you start with a cold mixture in your ice cream maker.
Fill ice cream maker three-quarters full
For best results, only fill the ice cream maker three-quarters full. It is important not to overfill it. If there is too much mixture in the bowl, it will not aerate properly when processed.
Add mix-in just before the churning has completed
To maintain the texture of your mix-ins (chocolate chips, nut, candy pieces), add them during the last minute of churning. The ice cream should already be done, you just want to distribute them evenly into the ice cream.
Toast mix-ins just before adding them to the ice cream
Toast nuts and coconut slivers or cookies, brownies and cakes before adding to your ice cream to extract their full flavor. Using toasted mix-ins help keep their crunchiness and prevents them from becoming soggy in the ice cream.
Store processed ice cream in rectangular containers
Once your ice cream has been processed, store it in the freezer in a shallow, flat, rectangular container. This will promote an even consistency to your ice cream.
Store processed ice cream in a container with a tight fitting lid
Use a rectangular container with a tight fitting lid to prevent odors in the freezer from changing the flavor of the ice cream.
Keep your ice cream covered with plastic wrap
Once the processed ice cream has been placed in a storage container, place a layer of plastic wrap or wax paper over the top of the ice cream before closing the lid. This will prevent ice crystals from forming on your ice cream.
Store ice cream in the main compartment of your freezer
Homemade ice cream is best stored in the main compartment of your freezer where the temperature remains mostly consist. This will keep the ice cream from partially thawing and re-freezing when the freezer door is opened which will help prevent ice crystals from forming on the ice cream.
Consumer your homemade ice cream within a week
Homemade ice cream keeps well in your freezer up to a week. After that, it will begin to lose its creamy texture and flavor.
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып Тема
Evaporation of milk.
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of writing skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Evaporation of milk.?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
Evaporation of milk.
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate: Evaporation of milk.
Evaporated milk is a milk product, usually sold in cans, that is made by removing about 60 percent of the water from ordinary milk.
Evaporated milk can be made from both whole milk or skim milk. In either case, the milk is homogenized and then the water is removed by gently heating it. The evaporated milk product is sealed in cans which are then heated to kill any bacteria in the milk. Thus evaporated milk is actually sterile, which, combined with the fact that it is stored in airtight cans, gives it an extremely long shelf life.
Canned evaporated milk can be stored for at least a year, although you should always check the use-by date printed on the can. Also, don't use any cans that are rusted, dented or bulging. Once you open the can, you should store the milk in the refrigerator, preferably not in the original can but in a glass container, and use it within seven days.
Evaporated milk is enriched with vitamin D. The process of heating the evaporated milk in the cans imparts a slightly sweet flavor to the milk, and it's also just a bit darker in color than ordinary milk. Note that evaporated milk is not the same thing as condensed milk. Condensed milk is also reduced by 60 percent, but it is heavily sweetened and usually used in baking and desserts.
Evaporated milk can be used as a substitute for milk or cream, like in coffee and tea or poured over cereal. Evaporated milk can also be used in recipes that call for milk or cream, such as French toast, mashed potatoes or creamed vegetables like this creamed spinach recipe. You can also use evaporated milk in cream sauces like this basic white sauce.
You could also use evaporated milk for making the white gravy that accompanies this pork cutlet recipe.
Although you can usually use evaporated milk directly from the can in recipes that call for milk, you can convert evaporated milk to back to regular milk simply by diluting it with an equal part of water - so add half a cup of water to half a cup of evaporated milk.
Have a partial can of evaporated milk that you need to use up? Try these ideas:
-
use it in place of the milk or cream in recipes. It works especially well inmashed potatoes, macaroni and cheeseand cream soups
-
add it to coffee or tea for a special treat
-
use it in place of the water in bread recipes to boost the nutritional value
-
reconstitute it (by adding enough water to double the volume). Then, use it like regular milk
-
whip up a basic white sauce
Want to avoid leftovers in the future? Learn how to make your own evaporated milk, and you can make just what you need:
-
How to Make Evaporated Milk
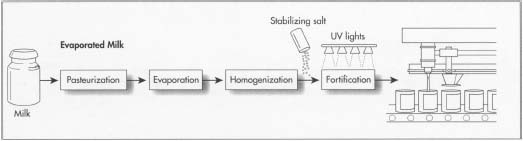 A diagram showing the manufacturing steps involved in making evaporated milk.
A diagram showing the manufacturing steps involved in making evaporated milk.





Canadians have been counting on CarnationEvaporated Milk for
ore than 100 years to make delicious, nutritious treats and meals he whole family asks for again and again. And sinceCarnation Evaporated Milk is thicker and creamier than milk, it's a perfect lower-fat substitute for cream in most recipes.
Try one of these quick and easy recipes. You can tell us what you think by rating recipes. And if you're a member, you can also add a comment and mark your favourites so they're easy to find.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
What does the Invisible Man drink at snack time?
Ответ: Evaporated milk
What did the chocolate bar say to the lollipop?
Ответ: Hello, sucker!
Where is the best place to see a man-eating fish?
Ответ: In a seafood restaurant.
What part of your body has the most rhythm?
Ответ: Your eardrums.
What kind of soda must you not drink?
Ответ: Baking soda.
Why are potatoes good detectives?
Ответ: Because they keep their eyes peeled.
What did the sock say to the foot?
Ответ: You are putting me on!
What clothing does a house wear?
Ответ: Address.
Can giraffes have babies?
Ответ: No, they only have giraffes!
What did Frankenstein say when a bolt of lightning hit him?
Ответ: Thanks, I needed that.
If you dropped a tomato on your toe, would it hurt much?
Ответ: Yes, if it was in a can.
Why does a dentist seem moody?
Ответ: Because he always looks down in the mouth
Why is an eye doctor like a teacher?
Ответ: They both test the pupils
What is both inside and outside a house?
Ответ: Front door.
What can't be burned in fire, nor drowned in water?
Ответ: Ice.
There is a six letter word of which la is the middle, is the beginning, and the ending. What is the word?
Ответ: Island.
What is a little dog's favorite drink?
Ответ: Pupsi-cola
What has a big mouth, yet never speaks?
Ответ: A jar
What is the first thing you do in the morning?
Ответ: Wake up
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып Тема
Cooling and storage of milk.
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Cooling and storage of milk.?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы Актуализация знаний
Cooling and storage of mil
 k
k
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate: Cooling and storage of milk.
Storage of Milk: Importance and Methods of Cooling!
Importance:
Milk drawn from a healthy cow is sterile but it contains bacteria that have entered the teat canal through the teat opening. They are pushed out during milking process. The number of bacteria varies from animal to animal. For milk contains greater number of bacteria than stripping (Singh and Prasad, 1987).
Milk gets easily contaminated with dirt, bacteria and odours. Milk furnishes an excellent medium for the growth of bacteria, particularly when not properly cooled. They produce chemical changes rendering it unpalatable.
Pathogenic bacteria can also very well multiply in milk. Therefore, milk may serve as a medium for dissemination of infectious diseases. Hence the quality and conditions of production of milk can be judged on the basis of microbial contents.
I.S. 1479 (Part III) 1982 prescribed the following standards for the bacteriological quality of raw milk:
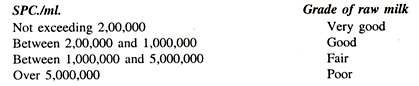
Therefore great care in production and handling of milk is necessary to put it in the hands of consumers in a satisfactory condition.
Handling the Milk Prior To Storage:Milk should be removed to the milk house immediately after it is drawn because the contamination may also take place if it is left in the barn, the milk should then be strained into cans. If the cows are carefully milked, straining may not be necessary.
It is impossible to strain bacteria out of milk. However, it is desirable to filter the milk to remove hairs, particles of feed or bedding or dirt, etc. that may have into milk during the production. A single service pad type strainer may be used for this purpose.
Necessity of Cooling Milk before Storage:It is impossible to produce milk without some bacteria. Therefore efforts should be to prevent multiplication of the bacteria that have gained access.- This can be achieved by cooling the raw milk.
Principles and Practices of Dairy Farm Management:This is of utmost importance specially when considerable time lapses between production and pasteurization. Even before it is transported to long distances the rails is cooled. The influence of temperature of storage on the bacterial density in fresh milk as reported by Ayres et al. (1918) is given in Table 18.1.
Table 18.1: Bacterial Count in Fresh Milk of Storage (Average of 20 Samples from Cows Clean & Bedded, Small Top Pails, Sterile Utensils):
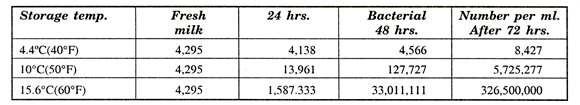
From the observations of Ayres et al. (1918) it is clear that milk should be stored at 4.5°C to arrest the growth of bacteria and milk will not become sour. Cooling to milk has a special significance in the tropical climate specially in summer. Therefore milk should be cooled to below 10°C. Freshly drawn milk is at about 38°C which is highly suited for bacterial growth.
Methods of Cooling:
1. Indigenous method:Milk venders who collect milk from villages are issued licence on the agreement that they will put the wet cloth around the can of milk to keep milk cool during the period of transportation by bicycle or cart, etc.
2. Scientific method:
There are four methods used under this. These are as follows:
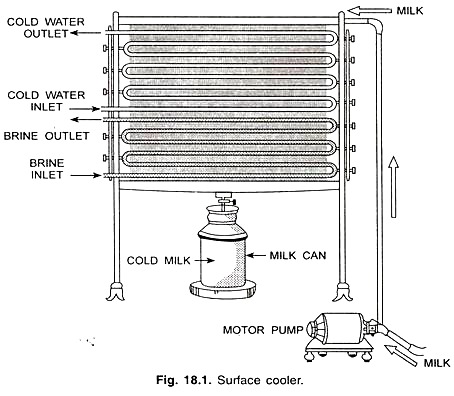
1. Use of surface coolers/surface tubular coolers. (See Fig. 18.1)
2. Cabinet coolers in vertical position.
3. Plate type chillers,
4. Double tube coolers.
The different cooling media used are as follows:
(a) Cold water to cool down pasteurized milk up to 15.5° to 21.1°C.
(b) Ammonia refrigerant to cool down milk up to 3.3°C to 4.3°C (35° to 40°F).
(c) Brine solution is effective in bringing temperature of milk to 3.3°C (35°F).
Storage of Milk in Tanks:
Modern storage tanks for milk are of two type's viz. horizontal and vertical cylindrical shape of 10,000 litre capacity. In countries of temperate climate where milk is not stored for more than 24 hrs. the insulation of tanks is not necessary. In tropical regions of warmer climate 7 to 10 cm cork insulation is desirable to maintain minimum temperature 4°C. Milk kept at low temperature will have longer keeping quality suitable for processing in dairy plant.
Objectives of having Bulk Milk Cooling Units:
1.To enhance the keeping quality of milk and also to avoid economic losses to farmers due to spillage/sourage of milk.
2.To produce improved quality products for export as well as to meet the domestic requirements.
3.To reduce the transportation cost by regulating transportation of the milk on alternative days and also through reduction in expenditure on purchase and maintenance of cans.
Thus,BMCUs provides a viable option for reducing the transportation cost as also maintaining the milk quality.
Beneficiaries of Bulk Milk Cooling Units (BMCUs) are Milk collection Agents,Village Milk Cooperative Societies of Cooperative Milk Union or Milk Collection Centers of private Dairies.
The operations involve collection and chilling of milk to a temperature of 4 Degrees C.
Advantages of using stainless steel Bulk Milk Cooler or Milk Chillers in modern dairy industry:
1.Elimination of souring/curdling of milk because of cooling at the collection center itself.
2.Adulteration of milk and spillage from cans can be eliminated during transport.
3.Transportation cost of milk can be brought down by regulating transportation to the main dairy either on alternative days or once in a day.
4.Saving of initial investment on purchase of cans and subsequent maintenance cost (Repairs, cleaning etc.) of those cans.
5.Improved quality of milk can be supplied to the main dairy to manufacture quality products for domestic as well as export markets.
6.Flexibility in milk collection time results in increase in volume of milk collected at the centers.
7.Farmers will get better returns for the quality of milk.
8.Chilling at the Main dairy can be avoided.
Economics of buying Bulk Milk Coolers:
Based on the various techno commercial parameters,the economics of the purchase of new Bulk Milk Coolers is very positive. The items of income include reduction in souring/curdling of milk, spillage and pilferage of milk, saving of expenditure on transportation, purchase and maintenance of cans and chilling cost received from the union while the expenditure includes the operational cost of cooler (fuel/power), repairs, maintenance and additional manpower.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту Закрепление знаний
Read and translate: Cooling and storage of milk.
Storage of Milk: Importance and Methods of Cooling!
KWL
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
РефлексияCollage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Storage of Milk: Importance and Methods of Cooling!
Importance:Milk drawn from a healthy cow is sterile but it contains bacteria that have entered the teat canal through the teat opening. They are pushed out during milking process. The number of bacteria varies from animal to animal. For milk contains greater number of bacteria than stripping (Singh and Prasad, 1987).
Milk gets easily contaminated with dirt, bacteria and odours. Milk furnishes an excellent medium for the growth of bacteria, particularly when not properly cooled. They produce chemical changes rendering it unpalatable.
Pathogenic bacteria can also very well multiply in milk. Therefore, milk may serve as a medium for dissemination of infectious diseases. Hence the quality and conditions of production of milk can be judged on the basis of microbial contents.
I.S. 1479 (Part III) 1982 prescribed the following standards for the bacteriological quality of raw milk:
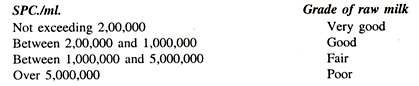
Therefore great care in production and handling of milk is necessary to put it in the hands of consumers in a satisfactory condition.
Handling the Milk Prior To Storage:Milk should be removed to the milk house immediately after it is drawn because the contamination may also take place if it is left in the barn, the milk should then be strained into cans. If the cows are carefully milked, straining may not be necessary.
It is impossible to strain bacteria out of milk. However, it is desirable to filter the milk to remove hairs, particles of feed or bedding or dirt, etc. that may have into milk during the production. A single service pad type strainer may be used for this purpose.
Necessity of Cooling Milk before Storage:It is impossible to produce milk without some bacteria. Therefore efforts should be to prevent multiplication of the bacteria that have gained access.- This can be achieved by cooling the raw milk.
Principles and Practices of Dairy Farm Management:This is of utmost importance specially when considerable time lapses between production and pasteurization. Even before it is transported to long distances the rails is cooled. The influence of temperature of storage on the bacterial density in fresh milk as reported by Ayres et al. (1918) is given in Table 18.1.
Table 18.1: Bacterial Count in Fresh Milk of Storage (Average of 20 Samples from Cows Clean & Bedded, Small Top Pails, Sterile Utensils):

From the observations of Ayres et al. (1918) it is clear that milk should be stored at 4.5°C to arrest the growth of bacteria and milk will not become sour. Cooling to milk has a special significance in the tropical climate specially in summer. Therefore milk should be cooled to below 10°C. Freshly drawn milk is at about 38°C which is highly suited for bacterial growth.
Methods of Cooling:1. Indigenous method:Milk venders who collect milk from villages are issued licence on the agreement that they will put the wet cloth around the can of milk to keep milk cool during the period of transportation by bicycle or cart, etc.

2. Scientific method:
There are four methods used under this. These are as follows:
1. Use of surface coolers/surface tubular coolers. (See Fig. 18.1) 2. Cabinet coolers in vertical position.3. Plate type chillers,4. Double tube coolers.
The different cooling media used are as follows:
(a) Cold water to cool down pasteurized milk up to 15.5° to 21.1°C.(b) Ammonia refrigerant to cool down milk up to 3.3°C to 4.3°C (35° to 40°F).(c) Brine solution is effective in bringing temperature of milk to 3.3°C (35°F).Storage of Milk in Tanks:Modern storage tanks for milk are of two type's viz. horizontal and vertical cylindrical shape of 10,000 litre capacity. In countries of temperate climate where milk is not stored for more than 24 hrs. the insulation of tanks is not necessary. In tropical regions of warmer climate 7 to 10 cm cork insulation is desirable to maintain minimum temperature 4°C. Milk kept at low temperature will have longer keeping quality suitable for processing in dairy plant.
Objectives of having Bulk Milk Cooling Units:
1.To enhance the keeping quality of milk and also to avoid economic losses to farmers due to spillage/sourage of milk.2.To produce improved quality products for export as well as to meet the domestic requirements.3.To reduce the transportation cost by regulating transportation of the milk on alternative days and also through reduction in expenditure on purchase and maintenance of cans.Thus,BMCUs provides a viable option for reducing the transportation cost as also maintaining the milk quality.Beneficiaries of Bulk Milk Cooling Units (BMCUs) are Milk collection Agents,Village Milk Cooperative Societies of Cooperative Milk Union or Milk Collection Centers of private Dairies.The operations involve collection and chilling of milk to a temperature of 4 Degrees C.
Advantages of using stainless steel Bulk Milk Cooler or Milk Chillers in modern dairy industry:1.Elimination of souring/curdling of milk because of cooling at the collection center itself.2.Adulteration of milk and spillage from cans can be eliminated during transport.
3.Transportation cost of milk can be brought down by regulating transportation to the main dairy either on alternative days or once in a day.4.Saving of initial investment on purchase of cans and subsequent maintenance cost (Repairs, cleaning etc.) of those cans.5.Improved quality of milk can be supplied to the main dairy to manufacture quality products for domestic as well as export markets.6.Flexibility in milk collection time results in increase in volume of milk collected at the centers.7.Farmers will get better returns for the quality of milk.8.Chilling at the Main dairy can be avoided.
Economics of buying Bulk Milk Coolers:Based on the various techno commercial parameters,the economics of the purchase of new Bulk Milk Coolers is very positive. The items of income include reduction in souring/curdling of milk, spillage and pilferage of milk, saving of expenditure on transportation, purchase and maintenance of cans and chilling cost received from the union while the expenditure includes the operational cost of cooler (fuel/power), repairs, maintenance and additional manpower.
Read and translate: Cooling and storage of milk.Storage of Milk: Importance and Methods of Cooling!
KWL
Storage of Milk: Importance and Methods of Cooling!
Importance:Milk drawn from a healthy cow is sterile but it contains bacteria that have entered the teat canal through the teat opening. They are pushed out during milking process. The number of bacteria varies from animal to animal. For milk contains greater number of bacteria than stripping (Singh and Prasad, 1987).
Milk gets easily contaminated with dirt, bacteria and odours. Milk furnishes an excellent medium for the growth of bacteria, particularly when not properly cooled. They produce chemical changes rendering it unpalatable.
Pathogenic bacteria can also very well multiply in milk. Therefore, milk may serve as a medium for dissemination of infectious diseases. Hence the quality and conditions of production of milk can be judged on the basis of microbial contents.
I.S. 1479 (Part III) 1982 prescribed the following standards for the bacteriological quality of raw milk:
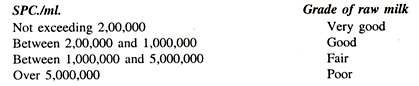
Therefore great care in production and handling of milk is necessary to put it in the hands of consumers in a satisfactory condition.
Handling the Milk Prior To Storage:Milk should be removed to the milk house immediately after it is drawn because the contamination may also take place if it is left in the barn, the milk should then be strained into cans. If the cows are carefully milked, straining may not be necessary.
It is impossible to strain bacteria out of milk. However, it is desirable to filter the milk to remove hairs, particles of feed or bedding or dirt, etc. that may have into milk during the production. A single service pad type strainer may be used for this purpose.
Necessity of Cooling Milk before Storage:It is impossible to produce milk without some bacteria. Therefore efforts should be to prevent multiplication of the bacteria that have gained access.- This can be achieved by cooling the raw milk.
Principles and Practices of Dairy Farm Management:This is of utmost importance specially when considerable time lapses between production and pasteurization. Even before it is transported to long distances the rails is cooled. The influence of temperature of storage on the bacterial density in fresh milk as reported by Ayres et al. (1918) is given in Table 18.1.
Table 18.1: Bacterial Count in Fresh Milk of Storage (Average of 20 Samples from Cows Clean & Bedded, Small Top Pails, Sterile Utensils):

From the observations of Ayres et al. (1918) it is clear that milk should be stored at 4.5°C to arrest the growth of bacteria and milk will not become sour. Cooling to milk has a special significance in the tropical climate specially in summer. Therefore milk should be cooled to below 10°C. Freshly drawn milk is at about 38°C which is highly suited for bacterial growth.
Methods of Cooling:1. Indigenous method:Milk venders who collect milk from villages are issued licence on the agreement that they will put the wet cloth around the can of milk to keep milk cool during the period of transportation by bicycle or cart, etc.

2. Scientific method:
There are four methods used under this. These are as follows:
1. Use of surface coolers/surface tubular coolers. (See Fig. 18.1)2. Cabinet coolers in vertical position.3. Plate type chillers,4. Double tube coolers.
The different cooling media used are as follows:(a) Cold water to cool down pasteurized milk up to 15.5° to 21.1°C.(b) Ammonia refrigerant to cool down milk up to 3.3°C to 4.3°C (35° to 40°F).(c) Brine solution is effective in bringing temperature of milk to 3.3°C (35°F).
Storage of Milk in Tanks:Modern storage tanks for milk are of two type's viz. horizontal and vertical cylindrical shape of 10,000 litre capacity. In countries of temperate climate where milk is not stored for more than 24 hrs. the insulation of tanks is not necessary. In tropical regions of warmer climate 7 to 10 cm cork insulation is desirable to maintain minimum temperature 4°C. Milk kept at low temperature will have longer keeping quality suitable for processing in dairy plant.
Objectives of having Bulk Milk Cooling Units:
1.To enhance the keeping quality of milk and also to avoid economic losses to farmers due to spillage/sourage of milk.2.To produce improved quality products for export as well as to meet the domestic requirements.3.To reduce the transportation cost by regulating transportation of the milk on alternative days and also through reduction in expenditure on purchase and maintenance of cans.
Thus,BMCUs provides a viable option for reducing the transportation cost as also maintaining the milk quality.Beneficiaries of Bulk Milk Cooling Units (BMCUs) are Milk collection Agents,Village Milk Cooperative Societies of Cooperative Milk Union or Milk Collection Centers of private Dairies.The operations involve collection and chilling of milk to a temperature of 4 Degrees C.
Advantages of using stainless steel Bulk Milk Cooler or Milk Chillers in modern dairy industry:
1.Elimination of souring/curdling of milk because of cooling at the collection center itself. 2.Adulteration of milk and spillage from cans can be eliminated during transport. 3.Transportation cost of milk can be brought down by regulating transportation to the main dairy either on alternative days or once in a day.
4.Saving of initial investment on purchase of cans and subsequent maintenance cost (Repairs, cleaning etc.) of those cans.
5.Improved quality of milk can be supplied to the main dairy to manufacture quality products for domestic as well as export markets.
6.Flexibility in milk collection time results in increase in volume of milk collected at the centers.
7.Farmers will get better returns for the quality of milk.
8.Chilling at the Main dairy can be avoided.
Economics of buying Bulk Milk Coolers:
Based on the various techno commercial parameters,the economics of the purchase of new Bulk Milk Coolers is very positive. The items of income include reduction in souring/curdling of milk, spillage and pilferage of milk, saving of expenditure on transportation, purchase and maintenance of cans and chilling cost received from the union while the expenditure includes the operational cost of cooler (fuel/power), repairs, maintenance and additional manpower.
Being the world's largest producer and consumer of dairy products, India represents one of most lucrative dairy markets.
The Indian dairy industry is contributing significantly to the country's economy,besides improving the health standard by increasing the nutritional value of the food.
At 100 million tons of milk production, India is the highest milk producing country in the world. Almost half of milk produced in the country is consumed as raw milk and the rest converted into different dairy products.Since the processed dairy products lacks quality standards and hygiene value, country is unable to export dairy products in large measures. Therefore Indian Dairy industry is looking at Bulk Milk Coolers to reduce the temperature of the milk for minimizing growth of bacteria which in turn would improve shelf life of the milk.
When Milk is extracted,it is at around 37 Degrees C.It milk continues to remain at room temperature after extraction, bacterial growth will affect the quality of the milk.Only rapidly cooling milk immediately after extraction to a temperature of around 4 Degrees C and maintaining it at this temperature minimizes further micro-organism growth.Thereby ensuring that milk remains as fresh as it was when extracted.
Bulk Milk Coolers is used to reduce the temperature of the milk for inimizing growth of bacteria which in turn would improve shelf life of the milk.These coolers rapidly cool milk and also ensure that the quality of milk remains high and keeps milk fresh.
In India,NABARD is also offers financial assistance to Indian dairy industry and dairy owners for purchase of bulk milk coolers,which is an added advantage and reason to buy BMCU.
Objectives of having Bulk Milk Cooling Units:
1.To enhance the keeping quality of milk and also to avoid economic losses to farmers due to spillage/sourage of milk.2.To produce improved quality products for export as well as to meet the domestic requirements.3.To reduce the transportation cost by regulating transportation of the milk on alternative days and also through reduction in expenditure on purchase and maintenance of cans.
Thus,BMCUs provides a viable option for reducing the transportation cost as also maintaining the milk quality.Beneficiaries of Bulk Milk Cooling Units (BMCUs) are Milk collection Agents,Village Milk Cooperative Societies of Cooperative Milk Union or Milk Collection Centers of private Dairies.
The operations involve collection and chilling of milk to a temperature of 4 Degrees C.
Advantages of using stainless steel Bulk Milk Cooler or Milk Chillers in modern dairy industry:
1.Elimination of souring/curdling of milk because of cooling at the collection center itself.
2.Adulteration of milk and spillage from cans can be eliminated during transport.
3.Transportation cost of milk can be brought down by regulating transportation to the main dairy either on alternative days or once in a day.
4.Saving of initial investment on purchase of cans and subsequent maintenance cost (Repairs, cleaning etc.) of those cans.
5.Improved quality of milk can be supplied to the main dairy to manufacture quality products for domestic as well as export markets.
6.Flexibility in milk collection time results in increase in volume of milk collected at the centers.
7.Farmers will get better returns for the quality of milk.
8.Chilling at the Main dairy can be avoided.
Economics of buying Bulk Milk Coolers:Based on the various techno commercial parameters,the economics of the purchase of new Bulk Milk Coolers is very positive. The items of income include reduction in souring/curdling of milk, spillage and pilferage of milk, saving of expenditure on transportation, purchase and maintenance of cans and chilling cost received from the union while the expenditure includes the operational cost of cooler (fuel/power), repairs, maintenance and additional manpower.
Krishna Industries,manufacturer of SS Dairy equipments,offers Bulk milk coolers.There Bulk Milk Cooling Units are Dependable and durable,you can count on years of trouble-free performance, the lowest operating costs,precise temperature control,and a wide range of standard features and options.They specialize in milk cooling and storage systems.
Krishna Industries is Leading ISO 9001:2000 Certified manufacturer and exporter of Dairy equipments ,Stainless Steel Milk Cans,Milking Machines,Milk Buckets, Milk Pails, Stainless Steel Milk Cans,Stainless Steel Milk Collection accessories,Bulk Milk Collers.They offer state of the art products in the ever expanding field of Dairy Equipments.They thrive to deliver the highest quality of products that meets the international standards.
Product
How to Store
Refrigerator (35-40 °F)
Freezer (0 °F)
Pasteurized Fresh Whole or Skimmed Milk
Refrigerate immediately in original container. Keep container closed.
1 to 5 days beyond "sell-by" date
3 months. Freezing may result in change in texture. Thaw in refrigerator.
Sweetened Condensed Milk(Opened)
Refrigerate tightly covered.
1 week
Do not freeze.
Evaporated Milk (Opened)
Refrigerate tightly covered.
1 week
Do not freeze.
Cultured Buttermilk
Refrigerate immediately in original container. Keep container closed.
2 weeks
Do not freeze.
Homogenized, Reconstituted Dry Nonfat and Skimmed Milk
Keep containers tightly closed. Don't return unused milk to original containers.
1 week
Do not freeze.
Sweet and Regular Cream
Refrigerate immediately in original container. Keep container closed.
1 to 5 days beyond "sell-by" date
Do not freeze. (Change of texture, body appearance. Separation of fat emulsion.)
Non-Dairy Whipped Topping
Keep covered.
3 months in aerosol can.
3 days if prepared from mix.
2 weeks if bought frozen and then thawed.
Do not freeze aerosol cans; others may be stored in freezer up to one year.
Butter
Refrigerate immediately in original container. Keep container closed.
2 weeks
Butter made from pasteurized cream: 6 to 9 months.
Sour Cream
Refrigerate immediately in original container. Keep container closed.
2 weeks
Do not freeze.
Ice Cream
Store in original container in freezer.
Do not store here.
2-3 weeks (Opened)
2 months (Unopened)
Yogurt
Keep covered.
7-10 days
Do not freeze.
Soft Custards, Milk Puddings, Cream and Custard Fillings for Cakes and Pies
Cool cooked dishes quickly and refrigerate within 2 hours. Refrigerate cold dishes immediately after preparation.
5-6 days
Do not freeze.
Safe Cold Storage Times for Milk & Dairy Products
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып Тема
Different types of cultured dairy products .
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
-
Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
-
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Different types of cultured dairy products?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу
Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
Different types of cultured dairy products .
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate: Different types of cultured dairy products .
What is cultured milk? Cultured milks are products made by use of special lactic acid bacteria cultures. They fall into two broad categories. Those made by use of lactic acid bacteria which grow well at ambient temperature (25-30°C). Such lactic acid bacteria are known as Mesophilic starter cultures. Maziwa lala or Mala as it is popularly known in Kenya, is made by use of such cultures. The other type of cultured dairy product is the one made by use of lactic acid bacteria which grow well under warm conditions (38 - 45(C) The lactic acid bacteria used are technically known as Thermophilic starter cultures. Yoghurt or yoghurt like products belong to this group.
Types of cultured milk and starter cultures. As mentioned above, cultured dairy products fall in two broad categories; those made by use of mesophilic starter cultures and those made by use of thermophilic starter cultures. Depending on the type of culture used, the flavour, texture and consistency can vary widely and may be grouped as follows: i) Products made by use of mesophilic lactic starter cultures may use one of the following starter culture types: O-type: These are starter cultures in which the main lactic acid bacteria are Lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. These produce mainly lactic acid. They are thus, homofermentative. D-type: These are starter cultures containing, in addition to the O-type bacteria also a flavour producing lactic bacteria known as Streptococcus lactis subsp. lactis var. diacetylactis. This, as the name implies, produces a flavour compound known as diacetyl which gives a flavour characteristic of cultured cream butter or its buttermilk by-product. In addition to production of diacetyl, it also produces carbon dioxide which contributes to the blend of a delicate flavour. L-type: This type of starter culture contain, in addition to the O-type bacteria, also Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides as the main flavour compound producing bacteria. It produces diacetyl, acetic acid, acetaldehyde and other flavour compounds but less carbon dioxide than the Dtype. LD-type: These contain a combination of Str. lactis subsp. lactis var diacetylactis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides to give a fine blend of dedicated flavour and aroma. Most "Maziwa lala" products can be made by use of any of these types of lactic starter cultures. They will all give products differing in flavour and texture. Which ever one chooses to use, care should be taken not to use those that lack the desired flavour or those which halve excessive gas production (good for some cheese, but not entirely welcome in good cultured dairy products!). Excessive production of acetaldehyde can also lead to a defect known as "green flavour" more akin to yoghurt than to "Maziwa lala" group of cultured products. ii) Products made by use of thermophilic starter cultures. The main product in this group is yoghurt. The typical lactic acid bacteria in yoghurt starter culture are Streptococcus salivaricus subsp. thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. The former is responsible for fermenting lactose to lactic acid whereas Lb. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus is responsible for flavour production, mainly in the form of acetaldehyde. Due to its proven health food qualities, other thermophilic lactic acid bacteria may be included in yoghurt starter cultures to enhance its dietetic and health food status. Lactobacillus acidophilus, which produces a natural antibiotic, acidophilin and Bifidobacterium spp., which are part of the natural bacterial flora of the human gut, are often included in special yoghurt starter cultures. Products such as Bioghurt are made by use of such specially blended cultures and are marketed under the banner of "Health foods" useful for the restoration of normal bacterial flora hollowing a course of oral 3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту Закрепление знаний
1.What is cultured milk?
2.Types of cultured milk and starter cultures..
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Read and translate: Different types of cultured dairy products .
What is cultured milk? Cultured milks are products made by use of special lactic acid bacteria cultures. They fall into two broad categories. Those made by use of lactic acid bacteria which grow well at ambient temperature (25-30°C). Such lactic acid bacteria are known as Mesophilic starter cultures. Maziwa lala or Mala as it is popularly known in Kenya, is made by use of such cultures. The other type of cultured dairy product is the one made by use of lactic acid bacteria which grow well under warm conditions (38 - 45(C) The lactic acid bacteria used are technically known as Thermophilic starter cultures. Yoghurt or yoghurt like products belong to this group.
Types of cultured milk and starter cultures. As mentioned above, cultured dairy products fall in two broad categories; those made by use of mesophilic starter cultures and those made by use of thermophilic starter cultures. Depending on the type of culture used, the flavour, texture and consistency can vary widely and may be grouped as follows: i) Products made by use of mesophilic lactic starter cultures may use one of the following starter culture types: O-type: These are starter cultures in which the main lactic acid bacteria are Lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. These produce mainly lactic acid. They are thus, homofermentative. D-type: These are starter cultures containing, in addition to the O-type bacteria also a flavour producing lactic bacteria known as Streptococcus lactis subsp. lactis var. diacetylactis. This, as the name implies, produces a flavour compound known as diacetyl which gives a flavour characteristic of cultured cream butter or its buttermilk by-product. In addition to production of diacetyl, it also produces carbon dioxide which contributes to the blend of a delicate flavour. L-type: This type of starter culture contain, in addition to the O-type bacteria, also Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides as the main flavour compound producing bacteria. It produces diacetyl, acetic acid, acetaldehyde and other flavour compounds but less carbon dioxide than the Dtype. LD-type: These contain a combination of Str. lactis subsp. lactis var diacetylactis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides to give a fine blend of dedicated flavour and aroma. Most "Maziwa lala" products can be made by use of any of these types of lactic starter cultures. They will all give products differing in flavour and texture. Which ever one chooses to use, care should be taken not to use those that lack the desired flavour or those which halve excessive gas production (good for some cheese, but not entirely welcome in good cultured dairy products!). Excessive production of acetaldehyde can also lead to a defect known as "green flavour" more akin to yoghurt than to "Maziwa lala" group of cultured products. ii) Products made by use of thermophilic starter cultures. The main product in this group is yoghurt. The typical lactic acid bacteria in yoghurt starter culture are Streptococcus salivaricus subsp. thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. The former is responsible for fermenting lactose to lactic acid whereas Lb. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus is responsible for flavour production, mainly in the form of acetaldehyde. Due to its proven health food qualities, other thermophilic lactic acid bacteria may be included in yoghurt starter cultures to enhance its dietetic and health food status. Lactobacillus acidophilus, which produces a natural antibiotic, acidophilin and Bifidobacterium spp., which are part of the natural bacterial flora of the human gut, are often included in special yoghurt starter cultures. Products such as Bioghurt are made by use of such specially blended cultures and are marketed under the banner of "Health foods" useful for the restoration of normal bacterial flora hollowing a course of oral.
1.What is cultured milk?
2.Types of cultured milk and starter cultures..
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Milk sterilization.
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of writing skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
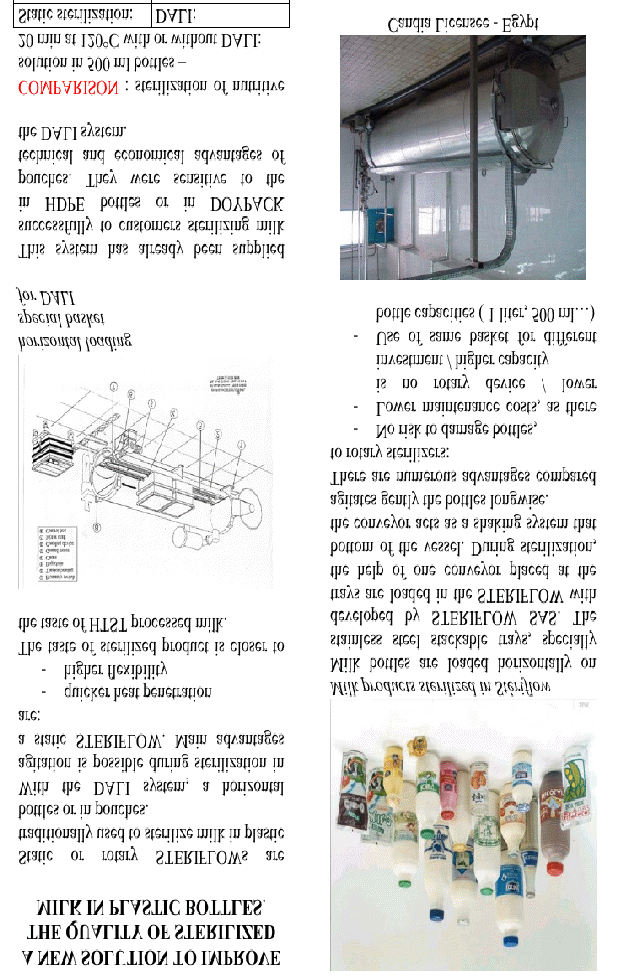
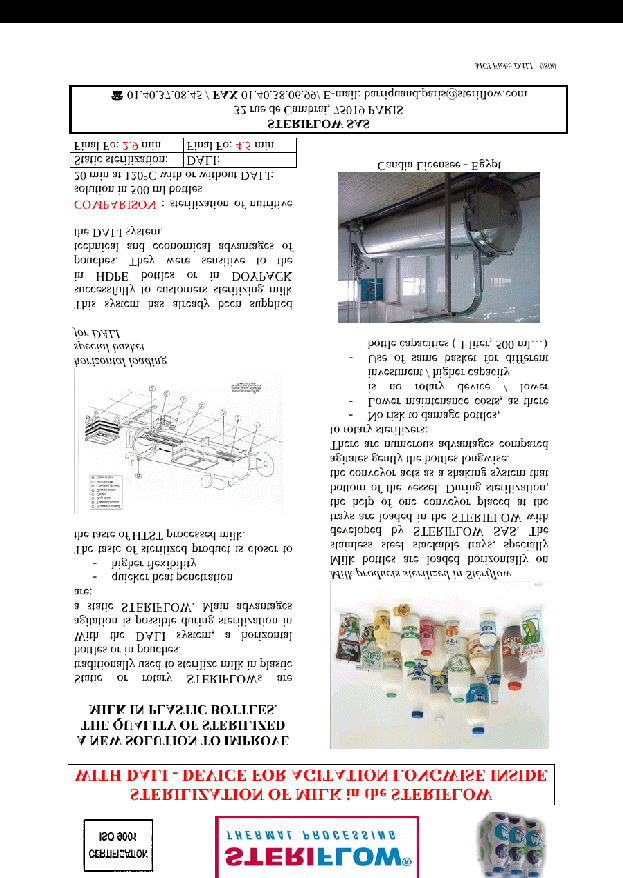
Milk sterilization.
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate: Milk sterilization.
The term "sterilization" when used in association with milk, means heating milk in sealed container continuously to a temperature of either 1150C for 15 minutes or at least 1300C for a period of 1 second or more in a continuous flow and then packed under aseptic condition in hermetically sealed containers to ensure preservation at room temperature for a period not less than 15 days from the date of manufacture (FSSA, 2013).
Sterilization of foods by the application of heat can either be in sealed containers or by continuous flow techniques.
Sterilized milk is kept for a long time so that it will show extensive gravity creaming if unhomogenized. Creaming as such is undesirable. Besides, partial coalescence of the closely packed fat globules will lead to formation of a cream plug, which is hard to mix throughout the remaining milk; oiling off may occur at somewhat elevated temperatures. Therefore, sterilized liquid milk is always homogenized.
Advantages:
(i) Remarkable keeping quality; does not need refrigerated storage;
(ii) No cream layer/plug;
(iii) Forms a soft digestible curd, and hence useful for feeding of infants and invalids;
(iv) Distinction rich flavor (due to homogenization);
(v) Economical to use;
(vi) Less liable to develop oxidized taints.
Disadvantage:
(i) increased cost of production;
(ii) More loss in nutritive value than pasteurization
(iii) Gerber test by normal procedure not so accurate.
Sterilized milk must
(i) Keep without deterioration, i.e., remain stable and be of good commercial value for a sufficient period to satisfy commercial requirement
(ii) Be free of any micro-organisms harmful to consumer health, i.e., pathogenic toxinogenic germs and toxins
(iii) Be free of any micro-organisms liable to proliferate, i.e. it should not show signs of bacterial growth (which leads, inter alia, to an absence of deterioration).
In-bottle sterilization
The raw milk, on receipt, should be strictly examined by the physic-chemical and bacteriological test and only high quality milk should be used for production of sterilized milk. Care should be taken to accept milk supplies which have no developed acidity and which contain the least number of spore-forming bacteria. The intake milk should be promptly cooled to 50C for bulk storage in order to check any bacterial growth. Next, it should be pre heated to 35-400C for efficient filtration/ clarification, so as to remove visible dirt, etc., and to increase its aesthetic quality. The milk should again be cooled to 50C so as to preserve its quality. It should then be standardized to the prescribed percentage of fat and solids-not-fat content in order to conform to legal standards. It must be stored at 50C until processing. The milk should be promptly pre heated to 600C for efficient homogenization to prevent any subsequent formation of a cream layer; usually single-stage homogenization is carried out at 2500 psi pressure. The homogenized milk must be clarified so as to remove the sediment formed during the homogenization process. The hot milk from the homogenizer should be filled into the cleaned and sanitized bottle coming from the bottle washing machine and then sealed with special caps. The filled and capped bottles should then be placed in metal crates for sterilization by the batch process, or fed into conveyors for the continuous process. Usually the milk is sterilized at 108-1110C for 25-35 minutes. The sterilized milk bottles should be gradually cooled to room temperature. Any sudden cooling may led to bottle breakage. Finally the milk-in-bottles should be stored in a cool place (De, 2001).
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту Закрепление знаний
2.Advantages-Disadvantage
3.Collage.
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.Marks.
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание table
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
 The term "sterilization" when used in association with milk, means heating milk in sealed container continuously to a temperature of either 1150C for 15 minutes or at least 1300C for a period of 1 second or more in a continuous flow and then packed under aseptic condition in hermetically sealed containers to ensure preservation at room temperature for a period not less than 15 days from the date of manufacture (FSSA, 2013).
The term "sterilization" when used in association with milk, means heating milk in sealed container continuously to a temperature of either 1150C for 15 minutes or at least 1300C for a period of 1 second or more in a continuous flow and then packed under aseptic condition in hermetically sealed containers to ensure preservation at room temperature for a period not less than 15 days from the date of manufacture (FSSA, 2013).
Sterilization of foods by the application of heat can either be in sealed containers or by continuous flow techniques.
Sterilized milk is kept for a long time so that it will show extensive gravity creaming if unhomogenized. Creaming as such is undesirable. Besides, partial coalescence of the closely packed fat globules will lead to formation of a cream plug, which is hard to mix throughout the remaining milk; oiling off may occur at somewhat elevated temperatures. Therefore, sterilized liquid milk is always homogenized.
Advantages:
(i) Remarkable keeping quality; does not need refrigerated storage;
(ii) No cream layer/plug;
(iii) Forms a soft digestible curd, and hence useful for feeding of infants and invalids;
(iv) Distinction rich flavor (due to homogenization);
(v) Economical to use;
(vi) Less liable to develop oxidized taints.
Disadvantage:
(i) increased cost of production;
(ii) More loss in nutritive value than pasteurization
(iii) Gerber test by normal procedure not so accurate.
Sterilized milk must
(i) Keep without deterioration, i.e., remain stable and be of good commercial value for a sufficient period to satisfy commercial requirement
(ii) Be free of any micro-organisms harmful to consumer health, i.e., pathogenic toxinogenic germs and toxins
(iii) Be free of any micro-organisms liable to proliferate, i.e. it should not show signs of bacterial growth (which leads, inter alia, to an absence of deterioration).
In-bottle sterilization
The raw milk, on receipt, should be strictly examined by the physic-chemical and bacteriological test and only high quality milk should be used for production of sterilized milk. Care should be taken to accept milk supplies which have no developed acidity and which contain the least number of spore-forming bacteria. The intake milk should be promptly cooled to 50C for bulk storage in order to check any bacterial growth. Next, it should be pre heated to 35-400C for efficient filtration/ clarification, so as to remove visible dirt, etc., and to increase its aesthetic quality. The milk should again be cooled to 50C so as to preserve its quality. It should then be standardized to the prescribed percentage of fat and solids-not-fat content in order to conform to legal standards. It must be stored at 50C until processing. The milk should be promptly pre heated to 600C for efficient homogenization to prevent any subsequent formation of a cream layer; usually single-stage homogenization is carried out at 2500 psi pressure. The homogenized milk must be clarified so as to remove the sediment formed during the homogenization process. The hot milk from the homogenizer should be filled into the cleaned and sanitized bottle coming from the bottle washing machine and then sealed with special caps. The filled and capped bottles should then be placed in metal crates for sterilization by the batch process, or fed into conveyors for the continuous process. Usually the milk is sterilized at 108-1110C for 25-35 minutes. The sterilized milk bottles should be gradually cooled to room temperature. Any sudden cooling may led to bottle breakage. Finally the milk-in-bottles should be stored in a cool place (De, 2001).
Sterilizers may be: (i) Batch; (ii) Continuous.
(i) Batch Sterilizers
These may either be rotary or non-rotary in type. The batch sterilizers are rectangular, horizontal, boiler shaped retorts with a steam inlet and condensate outlet, fitted with clamp-down covers, into which steam is adjusted for the required temperature and time for sterilization.
Advantages
Simplicity and flexibility of operation
Less initial capital and recurring expenditure
Disadvantages
1. Usually produces a brownish appearance and cooked taste in the finished product.
2. Sterilization may be faulty
3. Cooling has to be slow to avoid breakage
4. Economic advantages of large-scale processing are not obtained.
In the batch-rotary type, the filled bottles are put in to holders which are rotated at 6-7 rpm. The sterilized milk is of a slightly better quality in rotary-type sterilizers than in non-rotary ones.
(ii) Continuous sterilizers
In this type, the filled and sealed milk bottles are automatically placed by means of a slat conveyor in to the pockets of carrier cages. They then passed into water at or near boiling temperature; from there, they enter the sterilizing zone, which consists of a steam chamber at 108-1110C. Here the bottles remain for a pre-determined time, viz., 25-30 minutes, for milk sterilization
Cooling
After heat treatment in the batch/tank sterilizers, the milk bottles may be cooled in air or water. If cooling is too rapid, the bottles may crack; if too slow, there is a danger of browning due to caramelization. In the continuous system, after leaving the sterilizing zone, the bottles enter a column of hot water where the cooling process begins. This is followed by their passage through another tank of water for further cooling, and lastly through a shallow tank of cold water for final cooling. The bottles are then automatically discharged and conveyed to a point where they are placed in crates in which they are transferred to the storage room.Sterilization of milk is aimed at killing all microorganisms present, including bacterial spores, so that the packaged product can be stored for a long period at ambient temperature, without spoilage by microorganisms. Since molds and yeasts are readily killed, we are only concerned about bacteria. To that end, 30 min at 110°C (in-bottle sterilization), 30 sec at 130°C, or 1 s at 145°C usually suffices. The latter two are examples of so-called UHT (ultra-high-temperature, short time) treatment. Heating for 30 min at 110°C inactivates all milk enzymes, but not all bacterial lipases and proteinases are fully inactivated; it causes extensive Maillard reactions, leading to browning, formation of a sterilized milk flavor, and some loss of available lysine; it reduces the content of some vitamins; causes considerable changes in the proteins including casein; and decreases the pH of the milk by about 0.2 unit. Upon heating for 1 s at 145°C chemical reactions hardly occur, most serum proteins remain unchanged, and only a weak cooked flavour develops. It does not inactivate all enzymes, e.g., plasmin is hardly affected and some bacterial lipases and proteinases not at all, and therefore such a short heat treatment is rarely applied (Brennan and Grandison 2008).
The undesirable secondary effects of in-bottle sterilization like browning, sterilization flavor, and losses of vitamins can be diminished by UHT sterilization. During packaging of UHT-sterilized milk, contamination by bacteria has to be rigorously prevented. After UHT sterilization, certain enzymatic reactions and physicochemical changes still may occur.
Sterilized milk may be defined as (homogenized) milk which has been heated to a temperature of 1000C or above for such lengths of time that it remain fit for human consumption for at least 7 days at room temperatures. Commercially sterilized milk is rarely sterile in the strict bacteriological sense. This is because the requirement for complete sterility conflict with the consumer preference for normal color and flavor in the sterilized product. The spore -forming bacteria in raw milk, which are highly heat-resistant, survive the sterilization temperature-time employed in the dairy and ultimately lead to the deterioration of sterilized milk (De, 2001).
FSSA definition
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып Тема
Pasteurization.
Мақсат Цели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of writing skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Pasteurization of milk?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы Актуализация знаний
Complete the sentences using the words given below: 1. Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually ... . 2. ... is churned from cream. 3. Ice cream is the ... product. 4. Cheese is the product made from ... . 5. Industry processing milk is called ... industry. 6. After separation whole milk is separated into two fractions: .. and .. . 7. Clarifiers have one pipe for ... milk.
1. curd; 2. pasteurized; 3. whole; 4. cream; 5. butter; 6. dairy, 7. skim milk; 8. frozen
 Pasteurization of milk
Pasteurization of milk
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate: Pasteurization of milk
The value of heat for the preservation of foods has been known for thousands of years, but it was not realized until the 19th century that a very mild heat treatment, far below the boiling-point, made liquid foods such as milk keep much longer. The discovery followed the work of the French scientist Pasteur on wine and beer. The process, called after him "pasteurization", is a carefully controlled mild-heat treatment. It was found that the process served two purposes: it prevented the souring of milk, and it destroyed the dangerous disease germs which occur in some samples of milk.
Milk is rendered free of pathogenic bacteria by pasteurization. Milk is heated to a specified temperature and held at that temperature for a specified time. (145°F for 30 min when milk is pasteurized in a vat or at least 161°F for 15 sec when milk is pasteurized continuously).
Pasteurization on a batch operation requires a jacketed vat where steam or hot water can circulate and heat the milk. This treatment requires the longer times at lower temperatures to accomplish pasteurization (LTLT pasteurizer). Modern methods of processing milk and milk products utilize the high-temperature short-time (HTST) pasteurizer.
In Europe and to a limited amount in the United States, milk and milk products may be ultra-heat-treated (UHT). This process may use equipment similar to that used for HTST. The UHT processing requires a minimum heat treatment of 280°F for 2 sec. UHT dairy foods have extended shelf-life because all of the bacteria that would survive even HTST pasteurization have been destroyed.
How a pasteurizer works
A typical pasteurizer is completely automatic. You pour milk in one end and it flows between a set of heating pipes or plates for a set period of time (long enough to kill off most of the harmful bacteria), then between a set of cooling pipes, before emerging from an outlet pipe into the bottles:
Heating and cooling times and temperatures vary according to the type of pasteurization process being used.
Who invented the pasteurizer?
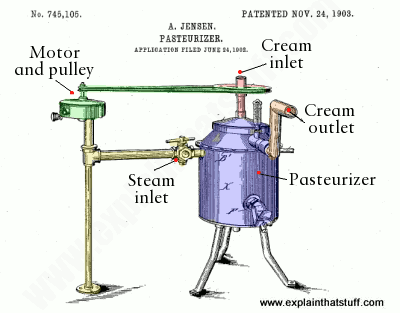
Steam pasteurizer: A typical early pasteurizing machine, developed by Aage Jensen of Topeka, Kansas in 1903. This one uses a steam-driven motor and pulley (green) to power an agitator that turns the cream inside a cylinder (blue) at several hundred times a minute. The exhaust steam from the motor feeds into the cylinder to heat and pasteurize the cream
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words:
1. Кратковременный метод при высокой температуре. 2. Тепловая обработка молока при сверхвысокой температуре. 3. Метод длительной тепловой обработки молока при температуре.
1. LTLT; 2. HTST; 3. UHT
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание table
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Complete the sentences using the words given below:
1. Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually ... . 2. ... is churned from cream. 3. Ice cream is the ... product. 4. Cheese is the product made from ... . 5. Industry processing milk is called ... industry. 6. After separation whole milk is separated into two fractions: .. and .. . 7. Clarifiers have one pipe for ... milk.
1. curd; 2. pasteurized; 3. whole; 4. cream; 5. butter; 6. dairy, 7. skim milk; 8. frozen
Read and translate: Pasteurization of milk
The value of heat for the preservation of foods has been known for thousands of years, but it was not realized until the 19th century that a very mild heat treatment, far below the boiling-point, made liquid foods such as milk keep much longer. The discovery followed the work of the French scientist Pasteur on wine and beer. The process, called after him "pasteurization", is a carefully controlled mild-heat treatment. It was found that the process served two purposes: it prevented the souring of milk, and it destroyed the dangerous disease germs which occur in some samples of milk.
Milk is rendered free of pathogenic bacteria by pasteurization. Milk is heated to a specified temperature and held at that temperature for a specified time. (145°F for 30 min when milk is pasteurized in a vat or at least 161°F for 15 sec when milk is pasteurized continuously).
Pasteurization on a batch operation requires a jacketed vat where steam or hot water can circulate and heat the milk. This treatment requires the longer times at lower temperatures to accomplish pasteurization (LTLT pasteurizer). Modern methods of processing milk and milk products utilize the high-temperature short-time (HTST) pasteurizer.
In Europe and to a limited amount in the United States, milk and milk products may be ultra-heat-treated (UHT). This process may use equipment similar to that used for HTST. The UHT processing requires a minimum heat treatment of 280°F for 2 sec. UHT dairy foods have extended shelf-life because all of the bacteria that would survive even HTST pasteurization have been destroyed.
How a pasteurizer works
A typical pasteurizer is completely automatic. You pour milk in one end and it flows between a set of heating pipes or plates for a set period of time (long enough to kill off most of the harmful bacteria), then between a set of cooling pipes, before emerging from an outlet pipe into the bottles:
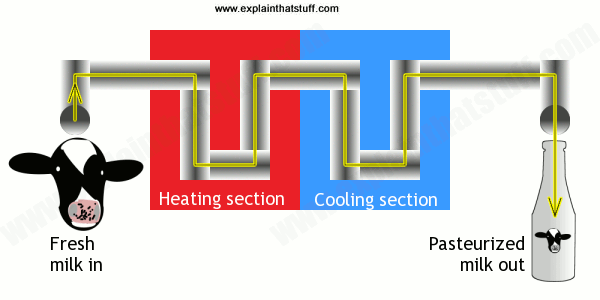
Heating and cooling times and temperatures vary according to the type of pasteurization process being used.
Who invented the pasteurizer?

Steam pasteurizer: A typical early pasteurizing machine, developed by Aage Jensen of Topeka, Kansas in 1903. This one uses a steam-driven motor and pulley (green) to power an agitator that turns the cream inside a cylinder (blue) at several hundred times a minute. The exhaust steam from the motor feeds into the cylinder to heat and pasteurize the cream
Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words:
1. Кратковременный метод при высокой температуре. 2. Тепловая обработка молока при сверхвысокой температуре. 3. Метод длительной тепловой обработки молока при температуре.
1. LTLT; 2. HTST; 3. UHT
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып Тема
Milk processing.
Мақсат Цели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
Тәрбиелік Воспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Combined lesson.Lesson formation of writing skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
text,words
Сабақтын барысы
Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about the milk?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
In 1873 Milton Snavely Hershey founded a candy shop in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. 6 years later it grew into Lancaster Caramel Company, whose use of fresh milk in caramels was a success. I n 1900, Hershey sold his caramel company for $1,000,000 (equal to $26,312,000 today) and began to concentrate on chocolate manufacturing.
Milton built a milk-processing plant in the year 1896, so he could create a recipe for milk chocolate candies. Three years later, he developed the Hershey process which is less sensitive to milk quality than traditional methods. In 1903, Hershey began construction of a chocolate plant in his hometown,
Derry Church. The milk chocolate bars manufactured at this plant proved successful, and the company grew rapidly. In 1907, Hershey introduced a new candy, small flat-bottomed conical-shaped pieces of chocolate that he named "Hershey's Kiss". Initially they were individually wrapped by hand. Since 1921 it is done by wrapping machine that adds a small paper ribbon to the top to say that it was a genuine Hershey product. Now, 80 million of the candies are produced each day.
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау)
Изложение нового материала
MILK PROCESSING
I. DAIRY PRODUCTS
Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually pasteurized, that is subjected to a temperature of 61.7°C for at least 30 min or 71.7°C for 15 sec, and then cooled and bottled. The importance of safety and cleanliness is stressed in the dairy industry. Milk may also be condensed or evaporated, dried, powdered, or separated into skim milk and cream.
Butter is churned from cream. Margarines are similar to butter but made of hydrogenated fats, usually vegetable in origin, with added butter-type flavours and colouring.
Ice cream is the frozen product made from a combination of milk products (cream, butter, or milk - either whole or evaporated, condensed, skimmed, or dried) and two or more of the following in-gredients: eggs, water, and sugar, with flavouring and colouring matter. In the manufacture of ice cream, freezing is accompanied by agitation of the ingredients to avoid crystallization and to incorporate air for proper texture.
Cheese is the product made from curd obtained from the whole, partly skimmed, or skimmed milk of cows or other animals, with or without added cream.
Many fermented products are produced from milk. These fermentations require the use of bacteria that ferment lactose or milk sugar.
II.COMMERCIAL PROCESSING OF MILK
Most raw milk collected at farms is pumped from stainless steel tanks into tank trucks for delivery to processing plants. Collection and intake.
The truck drivers are required to check flavour, temperature, and volume of milk in the farm tank and to collect a sample of raw milk for analysis before pumping the milk into the truck. At the receiving station of the processing plant the milk in the farm truck is weighed and pumped into the plant through flexible plastic and stainless steel pipelines. Separation and clarification.
The actual processing of raw milk begins with either separation or clarification. These machines are essentially similar except that in the clarifier the cream and skim milk fractions are not separated.
Separators have two discharge pipes, one for cream and one for skim milk. Clarifiers have only one pipe for whole milk. Separators have a device called cream screw by which the fat content in the cream is regulated. This screw allows more or less cream to pass out through the discharge pipe.
Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words:
для доставки на перерабатывающее предприятие; брать образец сырого молока на анализ; сепарация и очистка; порции сливок и обезжиренного молока; две отводные трубы; содержание жира в сливках; большее или меньшее количество сливок
Complete the sentences using the words given below:
1. Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually ... . 2. ... is churned from cream. 3. Ice cream is the ... product. 4. Cheese is the product made from ... . 5. Industry processing milk is called ... industry. 6. After separation whole milk is separated into two fractions: .. and .. . 7. Clarifiers have one pipe for ... milk.
1. curd; 2. pasteurized; 3. whole; 4. cream; 5. butter; 6. dairy, 7. skim milk; 8. frozen
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words:
для доставки на перерабатывающее предприятие; брать образец сырого молока на анализ; сепарация и очистка; порции сливок и обезжиренного молока; две отводные трубы; содержание жира в сливках; большее или меньшее количество сливок
Complete the sentences using the words given below:
1. Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually ... . 2. ... is churned from cream. 3. Ice cream is the ... product. 4. Cheese is the product made from ... . 5. Industry processing milk is called ... industry. 6. After separation whole milk is separated into two fractions: .. and .. . 7. Clarifiers have one pipe for ... milk.
1. curd; 2. pasteurized; 3. whole; 4. cream; 5. butter; 6. dairy, 7. skim milk; 8. frozen
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия What have you known?Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание Collage
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
In 1873 Milton Snavely Hershey founded a candy shop in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. 6 years later it grew into Lancaster Caramel Company, whose use of fresh milk in caramels was a success. I n 1900, Hershey sold his caramel company for $1,000,000 (equal to $26,312,000 today) and began to concentrate on chocolate manufacturing.
Milton built a milk-processing plant in the year 1896, so he could create a recipe for milk chocolate candies. Three years later, he developed the Hershey process which is less sensitive to milk quality than traditional methods. In 1903, Hershey began construction of a chocolate plant in his hometown,
Derry Church. The milk chocolate bars manufactured at this plant proved successful, and the company grew rapidly. In 1907, Hershey introduced a new candy, small flat-bottomed conical-shaped pieces of chocolate that he named "Hershey's Kiss". Initially they were individually wrapped by hand. Since 1921 it is done by wrapping machine that adds a small paper ribbon to the top to say that it was a genuine Hershey product. Now, 80 million of the candies are produced each day. Read and translate the text :
MILK PROCESSING
I. DAIRY PRODUCTS
Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually pasteurized, that is subjected to a temperature of 61.7°C for at least 30 min or 71.7°C for 15 sec, and then cooled and bottled. The importance of safety and cleanliness is stressed in the dairy industry. Milk may also be condensed or evaporated, dried, powdered, or separated into skim milk and cream.
Butter is churned from cream. Margarines are similar to butter but made of hydrogenated fats, usually vegetable in origin, with added butter-type flavours and colouring.
Ice cream is the frozen product made from a combination of milk products (cream, butter, or milk - either whole or evaporated, condensed, skimmed, or dried) and two or more of the following in-gredients: eggs, water, and sugar, with flavouring and colouring matter. In the manufacture of ice cream, freezing is accompanied by agitation of the ingredients to avoid crystallization and to incorporate air for proper texture.
Cheese is the product made from curd obtained from the whole, partly skimmed, or skimmed milk of cows or other animals, with or without added cream.
Many fermented products are produced from milk. These fermentations require the use of bacteria that ferment lactose or milk sugar.
II.COMMERCIAL PROCESSING OF MILK
Most raw milk collected at farms is pumped from stainless steel tanks into tank trucks for delivery to processing plants. Collection and intake.
The truck drivers are required to check flavour, temperature, and volume of milk in the farm tank and to collect a sample of raw milk for analysis before pumping the milk into the truck. At the receiving station of the processing plant the milk in the farm truck is weighed and pumped into the plant through flexible plastic and stainless steel pipelines. Separation and clarification.
The actual processing of raw milk begins with either separation or clarification. These machines are essentially similar except that in the clarifier the cream and skim milk fractions are not separated.
Separators have two discharge pipes, one for cream and one for skim milk. Clarifiers have only one pipe for whole milk. Separators have a device called cream screw by which the fat content in the cream is regulated. This screw allows more or less cream to pass out through the discharge pipe.
Find the English equivalents to the following Russian words:
для доставки на перерабатывающее предприятие; брать образец сырого молока на анализ; сепарация и очистка; порции сливок и обезжиренного молока; две отводные трубы; содержание жира в сливках; большее или меньшее количество сливок
Complete the sentences using the words given below:
1. Fluid milk for commercial distribution is usually ... . 2. ... is churned from cream. 3. Ice cream is the ... product. 4. Cheese is the product made from ... . 5. Industry processing milk is called ... industry. 6. After separation whole milk is separated into two fractions: .. and .. . 7. Clarifiers have one pipe for ... milk.
1. curd; 2. pasteurized; 3. whole; 4. cream; 5. butter; 6. dairy, 7. skim milk; 8. frozen
Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Йогурт
Yoghurt
Маргарин
Margarine
Масло кукурузное
Maize (corn) oil
подсолнечное
sunflower
прованское
olive
Масло сливочное
butter
топленое
clarified
Молоко
Milk
Молоко консервированное
Tinned (canned milk)
Молоко кислое
Sour milk
Молоко цельное
Whole milk
Мороженое
Ice-cream
Простокваша
Sour milk
Сливки
Cream
Сметана
Sour cream
Сыр
Cheese
Сыр плавленый
Processed cheese
Творог
Curds, cottage cheese
Яйца
Eggs
Бисквит
Sponge-cake
Варенье
Jam
Вафли
Wafer, wafer-cake
Джем
Jam
Карамель
Caramel
Конфеты
Candy, sweets {англ.)
Мармелад
Fruit jellies
Пастила
Fruit fudge, pastila
Печенье
Biscuits, cookies {USA)
Повидло
Jam
Шоколад
Chocolate
Шоколадные конфеты
Chocolates
Бисквит
Sponge-cake
Булка сдобная
Bun
Булочка
Roll
Вермишель
Vermicelli
Дрожжи
Yeast
Лапша
Noodle
Макароны
Macaroni
Мука
Flour
Печенье
Biscuit
Пирог
Pie
Пирожное
Fancy cake, pastry
Слойка
Puff
Сухари
Rusks
Торт
Cake
Горох
Peas
Горох лущеный
Speit peas
Гречка
Buckwheat
Зерно
Grain
Крупа
Groats, cereals
Кукуруза
Maize, corn (USA)
Кукурузные хлопья
Cornflakes
Манная крупа
Semolina
Овсяная крупа
Oatsmeal
Перловая крупа
Pearl-barley
Пшеница
Wheat
Пшено
Millet
Рис
Rice
Соя
Soya
Фасоль
Beans
Чечевица
Lentil
Ячмень
Barley
Ячневая крупа
Fine-barley
Апельсиновый напиток
Fanta
Апельсиновый сок
Orange juice
Безалкогольные напитки
Soft drinks
Вермут
Vermuth
Вино
Wine
Вино сладкое
Sweet wine
Вино сухое
Dry wine
Виски
Whisky
Водка
Vodka
Джин
Gin
Какао
Cocoa
Квас
Kvass
Кока
Coca
Кока-кола
Coca-cola
Коктейль
Cocktail
Коньяк
Cognac, brandy
Кофе
Coffee
Кофе растворимый
Instant coffee
Крепкие напитки
Strong drinks
Лимонад
Lemonade, Seven-up
Ликер
Liqueur
Минеральная вода
Mineral water
Молоко
Milk
Мороженое
Ice cream
Пепси
Pepsi
Пепси-кола
Pepsi-cola
Пиво
Beer
Повидло
Jam
Портвейн
Portwine
Ром
Rum
Севенап
Seven-up
Содовая вода
Soda-water
Спирт
Spirit
Тоник
Tonic-water
Чай
Tea
Шампанское
Champagne
Шоколадный напиток
Chocolate
Ванилин
Vanilla
Горчица
Mustard
Имбирь
Ginger
Корица
Cinnamon
Лавровый лист
Laurel (bay leaves)
Мускатный орех
Nutmeg
Перец
Pepper
Сахар
Sugar
Соль
Salt
Соус
Souce
Соус соевый
Soya souce
Уксус
Vinegar
Уксусная кислота
Vinegar acid
Хрен
Horse-radish
Антрекот
Entrecote
Бифштекс
Beefsteak
Булочка с сосиской
Hot dog
Бутерброд
Sandwich
Ветчина
Ham
Говядина
Beef
Грудинка
Bacon
Жаркое
Roast meat
Икра
Caviar
Каша
Porridge
Котлеты
Cutlet
Креветки
Shrimp
Кролик
Rabbit
Мозги
Brains
Мороженое
Ice cream
Мясо с картофелем
Hot-pot
Овсяная каша
Oatmeal porridge
Омлет
Omelet(te)
Отбивная котлета
Chop
Паштет
Pie; pate; paste
Печенка
Liver
Пирожное
Pastry
Почки
Kidneys
Пудинг
Pudding
Рагу
Stew, ragout
Сардельки
Paris (small sausages)
Сосиски
Frankfurters
Соус
Sauce
Суп
Soup
Телятина
Veal
Тефтели
Meat-balls
Угорь
Sels
Цыпленок
Chicken
Шницель
Schnitzel, cutlet
Эскалоп
Escalope, pork chop
Язык
Tongue
Яичница
Fried eggs (omelet)
Фирменное блюдо
Special dish
Первое блюдо
First course
Второе блюдо
Second course
Горячее блюдо
Hot dish
Холодная закуска
Cold hors d'oeuvre (snacks)
Холодное блюдо
Cold dish
Сладкое блюдо
Sweet dish
Мясное блюдо
Meat dish
Рыбное блюдо
Fish dish
Акула
Shark
Глось
Flounder
Икра зернистая
Caviar in grain
Икра кетовая
Salmons caviar
Икра паюсная
Pressed caviar
Кальмары
Calimars
Камбала
Plaice, bril, flat-fish
Карп
Carp
Кефаль
Grey mullet
Корюшка
Smelt
Лещ
Bream
Лосось
Salmon
Мерлан
Whiting
Минога
Sea lamprey
Окунь
Perch
Осетр
Sturgeon
Осьминог
Octopus
Палтус
Turbot
Рыба
Fish
Рыба вяленая
Dried fish
Рыба жареная
Fried fish
Рыба консервированная
Canned fish
Рыба копченая
Smoked fish
Рыба соленая
Salt fish
Сазан
Wild carp
Сардины
Sardines
Сельдь
Herrings
Сельдь копченая
Smoked herrings, kippers
Семга, лосось
Salmon
Скумбрия
Mackerel
Сом
Sheat fish
Ставрида
Horse-mackerel
Судак
Rine perch, zender
Треска
Cod
Тунец
Tuna
Устрицы
Oysters
Форель
Trout
Шпроты
Sprats
Щука
Pike
Баранина
Mutton
Бок
Flank
Бока
Sides
Ветчина, окорок
Ham
Вол
Ox
Вырезка
Striplion
Говядина
Beef
Грудинка копченая
Bacon
Гусь
Goose (geese)
Жирное мясо
Fat meat
Задки
Rumps
Задняя часть
Tail
Индейка
Turkey cock
Колбаса
Sausage
Кролик
Rabbit
Куропатка
Partridge
Мозги
Brains
Мороженое мясо
Chilled meat
Мясной фарш
Minced meat
Мясо
Meat
Нога
Leg
Ножки
Trotters
Огузок
Rump
Печень
Liver
Поросенок молочный
Sucking pig
Почки
Kidney
Птица домашняя
Pouitry
Рубец
Tripe
Рубленое (молотое) мясо
Lains
Сало
Fat
Сало внутреннее
Suet
Сало топленое
Lard
Сардельки
Chain-sausage
Свинина
Pork
Сердце
Heart
Сосиски
Hot dogs. frankfurters
Утка
Duck
Фазан
Pheasant
Фарш
Minced meat, stuffing
Фарш мясной
Minced meat
Филейная часть
Loin
Цыплята
Chicken
Ягненок
Lamb
Язык
Tongue
Абрикосы
Apricots
Айва
Ouince
Ананасы
Pineapples
Апельсины
Oranges
Бананы
Bananas
Брусника
Red blueberry
Виноград
Grapes
Вишня
Cherries
Гранаты
Pomegranates
Грейпфруты
Grape-fruits
Груши
Pears
Ежевика
Blackberry
Земляника
Wild strawberry
Изюм
Raisin(s)
Инжир
Figs
Каштаны
Chestnuts
Клубника
Strawberry
Лимоны
Lemon
Малина
Raspberry
Манго
Mango
Мандарины
Tangerines
Облепиха
Sea-buckthorn
Орехи
Nuts
Орехи грецкие
Walnuts
Орехи мускатные
Nutmegs
Персики
Peaches
Сливы
Plums
Смородина
Currant
Сухофрукты
Dry fruits
Финики
Dates
Чернослив
Prune
Шафран
Saffron
Шиповник
Sweet-brier, dog-rose
Яблоки
Apples
Арбузы
Watermelons
Баклажаны
Egg plants
Бурак
Beet
Грибы
Mushrooms
Дыни
Melons
Каперсы
Capers
Капуста
Cabbage
Капуста квашеная
Sauerkraut
Картофель
Potatoes
Лук зеленый
Spring (green onion)
Лук-порей
Leek
Лук репчатый
Onion
Маслины
Olives
Морковь
Carrot
Огурцы
Cucumbers
Перец
Pepper
Перец сладкий
Sweet pepper
Петрушка
Parsley
Помидоры
Tomatoes
Редиска
Radish
Репа
Turnips
Салат
Salad
Свекла красная
Beetroot
Сельдерей
Celery
Тыква
Pumpkin
Укроп
Dill, fennel
Цветная капуста
Cauliflower
Чеснок
Garlic
Шпинат
Spinach
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Сабақтың жоспары
План урока
Пән
Предмет
Prof. Engl.
Күні
дата
сабақтың №
№ занятия
Топ
группа
Тақырып
Тема
Mechanization in livestock:milking machines..
МақсатЦели
Білімділік Дидактическая •to fasten lexical and a writing skills on the topic
Дамытушылық Развивающая to develop monologue speech
ТәрбиелікВоспитывающая to bring up interest in the study of English culture.
Сабақтын типі (тұрпаты)
Тип урока
Lesson formation of reading skills.
Сабақтын әдісі
Метод обучения
Practical method.Collage.
Корнекілік
Оснащение
Text,tasks
Сабақтын барысы Ход урока
1. Бағдарлану - мотивациялық блок
Мотивационно - ориентировочный блок
Сабақтың тақырыбын шығу, жазу
Выход на тему, запись темы урока
Good morning, boys and girls! Nice to meet you! Sit down, please! What can you say about Mechanization in livestock?
Оқу мақсатын қою
Постановка цели, задач урока
formation of writing skills.
Сабақтың барысымен танысу Знакомство с ходом урока
Білім жаңғыртуы
Актуализация знаний
 Mechanization in livestock
Mechanization in livestock
2. Жана материалды мазмұндау (баяндау) Изложение нового материала
Read and translate:Mechanization in livestock raising
Further increase in animal productivity is achieved both by the introduction of new machinery and by wider electrification and automation of different processes on livestock farms.
Some kinds of livestock equipment are almost completely automatic, thus eliminating most of the hand labour. Many farms are using now automatic waterers which provide water to livestock at all times. At the press of the button silage unloaders remove silage from the silo and drop it into the conveyer that carries the silage to the feed troughs. The feeding of grain and hay to dairy cattle has also been almost completely mechanized on some farms. On most farms manure is collected and transported automatically.
Different machines are now being used which permit a better digestion of various feeds by livestock. For instance, grain grinders, feed mixers, forage cutters increase the feeding value of grain, roughages and other feeds.
Milk pipelines connected to milking machines carry the milk to milk tanks where it is automatically cooled to the proper temperature.
In some poultry houses time clock devices are installed so that chickens can be fed automatically at the desired time of the day. On many poultry farms eggs are cleaned, graded and packed primarily by automation.
3. Рефлексия бақылау блогы
Рефлексивно - оценочный блок
Білімдерін бекіту
Закрепление знаний
Learn the words.
automatic waterer - автопоилка to carry - тащить, перевозить digestion - переваривание, усваивание feed mixer - кормосмеситель feed trough - кормушка forage cutter - корморезка to grade - сортировать grain grinder - зернодробилка milk pipeline - молокопровод milk tank - цистерна для молока to remove вынимать, удалять silo - силосная башня, яма
1.Say in Russian:
a) что даёт механизация в области животноводства?;
b) какие процессы наиболее полно механизированы в животноводстве?
Обоснуйте свои ответы предложениями из текста.
2. Answer the following questions:
1. How is higher productivity achieved?
2. .Does mechanization eliminate hand labour?
3. What do silage unloaders do?
4. Is manure collected automatically?
5. What machines increase the feeding value of feeds?
6. What processes are mechanized in poultry breeding?
Нәтижелерді жинақтап, қортындылау
Обобщение результатов, подведение итогов Conclusion of the lesson.
Рефлексия
Рефлексия Collage.
Үй тапсырмасы
Домашнее задание retelling the text
қолы ___________________
подпись ________________
Frozen desserts are a cool and tasty way to finish off a meal. These frozen sweets have been consumed by mankind for thousands of years and date back to the ancient Chinese, Egyptians and Romans, who developed a fondness for the refreshing sweetness of flavored crushed ice. Frozen desserts in modern times still include crushed ice, such as the snow cones and water ices that are a favorite of all age groups, but there are many more types of concoctions available today. A modern frozen dessert menu can include gelato, sorbet, ice cream, custard, smoothies and yogurt, plus mousses, soufflés and even frozen fruit salad.
Making desserts that are frozen is usually not difficult, but it depends on the specific recipe. Busy cooks can choose to make simple but appetizing frozen desserts that take little time, such as aparfait, which whips up quickly, looks pretty and can be made well in advance of a meal. Another quick choice is a simple ice cream sandwich. Frozen desserts that take more time includehomemade ice cream, which can be as plain as vanilla or as complicated as pistachio and rose petal. Other homemade desserts can be more sophisticated, including a French bombe, also known as a dome, which requires a mold to prepare properly.
Ad
Frozen and chilled desserts do not have to be unhealthy choices. People who choose a healthy lifestyle can enjoy many dessert options. Choices include a frozen trifle made with raspberries and blueberries and low-calorie whipped cream, and low-fat versions of frozen cakes and tiramisu, among others.
The origin of frozen desserts can be traced back to about 3000 BCE, when Asian societies began enjoying flavored crushed ice. Pharaohs in Egypt about five centuries later treated their honored visitors to crushed ice covered in fruit juice. Ancient Romans used honey to sweeten their ice. Centuries later, in the 1500s, Italians created gelato, which many people still love today. The sweet treat is similar to ice cream but its ingredients are proportioned differently.
TFrozen gelato was so appealing in the 16th century that an Italian noblewoman, Caterina de Medici, insisted on serving it at her wedding. The man who made it for her, called Ruggeri, had made his living by raising chickens, but he rose to prominence when he won a frozen dessert contest sponsored by the Medici family. The new dessert was so favored that Caterina de Medici brought Ruggeri to France in a bid to outshine French desserts.
A frozen dessert having good texture and eating quality is made by mixing and then freezing from about 7% to about 18% protein solids and from about 10% to about 40% saccharides with from about 5% to about 25% of a triglyceride fat or oil, from about 0.2% to about 2% of a primary emulsifier which is either a polyglycerol ester or a sorbitan ester, from about 0.5% to about 15% by weight of the primary emulsifier of a secondary emulsifier which is an edible anionic surfactant, and with from about 45% to about 65% water.
A single package dry freezer dessert mix preparable with water is provided having the composition of 1.5-20% protein, 4% to 20% lipid material, stearoyl-2-lactylic acid or the alkali or alkaline earth metal salts thereof and optionally, a stabilizer to prevent ice crystal formation and an emulsifier. The single package dry system can be used to prepare frozen desserts by diluting with water or optionally milk, whipping and freezing.


