- Преподавателю
- Иностранные языки
- Проект по английскому языку
Проект по английскому языку
| Раздел | Иностранные языки |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Конспекты |
| Автор | Бармина О.Ю. |
| Дата | 13.10.2014 |
| Формат | docx |
| Изображения | Есть |
«ПАМЯТНИКИ КУЛЬТУРНОГО НАСЛЕДИЯ НА ТЕРРИТОРИИ АНГЛИИ»
Автор: Бармина Ольга Ювенальевна
Цель работы: исследовать памятники культурного наследия Англии, привитие интереса к истории, культуре и традициям страны изучаемого языка,
Методы проведения работы: использование информационных технологий для поиска информации и оформления результатов исследования; анализ и сравнение русско-англоязычных источников формирование читательской культуры; опрос обучающихся и анализ полученных данных.
В работе рассказывается о памятниках культурного наследия Великобритании. Проведен опрос среди обучающихся. Результаты опроса систематизированы, и представлен итог этой работы. В заключении работы рассказывается о наиболее интересном, с моей точки зрения, памятнике культурного наследия - Королевских садах.
.
World Heritage Sites in England
The constitution of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (commonly referred to as UNESCO) was ratified in 1946 by 26 countries, including the UK. Its purpose was to provide for the "conservation and protection of the world's inheritance of books, works of art and monuments of history and science".
There are 27 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom and overseas territories. The UNESCO list contains seventeen designated properties in England (the Frontiers of the Roman Empire is shared with Scotland), four in Scotland, three in Wales, one in Northern Ireland, and one in each of the overseas territories of Bermuda, the Pitcairn Islands, and Saint Helena.
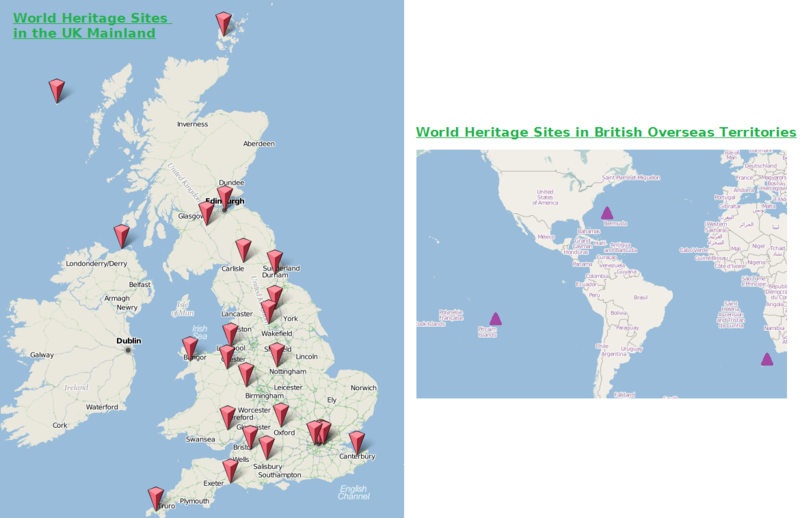
World Heritage sites in England.
There are 17 World Heritage sites in England
NNh
Name
Location
Date
1
Blenheim Palace
Woodstock,Oxfordshire, England
1705-1722
2
Canterbury Cathedral, St Augustine's Abbey, and St Martin's Church
Canterbury,Kent, England
11th century
3
City of Bath
Bath,Somerset, England
1st-19th century
4
Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape
Cornwall andDevon, England
18th and 19th centuries[20]
5
Derwent Valley Mills
Derwent Valley,Derbyshire, England
18th and 19th centuries
6
Dorset and East Devon Coast
Dorset and Devon, England
n/a
7
Durham Castle andCathedral
Durham,County Durham, England
11th and 12th centuries
8
Ironbridge Gorge
Ironbridge,Shropshire, England
18th century
9
Liverpool - Maritime Mercantile City
Liverpool,Merseyside, England
18th and 19th centuries
10
Maritime Greenwich
Greenwich,London,Greater London, England
17th and 18th centuries
11
Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and Canal
Trevor, Wrexham, Wales and Shropshire, England
1795-1805
12
Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew
Kew, Greater London, England
18th-20th century
13
Saltaire
Saltaire, City of Bradford,West Yorkshire, England
1853
14
Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites
Wiltshire, England
4th-2nd millennia BC
15
Studley Royal Parkincluding the Ruins of Fountains Abbey
North Yorkshire, England
1132 (abbey),19th century (park)
16
Tower of London
Tower Hamlets,Greater London, England
11th century
17
Westminster Palace,Westminster Abbey and Saint Margaret's Church
Westminster,Greater London, England
10th, 11th, and 19th centuries
I have asked 20 pupils if they know about these sites, and the result is the following:
-
90% knows about the Westminster Palace, Big Ben.
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Commonly known as the Houses of Parliament after its tenants, the Palace lies on the Middlesex bank of the River Thames in the City of Westminster, in central London.

Its name, which derives from the Westminster Abbey, may refer to either of two structures: the Old Palace, a medieval building complex that was destroyed by fire in 1834, and its replacement New Palace that stands today. For ceremonial purposes, the palace retains its original style and status as a royal residence.
-
43% knows about The Tower.

Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress, known as the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, separated from the eastern edge of the square mile of the City of London by the open space known as Tower Hill. It was founded towards the end of 1066 as part of the Norman Conquest of England. The White Tower, which gives the entire castle its name, was built by William the Conqueror in 1078, and was a resented symbol of oppression, inflicted upon London by the new ruling elite. The castle was used as a prison from 1100 (Ranulf Flambard) until 1952 (Kray twins), although that was not its primary purpose. A grand palace early in its history, it served as a royal residence. As a whole, the Tower is a complex of several buildings set within two concentric rings of defensive walls and a moat. There were several phases of expansion, mainly under Kings Richard the Lionheart, Henry III, and Edward I in the 12th and 13th centuries. The general layout established by the late 13th century remains despite later activity on the site.
The Tower of London has played a prominent role in English history. It was besieged several times and controlling it has been important to controlling the country. The Tower has served variously as an armory, a treasury, a menagerie, the home of the Royal Mint, a public records office, and the home of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom.
-
22% knows about the Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument in Wiltshire, England, about 2 miles (3.2 km) west of Amesbury and 8 miles (13 km) north of Salisbury. One of the most famous sites in the world, Stonehenge is the remains of a ring of standing stones set within earthworks. It is in the middle of the most dense complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred burial mounds.
Archaeologists believe it was built anywhere from 3000 BC to 2000 BC. Radiocarbon dating in 2008 suggested that the first stones were raised between 2400 and 2200 BC,[2] whilst another theory suggests that bluestones may have been raised at the site as early as 3000 .

-
All the rest sites were not mentioned. My classmates indicate some sights which don't belong to the UNESCO World Heritage Sites. They are: the Buckingham Palace, the British museum, the house-museum of Sherlock Holmes and others.
I would like to tell you about the most interesting site to my mind.
The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.

The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, usually referred to as Kew Gardens, comprises 121 hectares of gardens and botanical glasshouses between Richmond and Kew in Richmond upon Thames in southwest London, England. "The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew" and the brand name "Kew" are also used as umbrella terms for the institution that runs both the gardens at Kew and Wakehurst Place gardens in Sussex. The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, is an internationally important botanical research and education institution, Created in 1759,[2] the gardens celebrated their 250th anniversary in 2009.
The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is the world's largest collection of living plants. The organization employs more than 650 scientists and other staff. The living collections include more than 30,000 different kinds of plants, while the herbarium, which is one of the largest in the world, has over seven million preserved plant specimens. The library contains more than 750,000 volumes, and the illustrations collection contains more than 175,000 prints and drawings of plants. The Kew site includes four Grade I listed buildings and 36 Grade II listed structures in an internationally significant landscape.
History
Kew Gardens originated in the exotic garden at Kew Park formed by Lord Capel John of Tewkesbury. It was enlarged and extended by Augusta, Dowager Princess of Wales, the widow of Frederick, Prince of Wales, for whom Sir William Chambers built several garden structures. One of these, the lofty Chinese pagoda built in 1761 still remains. George III enriched the gardens, aided by William Aiton and Sir Joseph Banks. The old Kew Park (by then renamed the White House), was demolished in 1802. The "Dutch House" adjoining was purchased by George III in 1781 as a nursery for the royal children. It is a plain brick structure now known as Kew Palace.
Some of the early plants came from the walled garden established by William Coys at Stubbers in North Ockendon.[4] The collections grew somewhat haphazardly until the appointment of the first collector, Francis Masson, in 1771.[5] In 1840 the gardens were adopted as a national botanical garden, in large part due to the efforts of the Royal Horticultural Society and its president William Cavendish.[6] Under Kew's director, William Hooker, the gardens were increased to 30 hectares (75 acres) and the pleasure grounds, or arboretum, extended to 109 hectares (270 acres), and later to its present size of 121 hectares (300 acres). The first curator was John Smith.
The Palm House was built by architect Decimus Burton and iron-maker Richard Turner between 1844 and 1848, and was the first large-scale structural use of wrought iron. It is considered " the world's most important surviving Victorian glass and iron structure." The structure's panes of glass are all hand-blown. The Temperate house, which is twice as large as the Palm House, followed later in the 19th century. It is the largest Victorian glasshouse now.
Lancelot "Capability" Brown, who became England's most renowned landscape architect, applied for the position of master gardener at Kew, and was rejected.
Kew was the location of the successful effort in the 19th century to propagate rubber trees for cultivation outside South America.
In February 1913, the Tea House was burned down by suffragettes Olive Wharry and Lilian Lenton during a series of arson attacks in London.
Kew Gardens lost hundreds of trees in the Great Storm of 1987.
In July 2003, the gardens were put on the list of World Heritage Sites by UNESCO.
From November 1959 until August 2007 Kew Gardens had a flagpole, the tallest in Britain. Made from a single Douglas-fir from Canada, it was given to mark both the centenary of the Canadian Province of British Columbia and the bicentenary of Kew Gardens. The flagpole was removed after damage by weather and woodpeckers.
Attractions
-
The Davies Alpine House
In March 2006, the Davies Alpine House opened, the third version of an alpine house since 1887. Although only 16 meters long the apex of the roof arch extends to a height of 10 meters in order to allow the natural airflow of a building of this shape to aid in the all-important ventilation required for the type of plants to be housed.

Kew's collection of Alpine plants (defined as those that grow above the tree-line in their locale - ground level at the poles rising to over 2,000 meters (6,562 feet)), extends to over 7000. As the Alpine House can only house around 200 at a time the ones on show are regularly rotated.
-
Chokushi-Mon
Built for the Japan-British Exhibition (1910) and moved to Kew in 1911, the Chokushi- 'Imperial Envoy's Gateway') is a four-fifths scale replica of the karamon (gateway) of the Nishi Hongan-ji temple in Kyoto. It lies about 140 m west of the Pagoda and is surrounded by a reconstruction of a traditional Japanese garden.

-
Kew Palace
Kew Palace is the smallest of the British royal palaces. It was built by Samuel Fortrey, a Dutch merchant in around 1631. It was later purchased by George III. The construction method is known as Flemish bond and involves laying the bricks with long and short sides alternating.

To the rear of the building is the "Queen's Garden" which includes a collection of plants believed to have medicinal qualities. Only plants that were extant in England by the 17th century are grown in the garden.
The building underwent significant restoration before being reopened to the public in 2006. It is administered separately from Kew Gardens, by Historic Royal Palaces.
-
Princess of Wales Conservatory
Kew's third major conservatory, the Princess of Wales Conservatory, designed by architect Gordon Wilson, was opened in 1987 by Diana, Princess of Wales in commemoration of her predecessor Augusta's associations with Kew. In 1989 the conservatory received the Europa Nostra award for conservation. The conservatory houses ten computer-controlled micro-climatic zones, with the bulk of the greenhouse volume composed of Dry Tropics and Wet Tropics plants. Significant numbers of orchids, water lilies, cacti, lit hops, carnivorous plants and bromeliads are housed in the various zones. The cactus collection also extends outside the conservatory where some hardier species can be found.

-
Temperate House
This greenhouse has twice the floor area of the Palm House and is the world's largest surviving Victorian glass structure. It contains plants and trees from all the temperate regions of the world. It was commissioned in 1859 and designed by architect Decimus Burton and iron founder Richard Turner.
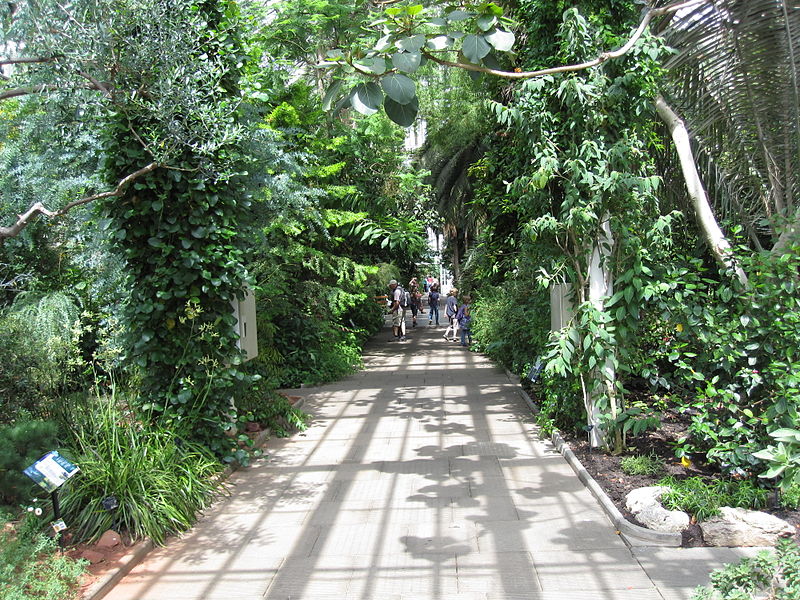

Covering 4880 square meters, it rises to a height of 19 meters. Intended to accommodate Kew's expanding collection of hardy and temperate plants, it took 40 years to construct, during which time costs soared. There is a viewing gallery in the central section from which visitors may look down on that part of the collection.
-
Treetop walkway
A new treetop walkway[45] opened on 24 May 2008. This walkway is 18 meters (59 ft) high and 200 meters (660 ft) long and takes visitors into the tree canopy of a woodland glade. Visitors can ascend and descend by stairs or by a lift. The floor of the walkway is made from perforated metal and flexes as it is walked upon. The entire structure sways in the wind.

The accompanying image shows a section of the walkway and the steel supports that were designed to rust to a tree-like appearance to help the walkway fit in with its surroundings.
There are a lot of other attractions in Kew and you may spend a lot of time there. As well as stunning landscapes, vistas and permanent attractions at Kew, they have an exciting program of events including festivals, art exhibitions, talks, guided walks and activities for kids.
In conclusion I would like to say that the world is very big but it is very fragile and we must protect the world to let our children and grandchildren live and enjoy it for their lives.
Список используемых источников:
-
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_World_Heritage_Sites_of_the_United_Kingdom
-
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Botanic_Gardens,_Kew
-
kew.org/visit-kew-gardens/whats-on
-
parliament.uk/about/living-heritage/building/palace/
-
stonehenge.co.uk/
-
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tower_of_London
11


