- Преподавателю
- Иностранные языки
- Работа НОУ 10 класс
Работа НОУ 10 класс
| Раздел | Иностранные языки |
| Класс | 10 класс |
| Тип | Другие методич. материалы |
| Автор | Черных Т.Н. |
| Дата | 17.12.2015 |
| Формат | doc |
| Изображения | Есть |
Районная сессия научного общества учащихся
Секция: «Английский язык»
«STONEHENGE»
Выполнила работу:
ученица 10 класса
МБОУ МСОШ №1
Баркина Айсулу
Руководитель проекта:
учитель иностранного языка
МБОУ МСОШ №!
Черных Т.Н.
с.Майма
2012 г.
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................3
STONEHENGE - FOREVER A MYSTERY.............................................................4
THEORIES OF BUILDING STONEHENGE...........................................................4
THE MYSTERY OF STONEHENGE........................................................................5
THE HEEL STONE AND THE FIRST RAYS..........................................................5
WHAT STONEHENGE IS..........................................................................................6
CONSTRUCTION OF STONEHENGE....................................................................6
PERIODS OF STONEHENGE BUILDING............................................................. 7
ASTRONOMICAL SIGNIFICANCE........................................................................9
HOW THEY REBUILT STONEHENGE..................................................................9
STONEHENGE LEGENDS......................................................................................10
DRUID CONNECTION.............................................................................................11
SPIRITUAL REBIRTH..............................................................................................11
CONCLUSION...........................................................................................................11
BIBLIOGRAPHY...................................................................................................... 12
APPLICATION...........................................................................................................13
INTRODUCTION
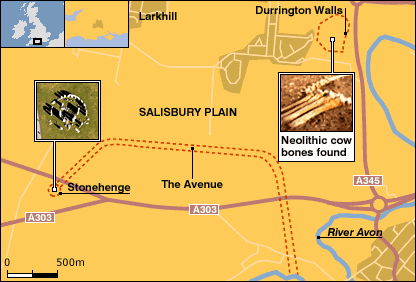
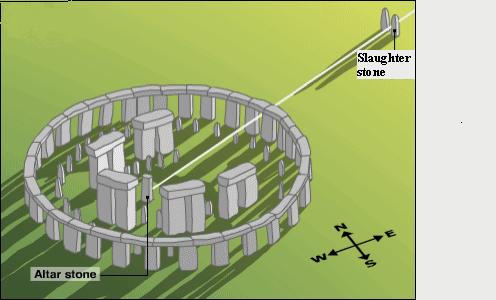
Stonehenge is one of the most famous and mysterious ruins in the world today. An ancient megalith or stone monument, it is situated in the middle of Salisbury Plain, to the northwest of Southampton. Located in southern England near the picturesque cathedral town of Salisbury, it is a stone and earth monument whose history goes back nearly 5,000 years. It has been associated with all sorts of astronomical and religious myths. On June 21 when the sun rises immediately over the Hell Stone of the circle and casts its shadow on the Altar Stone in the middle, each year thousands of visitors gather for a festival to mark the summer solstice, or mid-summer.
(р. № 1, 2, 3)
But what does it all mean, and who were the people who built it?
What was Stonehenge used for?
Why was Stonehenge built?
How these vast stones were transported so far and erected?
How were they got to stand upright?
These are the questions that ring in the mind of every person who has ever seen this awesome and puzzling place.
STONEHENGE - FOREVER A MYSTERY
Stonehenge is probably the world's best-known megalithic site. A megalith is a standing stone monument. It is a stone and earth monument whose history goes back nearly 5,000 years.
The monument consists of 162 stones and is about 30 meters across. The stones are called menhirs. Some are sandstone, and others are blue stone. The ruins of the magnificent circular stone structure stand inside a bank and ditch arrangement. Scientists have named the outer ring of stones, the sarsen circle. Inside that circle is another circle, of bluestones, and then a sarsen horseshoe. The innermost structure is a horseshoe of bluestones. All of this is around the Altar Stone, a bluestone that is situated near the back of the inner horseshoe. (p. №4)
THEORIES OF BULDING STONES
There have been many theories over the years as to who built the site and why. Probably the most famous one is that the Druids built it as a place of worship. The problem with this theory is that there were no Druids in England at the time it was built, and the Druids preferred places with trees for their worship. (p. №5)
Another theory is that it was some sort of religious site where human sacrifices were made, but this theory is the weakest of all, since no human remains have been found there. There is some evidence that ashes of cremated bodies were placed in the Aubrey holes, but much later than the original time the site was built.
One more, and the best theory, is that it was some sort of astronomical observatory. The sun rises directly over the heel stone on midsummer's day. It is not very likely that this is a coincidence. The problem with this theory is that over the 5000 years that it has stood, midsummer's day has changed, and so has the position of the sun. However, people have estimated that 5000 years ago, midsummer's day was June 24, and that the sun would have risen over the Heel Stone then. (p.№6)
Other calculations show that it could have been used to predict solar and lunar eclipses, and perhaps even as a daily calendar. We will probably never know exactly
Why the site was built. One thing is certain, though. It was built for an important purpose.
THE MYSTERY OF STONEHENGE
Stonehenge is one of the most intriguing puzzles of the history. It is a circular group of huge stones was built on Salisbury plain in western England between 3000 and 1000 BC. There are two stone circles in Stonehenge. The first stone - circle is consisted of small bluestones. They say the stones were brought from the Prescelly Mountains. They are located 240 miles away from Stonehenge. The bluestones weigh up to 4 tons each.
The giant sarsen stones form the second circle. They weigh up to 50 tons each. They were transported from the Marlborough Downs, located 20 miles to the north.
Who built Stonehenge? How did the "builders" transport giant stones? These questions are unanswered even today.
The legend of King Arthur says that a great magician Merlin brought the stones to the Salisbury plain from Ireland.
Historians and scientists can't determine the social functions of Stonehenge. It could be used as a market, a temple, a calendar or the gathering place for religious ceremonies connected with the Sun and Moon. Stonehenge, maybe, was a kind of huge computer itself. Who knows?
"Stonehenge" came from the Saxons. Originally, they called it Stonehenge. Stan is Old English for stone, and henge means, "to hang." There are several theories as to the origin of this unusual name.
THE HEEL STONE AND THE FIRST RAYS
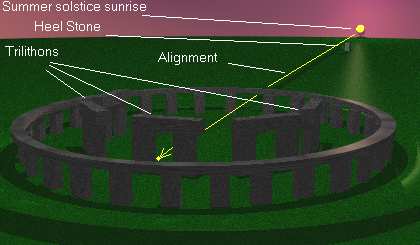
For most parts of the year, the sunrise can't even be seen from the center of the monument. But on the longest day of the year, the June 21st summer solstice, the rising sun appears behind one of the main stones, creating the illusion that it is balancing on the stone.
This stone, called the "Heel Stone", sits along a wide laneway, known as the Avenue, which extends from the northeast corner of the main monument. The rising Sun creeps up the length of the rock, creating a shadow that extends deep into the heart of five pairs of sarsen stone Trilithons - two pillar stones with one laid across the top - in the shape of a horseshoe that opens up towards the rising sun. (p.№7)
Just as the Sun clears the horizon, it appears to hover shortly on the tip of the Heel Stone. A few days later, on midsummer's day, the sun will appear once again, but this time, it will begin to move to the right of the heel stone. The same phenomenon happens again during the winter solstice, only it's in the opposite direction and a sunset. Both indicate a change of the season.
WHAT STONEHENGE IS
The megalithic ruin known as Stonehenge is not a single structure but consists of a series of earth, timber, and stone structures that were revised and re-modeled over a period of more than 1400 years.
The Sarsen Circle, about 33 meters in diameter, was originally comprised of 30 neatly trimmed upright sandstone blocks of which only 17 are now standing. The stones stand on average 4 meters above the ground. They are about 2 meters wide and 1 meter thick and taper towards the top. They originally supported sarsen lintels forming a continuous circle around the top. The average length of the rectangular lintels is 3.2 meters .The Sarsen Circle with its lintels is perhaps the most remarkable feature of Stonehenge in terms of design, precision stonework, and engineering Sarsen stones are hard-grained sandstone with siliceous cement.
The Trilithons are ten upright stones arranged as five freestanding pairs each with a single horizontal lintel. They were erected within the Sarsen Circle in the form of a horseshoe with the open side facing north-east towards the main entrance of the monument. They were arranged symmetrically and graded in height; the tallest is in the central position. Only three of the five Trilithons are now complete with their lintels. The other two both have only one standing stone with the second stone and lintel lying on the ground.
CONSTRUCTION OF STONEHENGE
Lying on the windswept plains of southern England, Stonehenge, with its construc-tion of massive stones, or megaliths, evokes wonder and haunts our imagination: how was Stonehenge created, and why?
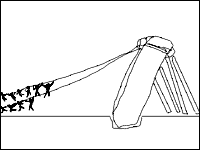
Like Rome, Stonehenge wasn't built in a day. Over 25 generations were involved. Most of it was the result of human muscle and a system of ropes and wooden levers used to transport the massive stones. Primitive tools, such as red deer antlers, were used to dig up the chalky countryside of Salisbury Plain, which was then taken away on ox shoulder blades. (p. №8)
A thousand years later, new builders erected a monumental circle of linked sarsen stones, a form of very hard sandstone. They also raised an inner horseshoe-shaped design of ten megaliths, which stand up to 7 meters tall and weigh as much as 45 tons each. Perhaps using a system of levers, timber, and ropes, the builders topped these slabs with horizontal stones called lintels, thus forming five Trilithons, or squared arches. (р.9)
The bluestones are believed to have come from much farther-the Presley Mountains, nearly 385 kilometers away. They were rafted from Wales by sea and river. The sarsens were dragged from the Avebury Hills by haulage teams, probably aided by oxen. The stones were then tipped end-first into pits dug into the sub-surface chalk. The lintels for the Trilithons were raised on wooden cribs or by using earthen ramps. (p. №10)
PERIODS OF STONEHENGE BULDING
About 100 years later the bluestones were dismantled and the Stonehenge as we see it today started to show. (р.№11)
Construction of Stonehenge was broken into three periods:
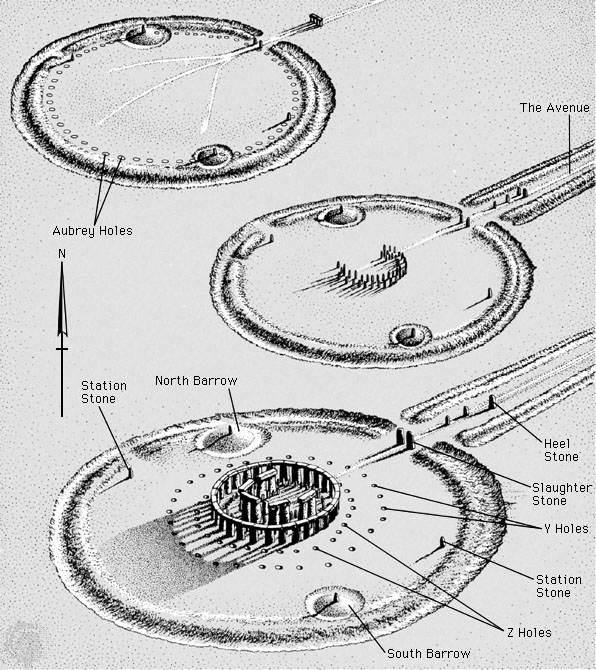
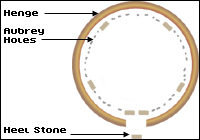
Stonehenge Period I (c. 2950-2900 BC) the first period of Stonehenge was a circular enclosure outlined by two banks and a ditch with an entrance to the northeast and a standing stone a bit away from the entrance. The outer circle was made from earth and even though it is now mostly destroyed, it was about 380 feet in diameter, 8 feet wide and 2 or 3 feet high. The ditch was not uniform in shape or Depth and it varied in width from 10-20 feet and a depth of 4.5- 7 feet. (p. №12)
Archaeologists have been able to use the varied fragments found near the bottom of the ditch to help date its construction.
From the center of the circle, facing northeast is the entrance into Stonehenge. It is about 35 feet wide and is set so that a person standing in the center of Stonehenge can see the sunrise on midsummer morning just to the left of the heel stone.
Inside the circle are 56 Aubrey holes (named after their 17th century discoverer John Aubrey). They were spaced quite accurately in a 288-foot diameter circle with an average center point for each hole of 19 inches.
At this time The Heel, stone was also placed. It is the considered the most important stone at the site, weighing 35 tons. During the summer solstice if you stand in the center of the circle, you will see the sunrise directly over the pointed tip of the heel stone. (p. №13)
Lastly, Stonehenge's old ditch bank entrance was widened another 25 feet and a 40-foot wide "Avenue" lined by parallel banks and ditches 47 feet apart extended out from it.
Two parallel stones were erected at the entrance to the circle, one of which, the Slaughter Stone, still survives.
Stonehenge Period II (c. 2900-2400 BC) during this stage of construction, a double circle of about 60-80 stones was placed in the middle of the circle formed by the ditch. They are the smallest stones used at the site, but they still each weighed about 4 tons. They came from the Presale Mountains in South Wales, nearly 250 miles away. It is intriguing to wonder, however, what makes the Stonehenge site so special that so much effort would be expended to drag the giant stones 250 miles instead of constructing the monument near the quarry.
Although no one knows for sure how they got there, it is thought they were transported mostly on barges, using the sea and rivers, and barely had to travel over
Land at all. For some reason, this circle of stones was never completed and was part replaced with a horseshoe arrangement of larger stones.
Stonehenge Period III (c. 2550-1600 BC) Stonehenge's third period was the longest and contained the most changes of all the periods.
A 100-foot diameter circle of 30 sarsen-stone uprights capped by a continuous ring of sarsen lintels was erected in the center of the site. This circle surrounded a horseshoe -shaped setting of five sarsen Trilithons with its opening pointing to the northeast side.
Within this stone ring was erected a horseshoe formation of the same construction, using 10 upright stones. The horseshoe shape opens directly towards the Slaughter Stone and down the Avenue, aligned with the summer solstice sunrise.
The Altar Stone is the biggest of these newly-arranged bluestones that remains. (р.14)
ASTRONOMICAL SIGNIFICANCE
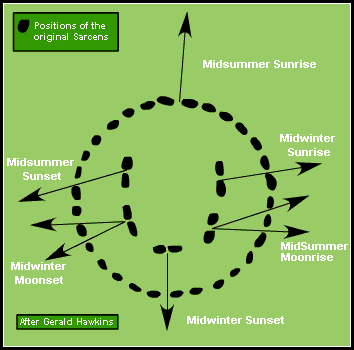
Already in the 18th century, the British antiquarian William Stukeley had noticed that the horseshoe of great Trilithons and the horseshoe of 19 bluestones at Stonehenge opened up in the direction of the midsummer sunrise. It was quickly surmised that the monument must have been deliberately oriented and planned so that on midsummer's morning, the sun rose directly over the Heel Stone and the first rays shone into the center of the monument between the open arms of the horseshoe arrangement.
At the midwinter solstice, the setting sun sinks between the two uprights of the largest Trilithon and behind the altar stone - thought by many to symbolize the death of the year.
This discovery has had tremendous impact on how Stonehenge has been interpreted. This alignment implied a ritualistic connection with sun worship and it was generally
concluded that Stonehenge was constructed as a temple to the sun. It can be used to predict such events as eclipses.
The alignment also made it clear that whoever built Stonehenge had precise astronomical knowledge of the path of the sun and, moreover, must have known before construction began precisely where the sun rose at dawn on midsummer's
morning while standing on the future site of the monument. (р.15)
HOW THEY REBUILT STONEHENGE
The first restoration of Stonehenge was launched 100 years ago this year. The Stonehenge makeover was to gather momentum and more work was carried out in 1919, 1920, 1958, 1959 and 1964. Christopher Chippendale, author of Stonehenge Complete, admits: 'Nearly all the stones have been moved in some way and are standing in concrete.
A stone was straightened and set in concrete in 1901, six further stones in 1919 and 1920, three more in 1959 and four in 1964. There was also the excavation of the Altar stone and re-erection of the Trilithon in 1958.
A number of the leaning and fallen stones have been straightened and re-erected. These pictures clearly show the rebuilding in progress. (р.16, 17)
STONEHENGE LEGENDS
The story of Stonehenge wouldn't be complete without its legends. One such story says that the hangs are gateways to where we originally came from. The legend goes on to suggest that every 5,000 years or so, someone attempts to open one of them, which brings about some horribly catastrophic event.
But the most popular myth stems from a story written in the 12th century by Geoffrey of Monmouth. According to Monmouth, the king of the Britons, Aurelius, wanted to build a monument over the site of several hundred graves believed to be slain Saxon soldiers. King Aurelius, or the father of King Arthur, asked Merlin the magician where such a monument could be found. Merlin told him to look in a
mountain of Ireland where a circle of massive stones stood, named the Giant's Dance. Merlin suggested an expedition to Ireland for the purpose of transplanting the Giant's Ring stone circle to Britain.
These stones, believed to have the ability to heal, were so named after a myth that they were brought from Africa long ago by giants. King Aurelius and his army tried to dismantle the stones without success. Merlin once again came to help and used his own gear of "engines and other contrivances" to take apart the monument for transport. He later reconstructed the site on Salisbury Plain. It is only one of probably many legends that reflect the inability to explain how the heavy stones could have ever been transported by primitive humans.
Evil powers have also been associated with Stonehenge. One myth tells the story of the devil who buys magical stones from an Irish woman. He transports them through the air to Salisbury Plain and then dares the entire village to count the stones in a bizarre-type of riddle. The friar of the village tells him there are too many to tell.
It is supposedly impossible to count all the stones. The devil once bet that no one in the nearby village would be able to come up with the right answer. However, a monk replied 'more than could be told'. The devil angrily threw one of the stones at the monk and it bounced off the back of his foot - the outlying stone was then named the Heel Stone.
DRUID CONNECTION
In the 17th Century John Aubrey made the connection of the ancient Druids to Stonehenge. He had suggested that the Druids were probably responsible for building Stonehenge.
SPIRITUAL REBIRTH
Druids are believers in reincarnation. They believe that the soul is immortal and after a person dies, they are transported to the 'Otherworld'. They also believe that that
person will come back again in another human body. The traditional meeting place of the Druids is Stonehenge. Druids claim that their religion has marked the summer solstice at Stonehenge for nearly 800 years. (р. №18, 19, 20)
CONCLUSION
Over the years many theories have appeared and people continue to present their versions. Nobody really knows the truth. But we see that ancient people were very clever, and could construct huge monuments though they did not have machines.
No matter what the claim has been for Stonehenge's original purpose, the truth is that it has inspired countless generations of people to strive to learn and figure out the history of our past. Stonehenge is somewhat a "gateway to the realms" providing insights into humanities past and showing that maybe we were not as "technically challenged" as some would like us to believe.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Фарлонг Д . Стоунхендж и пирамиды Египта: Ключи от храма жизни
(пер. Медникова В.). Серия: Тайны древних цивилизаций. 2001
2. Гарри Гаррисон, Леон Стоувер. «Стоунхендж». 2002
3. Уайт Дж., Хокинс Дж. «Разгадка тайны Стоунхенджа»
4. icompas.ru/compas/stonehenge
5. garshin.ru/history/archeology
6. celtica.ru/content/blogcategory
7. dic.academic.ru
8. abc-people.com
Application
Picture №1
Picture №2

Picture №3

Picture №4

Picture №5
Picture№6

Picture №7
Picture №8
Picture №9

Picture №10
Picture№11

Picture №12
Picture№13
P icture №14
icture №14
Picture №15
A photograph
of the sun rising
over the Heel Stone

Picture №16

Picture №17

Picture №18

Picture №19

Picture №20


