- Преподавателю
- Иностранные языки
- Методическая разработка открытого урока по профессиональному иностранному языку на тему: Earths outer layers. Atmosphere
Методическая разработка открытого урока по профессиональному иностранному языку на тему: Earths outer layers. Atmosphere
| Раздел | Иностранные языки |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Другие методич. материалы |
| Автор | Ибатулина Д.Ж. |
| Дата | 31.12.2015 |
| Формат | docx |
| Изображения | Есть |
|
| КГКП «Геологоразведочный колледж» управления образования Восточно-Казахстанского областного акимата
|
Согласовано
Методист
Жумагалиева А.Ж. ___________
Утверждаю
Заместитель директора по УР
_________________Минаева Н.Т.
« » ___________________2016 г.
Методическая разработка
открытого урока
по предмету Профессиональный иностранный язык
преподаватель Ибатулина Д.Ж.
Рассмотрено на заседании ПЦК
протокол № 4 от «4» декабря 2015 г.
председатель ПЦК Бейсембинова Б.Ж.
____________________ ФИО
(подпись)
г. Семей
Lesson Plan № 38
Subject Professional English
Lesson # 38
Date ____4.02.2016____ Group ____G-41E____
The lesson theme: Earth's outer layers. Atmosphere.
The lesson aims:
teaching: to evaluate knowledge of information about the major structural units of Earth; to define Earth's outer layers, to characterize and describe atmosphere; to introduce vocabulary; to train pronunciation;
developing: to generate curiosity to study and explore our surroundings;
up-bringing: to foster love for future job;
Basic competences: БК1 - to renew knowledge and skills during the life; БК5 - to gather and systematize necessary information
Type of the lesson: combined lesson
The equipment of the lesson: handouts, presentation PG2-38, video PG2-38, flipchart PG2-38
Intersubject connections: Geology, Geography, Practice of oral and written speech
Methods used at the lesson: a Task-Based Learning Activity, Lexical approach, Language Immersion, Multiple Intelligences
Contents of the lesson:
1. Organization moment 2 min.
2. Introduction of the theme and aims 2 min.
3. Homework checking 25 min.
4. Actualization of students' base 1 min.
5. Explanation of the new theme 10 min.
6. Consolidation 35 min.
7. Homework 2 min.
8. Resume of the lesson 3 min.
Contents of the lesson
№
Stages of the lesson
Contents of the lesson
Organization moment
Good morning, students. I'm glad to see you. How are you?
What is the date today? What is the day today? Who is on duty today? Who is absent?
Introduction of the theme and aims
The theme of the lesson is Earth's outer layers. Atmosphere.
The aim of the lesson is to evaluate knowledge of information about the major structural units of Earth; to define Earth's outer layers, to characterize and describe atmosphere; to introduce vocabulary; to train pronunciation
Homework checking
I. General questioning on vocabulary. Students give the English equivalents.
-
внутренние слои
internal layers
-
мантия и ядро
mantle and core
-
косвенные доказательства
indirect evidence
-
жидкое внешнее ядро
liquid outer core
-
землетрясение
earthquake
-
состоять из железа и никеля
to be made up of iron and nickel
-
твердое внутреннее ядро
solid inner core
-
солнечная радиация
solar radiation
-
жидкое внешнее ядро
liquid outer core
-
защищать планету
to protect the planet
-
оливин и пироксен
olivine and pyroxene
-
самый внешний слой
outermost layer
-
низкая плотность
low density
-
континентальная кора
continental crust
-
плотные вулканические породы
dense volcanic rocks
-
океаническая кора
oceanic crust
II. General questioning on the text "The major structural units of Earth". Students answer the questions.
-
What are compositional layers of the Earth? (Compositional layers are crust, mantle, and core.)
-
What parts is the core divided into? (It is divided into a solid inner core and a liquid outer core.)
-
What is the inner core made up of? (It is made up of iron and nickel)
-
How is the outer different from the inner core? (The outer core is also made up of iron and nickel, but it's quite different because it is a liquid.)
-
What does the outer core create? (The outer core creates the Earth's magnetic field.)
-
What is the mantle composed of? (The mantle is composed of iron and magnesium silicate rock, fragments of which have been brought to the surface by volcanic eruptions.)
-
How is the boundary between the crust and the mantle called? (The Mohorovičić Discontinuity)
-
What two types of crust do you know? (The continental and the oceanic crust.)
-
What is the continental crust composed of? (The continental crust is composed of relatively light "granitic" rock that includes the oldest rock of the crust.)
-
What is the oceanic crust composed of? (The oceanic crust is composed of dark, dense volcanic rocks (basalt) with densities much greater than that of granite.)
III. Retelling of the text:
-
One student retells
-
Two students retell (one by one)
-
Questions to a student
-
Students' battle
IV. Individual work at the blackboard (1 student)
Card
I. Complete the sentences with necessary words.
-
The asthenosphere is a distinctive zone in the upper ______________.
-
Crust is the __________ ______________ shell of the Earth.
-
_________ is the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
-
_________ is a very large area of land that consists of several countries.
-
The region between the asthenosphere and the core-mantle boundary is called the ______________.
II. Translate the following words orally.
-
правильное расстояние от солнца
-
северное полушарие
-
происхождение и развитие
-
удерживать атмосферу
-
естественный спутник
-
двигаться против часовой стрелки
-
огромные потухшие вулканы
Answers:
-
The asthenosphere is a distinctive zone in the upper mantle.
-
Crust is the outermost solid shell of the Earth.
-
Lithosphere is the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
-
Continent is a very large area of land that consists of several countries.
-
The region between the asthenosphere and the core-mantle boundary is called the mesosphere.
V. Individual work. Quiz (2 students)
Card 1
I. Give the English equivalents:
-
физические свойства пород
-
высокое давление
-
вращение Земли
-
создавать магнитное поле
-
деформированная мантия
-
жидкое внешнее ядро
-
зона землетрясений
-
граница
-
твердое внутреннее ядро
-
происхождение и развитие
II. Give antonyms:
-
small, tiny
-
wrong
-
close (adj)
-
external
-
to move clockwise
-
to be similar
III. Describe the planet Mercury.
Card 2
I. Give the English equivalents:
-
физические свойства пород
-
высокое давление
-
вращение Земли
-
создавать магнитное поле
-
деформированная мантия
-
жидкое внешнее ядро
-
зона землетрясений
-
граница
-
твердое внутреннее ядро
-
происхождение и развитие
II. Give the synonyms:
-
состоять из
-
внутренняя часть; внутренний
-
твердый
-
малый
-
дальний, далекий
III. Describe the planet Jupiter.
Actualization of students' base
We've consolidated the major structural units of Earth. What outer layers of the Earth do you know? SS' answers.
Explanation of the new theme
Teacher explains new material:
I. Introducing new vocabulary
1. SS read aloud the following words:
atmosphere ['ætməsfɪə], biosphere ['baɪəsfɪə], argon ['ɑːgɔn], gaseous ['gæʃəs], absorb [əb'zɔːb], ultraviolet [ˌʌltrə'vaɪələt], thermosphere ['θɜːməˌsfɪə], stratosphere ['strætəˌsfɪə], mesosphere [ˈmezəˌsfiə], exosphere ['ɛksəʊˌsfɪə], meteor ['miːtɪə], stratopause ['strætəˌpɔːz], aurora [ɔː'rɔːrə], ionosphere [aɪ'ɔnəsfɪə], collide [kə'laɪd], helium ['hiːlɪəm]
2. SS read the following words and try to remember them:
gaseous envelope
газовая оболочка
heat retention
тепловая инертность
troposphere
тропосфера
stratosphere
стратосфера
mesosphere
мезосфера
thermosphere
термосфера
exosphere
экзосфера
overlying layer
налегающий слой, лежащий сверху слой
aurora
полярное сияние
ionosphere
ионосфера
to absorb
поглощать
to collide
сталкиваться; соударяться
3. SS guess and match word phrases with their Russian equivalents:
-
mixture of gases
-
азот и аргон
-
nitrogen and argon
-
изменяемое, непостоянное количество
-
a variable amount
-
содержать озоновый слой
-
to absorb radiation
-
поглощать радиацию
-
ultraviolet rays
-
водород и гелий
-
to contain the ozone layer
-
смесь газов
-
hydrogen and helium
-
ультрафиолетовые лучи
Answers: 1. 6 2. 1 3. 2 4. 4 5. 7 6. 3 7. 5
Consolidation
4. Watching a video "Atmosphere"
SS watch a video. While watching the video SS are to complete the sentences with necessary words.
4.1. SS complete the sentences with necessary words from the video.
-
The atmosphere is divided into the following layers: __________________, ______________, mesosphere, thermosphere, __________________.
-
The troposphere begins at the surface and extends to _______ km at the poles and 17 km at the ___________.
-
The overlying layer is the stratosphere, which extends to about _____ km above the surface.
-
This is the layer where most __________ burn up entering the atmosphere.
-
The __________ here can rise to 1,727 °C.
-
The __________ is mainly composed of ___________ and helium.
Answers:
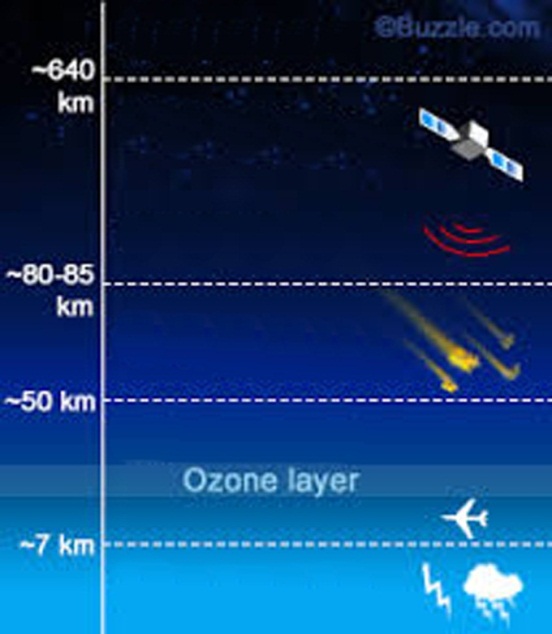
-
The atmosphere is divided into the following layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere.
-
The troposphere begins at the surface and extends to between 7 km at the poles and 17 km at the equator.
-
The overlying layer is the stratosphere, which extends to about 50 km above the surface.
-
This is the layer where most meteors burn up entering the atmosphere.
-
The temperature here can rise to 1,727 °C.
-
The exosphere is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium.
4.2. SS match the names of the layers (Flipchart "Magic Box")
stratosphere
thermosphere
mesosphere
exosphere
troposphere
Teacher checks the sentences.
Answers:
-
The atmosphere is divided into the following layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere.
-
The troposphere begins at the surface and extends to between 7 km at the poles and 17 km at the equator.
-
The overlying layer is the stratosphere, which extends to about 50 km above the surface.
-
This is the layer where most meteors burn up entering the atmosphere.
-
The temperature here can rise to 1,727 °C.
-
The exosphere is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium.
5. Reading the text.
SS read the text about the atmosphere and complete the text with an appropriate sentence from the video.
The outermost layers of Earth are the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Our atmosphere is unique in the solar system. The atmosphere is the thin, gaseous envelope that surrounds Earth. Air is the mixture of gases that is composed of 78 % of nitrogen, 21% of oxygen, 0.93% of argon, 0.039% of carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. All of these gases combine to absorb ultraviolet radiation from the Sun and warm the planet's surface through heat retention.
1) __________________________________________________________________.
The atmosphere is divided into the following layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere. The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. There is air here.
2) _________________________________________________________________.
The troposphere begins at the surface and extends to between 7 km at the poles and 17 km at the equator. This part of the atmosphere is the most dense. The temperature drops from about 17 degrees C to -52 degrees C. The troposphere is known as a weather layer, as the clouds and fogs appear and the weather is formed.
3) __________________________________________________________________.
The overlying layer is the stratosphere, which extends to about 50 km above the surface.
Compared to the troposphere, this part of the atmosphere is dry and less dense. The temperatures in this region increases gradually to -3 degrees C. The stratosphere is important because it contains the ozone layer. This layer absorbs much of the sun's stronger ultraviolet rays. Many airplanes fly in the stratosphere because it is very stable.
The mesosphere extends to 85 km. The temperature there again as low as -93 degrees C.
4) __________________________________________________________.
This is the layer where most meteors burn up entering the atmosphere.
The top of the mesosphere called mesopause is the coldest part of the Earth's atmosphere. The thermosphere extends up to 600 km. There is the highest temperature in this layer that is why it is called thermosphere.
5) __________________________________________________________________
The temperature here can rise to 1,727 °C.
The thermosphere is a layer with auroras. Aurora is an interesting phenomenon; it is a polar light in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. The thermosphere is divided into the ionosphere and exosphere.
The ionosphere contains a high concentration of electrically charged particles (ions); these particles are responsible for reflecting radio signals important to telecommunications.
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere. Here the particles are so far apart that they can travel hundreds of km without colliding with one another.
6) __________________________________________________________.
The exosphere is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium.
5. True/false
-
The outermost layers of Earth are the crust, mantle and core. (False. The outermost layers of Earth are the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.)
-
The atmosphere is the thin, water envelope that surrounds Earth. (False. Gaseous envelope).
-
The atmosphere is composed of 78 % nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. (True)
-
The atmosphere is divided into three layers: troposphere, thermosphere and exosphere. (False. The atmosphere is divided into the following layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere.)
-
The troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere, there is the air. (True)
-
The mesosphere is important because it contains the ozone layer. (False. The stratosphere is important because it contains the ozone layer.)
-
The stratosphere is the layer where most meteors burn up upon entering the atmosphere. (False. The mesosphere is the layer where most meteors burn up upon entering the atmosphere).
-
The thermosphere extends up to between 600 km. (True)
-
The thermosphere is divided into the ionosphere and exosphere. (True)
-
The troposphere is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium. (The exosphere)
6. SS answer the questions:
-
What are the outermost layers of Earth? The outermost layers of Earth are the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
-
What is the atmosphere? The atmosphere is the thin, gaseous envelope that surrounds Earth.
-
What is air? Air is the mixture of gases that is composed of 78 % of nitrogen, 21% of oxygen, 0.93% of argon, 0.039% of carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases.
-
What layers is the atmosphere divided into? The atmosphere is divided into the following layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere.
-
Where does the troposphere begin? The troposphere begins at the surface and extends to between 7 km at the poles and 17 km at the equator.
-
Why is the stratosphere important? The stratosphere is important because it contains the ozone layer. This layer absorbs much of the sun's stronger ultraviolet rays.
-
What layer do most meteors burn up entering the atmosphere? The mesosphere
-
What layer has the highest temperature? The thermosphere
-
What layers is the thermosphere divided into? The thermosphere is divided into the ionosphere and exosphere.
-
What does the ionosphere contain? The ionosphere contains a high concentration of electrically charged particles (ions).
-
What is the exosphere mainly composed of? The exosphere is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium.
7. SS give the English for:
-
тонкая газовая оболочка
thin, gaseous envelope
-
радиация от солнца
radiation from the Sun
-
облака и туман
clouds and fogs
-
содержать озоновый слой
contain the ozone layer
-
поглощать ультрафиолетовые лучи
absorbs ultraviolet rays
-
где сгорают метеориты
where meteors burn up
-
в основном состоит из
is mainly composed of
8. SS give the Russian for:
-
unique in the solar system
уникальна в солнечной системе
-
combine to absorb ultraviolet radiation
соединяются, чтобы поглотить ультрафиолетовую радиацию
-
to warm the planet's surface
нагревать поверхность планеты
-
at the equator
на экваторе
-
through heat retention
путем удержания тепла
-
interesting phenomenon
интересное явление
-
high latitude
высокие широты
-
electrically charged particles
электрически заряженные частицы
Additional exercises (reserve)
9. SS give the definitions to the following words:
-
Atmosphere
The atmosphere is the thin, gaseous envelope that surrounds Earth.
-
Air
Air is the mixture of gases that is composed of 78 % of nitrogen, 21% of oxygen, 0.93% of argon, 0.039% of carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases.
-
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere.
-
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is a layer that contains the ozone layer.
-
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the layer where most meteors burn up entering the atmosphere.
-
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is a layer with the highest temperature.
-
Aurora
Aurora is an interesting phenomenon; it is a polar light in the sky.
-
Exosphere
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
Home work
To learn new words, to retell the text
Resume of the lesson
You've done the great job today.
Teacher: D.Zh. Ibatulina ______________ signature



