- Преподавателю
- Иностранные языки
- Методическое пособие по дисциплине Английский язык для студентов 1 курса заочного отделения специальностьНалоги и налогообложение
Методическое пособие по дисциплине Английский язык для студентов 1 курса заочного отделения специальностьНалоги и налогообложение
| Раздел | Иностранные языки |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Другие методич. материалы |
| Автор | Шишкевич С.А. |
| Дата | 21.10.2015 |
| Формат | docx |
| Изображения | Есть |
 Кафедра "Иностранные языки-3", автор-составитель Шишкевич С.А.
Кафедра "Иностранные языки-3", автор-составитель Шишкевич С.А.
Контент по дисциплине "Иностранный язык" - английский язык - для студентов I курса заочной формы обучения по специальности
"Налоги и налогообложение".
Основной целью обучения студентов английскому языку в неязыковом вузе
является овладение ими навыками практического владения этим языком, что предполагает формирование умения самостоятельно читать литературу по специальности с целью извлечения информации из иноязычных источников.
В условиях заочного обучения такие виды речевой деятельности, как устная речь (говорение и аудирование) и письмо используются на протяжении всего курса как средство обучения.
Перевод (устный и письменный) на протяжении всего курса обучения используется:
а) как средство обучения; б) для контроля понимания прочитанного; в) в качестве возможного способа передачи полученной при чтении информации.
Поскольку лица, обучающиеся на заочном отделении вуза, имеют иногда значительный
перерыв в изучении иностранного языка, и уровень их подготовки по данной дисциплине очень различается, данный контент включает грамматический и лексический материал, необходимый для овладения умениями и навыками чтения и понимания литературы по специальности вуза.

Module I
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
Family Life, Education, Future Career and Resume
In most families, it's a small family group who live in the same house, mother, father and the children before they get married. But if one of the grandparents dies, the other usually sells their home and goes to live with their children. So it's quite common to have one grandparent living with you. Most children leave home when they get married. But there are some people who want to lead independent lives and they find a flat as soon as they start their first job, even before they get married. Of course, the main problem is that flats are so expensive to rent here, and we simply have to live with our parents.
After 9th form pupils have to sit for examinations. Also they have a choice between entering the 10th grade of a general secondary school and enrolling in a specialized secondary or vocational school.
Finishing school is the beginning of the independent life for millions of school leavers. Many roads are open before them: technical schools, institutes and universities. But it is not easy thing to choose a profession out of more than 2000 existing in the world.

Some pupils follow the advice of their parents, others can't decide even after leaving school. Studying to be a lawyer represents the fulfillment of one of my longest held dreams. Whatever I could do as a lawyer to help people who are victimized by unscrupulous businessmen, as well as their own ignorance of the law, would give me a great satisfaction. The duty of the lawyer is not only to punish people for various crimes: from espionage to serial murder and terrorism, but they must do their best to prevent crimes, to fight against evil in our society. They should help those people, who committed an error (broke the law) to find the right road in their life. The lawyers protect the rights and legal interests of citizens, institutions and organizations. I want to help people, businesses to solve their problems; I want to help everybody to know the rules that we all have to get along. I think that the profession of a lawyer is one of the most important in the law-governed state, which we are creating now.
Persons, who finish the general secondary school, receive a secondary education certificate, giving them the right to enter any higher educational establishment. Entrance examinations are held in July and August. Institutions are headed by rectors; the faculties are headed by the deans. One has to study in the institute for 5 years. Higher educational institutions train students in one or several specializations.
Then you look for a job. That is why you have to know how to write a resume. No matter what method of job hunting you use, inevitably somebody will ask you for a resume. Most companies require a resume before seriously considering a job candidate from the outside. Resumes are sometimes also required in order to receive a job transfer within a company.
The purpose of a resume is to help you obtain a job interview, not a job. Very few people are hired without a personal interview.

Effective resumes are straightforward, factual presentations of a person's experience and accomplishments. They are neither over detailed nor too sketchy. A general rule is that two or three pages in length is best.
Notes:
to lead independent lives - жить отдельно
to get married - жениться (выходить замуж)
to enroll - записаться
to follow the advice - следовать совету
ignorance of the law - незнание закона
fulfillment of dreams - исполнение мечты
unscrupulous - беспринципный
higher educational establishment - высшее образовательное учреждение
to be headed by - возглавляться
to commit an error - совершить ошибку
in order to receive - для того, чтобы получить
experience and accomplishment - опыт и достижение
neither ... nor - ни... ни
Questions:
1. Why do young families want to live apart from their parents?
2. When do they start living independent life?
3. Why is it not easy to choose your future profession?
4. Why do people choose the career of a lawyer?
5. What do persons who finish the general secondary school do after school?
6. What do you do after getting the higher education?
7. Why do you need to know how to write a resume?
8. What is the main aim of a resume?
9. What makes a good resume?
10. How many pages are enough for a good resume?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант.
1. Most children ... home when they get married.
a) lives b) is living c) live
2. ... school is the beginning of the independent life
a) finishing b) to finishing c) finished
3. There ... some people who want to lead independent lives.
a) is b) are c) am
4. I ... a family.
a) has b) have c) is having
5. Many school leavers ... a higher institution
a) is enter b) enters c) will enter
6. Did you ... a good family life?
a) had b) have c) has
7. The profession of a lawyer ... one of the most important in the law-governed state.
a) is b) are c) am
8. Entrance examinations usually ... in July and August.
a) was b) is c) are
9. If my friend ... a good resume he will find a good job.
a) have b) has c) will has
10. The purpose of a resume ... to help you obtain a job interview, not a job.
a) are b) were c) is
Задание 3.
Определите, соответствуют ли данные предложения тексту.
Верно - true (T), неверно - false (F).
1. The purpose of a resume is to help you obtain a job.
2. Persons, who finish the general secondary school, receive a higher education.
3. It is not easy thing to choose a profession.
4. It is not important to know how to write a resume.
5. Most companies require a resume.
6. After 9th form pupils have to take examinations.
7. The lawyers protect the rights and legal interests of citizens only.
8. Most children leave home because they want independence.
9. Institutions are headed by deans.
10. Few pupils follow the advice of their parents.
Final Test
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. My wife can ... a car, but she … a driving license.
a) drive, hasn't got b) push, hasn't got c) drive, has got
2. One hundred minus forty-six is … .
a) forty-four b) fifty-five c) fifty-four
3. This … an piece … information.
a) is, by b) is, of c) are, in
4. Most of … generally like to … on the sofa and watch TV after work.
a) man, lie b) men, lie c) mans, sleep
5) I … a lot of free time … weekends.
a) haven' t got, at b) not have, on c) hasn't got, of
6. Our English lessons … school were boring. We … a lot of grammar rules by heart.
a) at, had to learn b) in, have to translate c) on, must learn
7. The tea isn't … enough … me.
a) favourite, with b) big, to c) sweet, for
8. … speak louder than words.
a) people b) actions c) silence
9. I sometimes ask my mother to … my children when I come home … .
a) look at, early b) look for, slowly c) look after, late
10. В феврале 29 дней.
a) February has twenty-nine days. b) February has twenty-nine day.
c) February has the twentieth nine days.
11. When I … short of money I feel … .
a) am, inhappy b) am, unhappy c) am not, unhappy
12. You had busy days … week, … ?
a) last, had you b) last, didn't you c) next, did you
13. Mary … a flat on the … floor.
a) has got, fifth b) have got, five c) has, fifty
14. How long does … take … to go… the nearest shop?
a) she, you, in b) it, your, from c) it, you, to
15. She likes … apples. … are very tasty.
a) this, they b) that, it c) these, they
16. … is your favourite season? - I … summer.
a) what, like b) who, want c) how, prefer
17. Mike … here two hours ago, but his parents … .
a) is, were b) was, weren't c) isn't, weren't
18. A change of work … .
a) is as good as a rest b) home as best c) must have an end
19. … I speak … Jane, please? - Just a minute.
a) may, with b) can, to c) must, about
20. Most of my friends … interested … Japanese cookery.
a) is, of b) are, at c) are, in
21. … is … house.
a) these, Toms' b) that, Tom c) this, Tom's
22. Kelly … be at work. She … at home.
a) must, is b) must, isn't c) mustn't, isn't
23. The café … is on the High Street … very good.
a) which, is b) where, was c) what, isn't
24. plays / piano / she / the / beautifully
a) She plays the piano beautifully. b) She plays beautifully the piano.
c) She beautifully plays the piano.
25. … you got … pain in the right side?
a) do, some b) has, no c) have, any
26. … you got … unemployed people in your town?
a) have, much b) have, many c) have, a little
27. There is … in the fridge. We … to buy … .
a) nothing, have, something b) no, must, anything c) some, can, nothing
28. … my jeans? - … in the wardrobe.
a) where is, they is b) where are, they are c) where is, it is
29. hobbies / you / have / what / interests / and?
a) You have interests got and hobbies? b) Have you got what interests and hobbies?
c) What interests and hobbies have you got?
30. Where is the bus station? - … is … the park.
a) it, near b) she, at c) this, in
Module II
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
Education in Russia and Great Britain 
Education is very important in modern world, which is full of technological advances.
All countries have traditional systems of education, according to which pupils start school at the age of 5, 6 or 7 and study at school for 11 or 12 years. This system of education seems good because pupils are taught by well-qualified teachers and they get the necessary amount of knowledge specified by a national curriculum. But some people believe that the current system is a failure because it doesn't teach children how to become good thinkers. School is about passing exams, but education should be about life.
In many countries education is compulsory, but school isn't. So many parents choose alternative ways of education for their children, for example, home education. Everyone continues studying after finishing school. There is no doubt that without good education you won't be able to find an interesting and highly-paid job because every company needs well-qualified employees. University life is usually interesting and exciting.
Education in Russia
Citizens of Russia have the right to education which is guaranteed by the Constitution and ensured by the broad development of compulsory secondary education, vocational, specialized secondary and higher education, by the development of correspondence and evening courses, by the provisions of state scholarships, grants and privileges for students.
In Russia there is a nine-year compulsory education, but to enter a university one has to study two years more. School starts at the age of 6 or 7 for Russian children. At school pupils study academic subjects, such as Russian, Literature, Mathematics, History, Biology, foreign languages and others.
After finishing secondary school, lyceum or gymnasium one can go on to higher education. Entrance competitive examinations are held in July and August.
Higher educational institutions are headed by Rectors. Prorectors are in charge of the academic and scientific work. Higher educational institutions train undergraduates and graduate students in one or several specializations. The faculties are headed by the Deans.
Institutions of higher education include: technical training schools, teachers training colleges, universities which offer masters and doctoral, degrees programmes. The faculties have specialized councils for conferring advanced academic degrees.
University education in Great Britain
 Oxford
Oxford  Cambridge
Cambridge
There are about 90 universities in Britain. Oxford and Cambridge, the oldest universities are world-known for their academic excellence. The University of London has the size and breadth to rank among the UK's top universities.
A university usually consists of colleges. The departments of the colleges are organized into faculties.
An undergraduate programme consists of a series of lectures, seminars, tutorials and laboratory classes which in total account for about 15 hours per week.
Lectures are given to large groups of students (from 20 to 200). Seminars and tutorials are much smaller than lecture classes and in some departments can be on a one-to-one basis (one member of staff and one student). Following a particular programme students take series of lecture courses which may last one academic term or the whole year.
Students prepare work in advance for seminars and tutorials. And this can take the form of researching a topic for discussion by writing essays or by solving problems. Lectures, seminars and tutorials are all one hour in length, laboratory classes last two or three hours.
The academic year is split into three terms. Formal teaching takes place in the first two terms which last for twenty four weeks in total. The third term is reserved for classes and examinations and lasts for six weeks.
University degree courses extend from three to four years. After three years of study a university graduate will leave with the Degree of Bachelor of Arts or Science. He can continue to take his Master's Degree and then the Doctor's.
Notes:
well-qualified - квалифицированный
curriculum - учебный план
compulsory - обязательный
competitive - конкурсный
correspondence - заочный
scholarship - стипендия
graduate student - аспирант
tutorials - практические занятия
term - семестр
Degree of Bachelor of Arts or Science - степень бакалавра гуманитарных или естественных наук
essay - письменная работа
staff - штат преподавателей (персонал)
academic year - учебный год
degree course - курс, ведущий к получению степени
Questions:
1. Why is education so important in modern life?
2. How are citizens of Russia encouraged to be educated?
3. What subjects do pupils study at school?
4. How long does anyone have to study at school to continue the education at the university?
5. What institutions does higher education include?
6. How many universities are there in Great Britain? What are the oldest?
7. What does an undergraduate programme consist of?
8. How are lectures, seminars and tutorials given to students?
9. How long may a lecture course last?
10. How long one must study to get the Degree of Bachelor?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант.
1. School isn't compulsory so many parents … alternative ways of education for their children.
a) choose b) will choose c) chose
2. Lecture courses usually … one academic term or the whole year.
a) lasted b) lasts c) last
3) 31 former polytechnics … university status in 1992 in Britain.
a) got b) get c) getted
4. To get ready for seminars and tutorials students … to prepare work in advance.
a) has b) have c) had
5. If an undergraduate … three years of study a university he … with the Degree of Bachelor of Arts or Science.
a) spends, leave b) will spend, will leave c) spends, will leave
6. I am finishing the 11th form this year. My school years … at the age of 6.
a) start b) started c) will start
7. Nowadays both colleges and universities … courses in teacher training, technology and medicine.
a) offered b) will offer c) offer
8. After finishing a secondary, vocational, technical school or a college, young people can start working or … an institution of higher education.
a) enter b) will enter c) enters
9. After having final formal teaching in the second term my British friend … examinations in the third term soon.
a) pass b) passed c) will pass
10. I … a course on Business English three years ago and I need it again.
a) take b) took c) taken
Задание 3.
Определите, соответствуют ли данные предложения тексту.
Верно - true (T), неверно - false (F).
1. Pupils start school at the age of 5, 6 or 7 and study at school for 8 or 10 years.
2. The academic year is split into four terms in Britain.
3. In Russia there is a nine-year compulsory education, and further anyone can go on to higher education.
4. Lectures, seminars and tutorials are all one hour in length, laboratory classes last two or three hours in British institutions of higher education.
5. In Russia young people may enter a university without passing entrance competitive examinations.
6. Higher educational institutions train undergraduates and graduate students in one specialization each one.
7. Oxford and Cambridge are the oldest universities in Great Britain and world-known for their academic excellence.
8. University degree courses extend from two to three years.
9. Higher educational institutions are headed by Rectors. The faculties are headed by the Deans.
10. Students of institutes and universities get state scholarship.
Final Test 
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. My aunt Vanessa is … artist. She lives in … beautiful old cottage by ... sea. She paints … small pictures of wild nature. Vanessa doesn't like leaving … cottage, but once … year she travels by … train to London and has … tea with me at … Savoy Hotel. Now I'm worried about her because Vanessa's in … hospital but I'm sure she will be better soon.
a) an, a, the, -, the, a, -, a, the, the b) a, the, the, a, the, a, the, a, the, a
c) an, the, the, -, a, a, -, -, the, the
2. It's … to imagine the world without tolerance and kindness.
a) inpossible b) impossible c) unpossible
3. 7 542 is …
a) seven thousand and five hundred and forty two b) seven thousand four hundred and forty second c) seven thousand five hundred and forty two
4. Oxford is the … university in Britain. To study there is considered … than somewhere else.
a) old, most prestigious b) oldest, more prestigious c) oldest, most prestigious
5. My … weather is when the sun shines … . It doesn't matter if it's summer or winter.
a) most favourite, bright b) the most favourite, brightly c) most favourite, brightly
6. Ann is the … girl in our group but Lucy is as … as Ann.
a) prettiest, clever b) most pretty, cleverer c) prettiest, cleverest
7. It's … colder today than yesterday. My house's … than yours.
a) most, warmest b) much, warmer c) very, warm
8. John … twice as … as his brother.
a) work, hardly b) working, harder c) works, hard
9. I … find mistakes. Maybe you can find … .
a) not, some b) didn't, some c) wasn't, any
10. Next year when tourists …, they … many new shops and restaurants.
a) will arrive, will see b) arrive, will see c) arrive, see
11. I … her business card, but strangely I … her at all.
a) have, don't recall b) has, don't recall c) don't have, recall
12. A month ago when we finally … Paris, we … completely tired.
a) did reach, were b) reach, was c) reached, were
13. I don't think next time Mike … it by himself. He … help.
a) will do, needs b) does, needs c) do, need
14. She … tired and … me not to … so much noise.
a) is, asked, make b) was, asked, make c) was, ask, made
15. Why did Poll … you if you … a car? He … to borrow it.
a) ask, have, wants b) ask, had, wanted c) asked, had, wanted
16. If you … something to eat, I … glad to … washing up.
a) make, will be, do b) will make, will be, do c) make, am, do
17. Do you ever gaze into … space and wonder if … other life forms exist in … universe?
a) a, -, the b) -, -, - c) -, -, the
18. Pam … to live abroad last week. I'm sad because we … friends since childhood.
a) moved, were b) moves, are c) move, was
19. Tomorrow the sky … cloudy. Nevertheless, we … to the beach because I want to swim.
a) be, go b) will be, go c) will be, will go
20. It usually … me an hour to get to work and I … to get up earlier than my wife.
a) take, need b) takes, need c) takes, needs
21. I didn't know if my colleague … any help when he … to me.
a) needed, comes b) needs, came c) needed, came
22. If you … it on your own, you can always … your parents.
a) can't do, consult b) do, consult c) not can do, consult
23. When my door neighbour … me she never … to me.
a) meet, talk b) meets, talks c) meets, doesn't talk
24. Today's students are … shy … it some years ago.
a) less, than b) less, as c) as, than
25. I … a new car last week, but I haven't sold my old car yet, so now I … much money.
a) bought, didn't have b) bought, doesn't have c) bought, don't have
26. Nick … married to Liza, but she … him.
a) is, don't trust b) was, not trust c) is, doesn't trust
27. Suddenly heavy rain … and my children … to the house fast.
a) begins, ran b) began, ran c) did begin, ran
28. Don't forget … me as soon as you … at the station.
a) to call, will arrive b) to call, arrive c) call, will arrive
29. I … travelling. My sister … to go round the world.
a) don't enjoy, prefers b) doesn't enjoy, prefer c) not enjoy, prefers
30. I … with my family, but now I …a flat with my boyfriend.
a) am used to live, do share b) was used to live, share c) used to live, share
Текущий контроль (I-II modules) 
Задание 1.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. policeman \ from \ is \ John \ a \ New York
a) John is a policeman from New York. b) Policeman John is from a New York.
c) from is New York a policeman John.
2. married \ sister\ is \ your?
a) Your married sister is? b) Your sister is married? c) Is your sister married?
3. mountains \ son \ skiing \ goes \ the \ in \ my
a) My son goes in the mountains skiing. b) My son goes skiing in the mountains.
c) My son goes in mountains the skiing.
4. your \ what \ name \ teacher's \ is?
a) What is your name teacher's? b) Your teacher's what is name? c) What is your teacher's name?
5. surname \ how \ spell \ do \ your \ you?
a) How do you spell your surname? b) Your surname how you spell do? c) You how spell your do surname?
Задание 2.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. … do you go to bed?
a) what b) who c) what time
2. … languages do you speak?
a) where b) how many c) how
3. … is a cup of coffee and a sandwich?
a) how much b) what c) when
4. … do you usually sit next to?
a) what b) who c) whose
5. … do you do at weekends?
a) what time b) where c) what
6. … do you go on holiday?
a) where b) when c) what
Module III
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
Geography, Political System, Economics of the Russian Federation, the UK and the USA
 The Russian Federation (or Russia) is a country that stretches over a vast expanse of Europe and Asia and occupies about one-seventh of the earth's surface. With an area of more than 17 million square kilometers, it is the largest country in the world by land mass, washed by 12 seas of 3 oceans. Russia is now an independent country and an influential member of the Commonwealth of Independent States since 1991.
The Russian Federation (or Russia) is a country that stretches over a vast expanse of Europe and Asia and occupies about one-seventh of the earth's surface. With an area of more than 17 million square kilometers, it is the largest country in the world by land mass, washed by 12 seas of 3 oceans. Russia is now an independent country and an influential member of the Commonwealth of Independent States since 1991.
Russia is a parliamentary republic with the President as the Head of State. The legislative powers are exercised by the Duma. The capital of Russia is Moscow, one of the oldest cities, the largest political, scientific, cultural and industrial centre.
Though Russia is very rich in coal, iron ore, copper, nickel and other mineral resources, it remains heavily dependent on exports of oil, natural gas, metals, and timber, which account for about 80% of exports. In recent years, however, the economy is showing the strengthening of its own internal market.
But in spite of the problems Russia is facing at present, there are a lot of opportunities for this country to become one of the leading countries in the world.
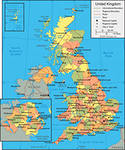 The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (or Britain) is situated on the British Isles. The British Isles consist of two large islands, Great Britain and Ireland, and above five thousand small islands. Their total area is over 244 000 square kilometers. The United Kingdom is made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (or Britain) is situated on the British Isles. The British Isles consist of two large islands, Great Britain and Ireland, and above five thousand small islands. Their total area is over 244 000 square kilometers. The United Kingdom is made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The UK is a constitutional monarchy. In law, the Head of State is the Queen, but in practice, the Queen reigns, but does not rule. The country is ruled by the elected government with the Prime Minister at the head. The British Parliament consists of two chambers: the House of Lords and the House of Commons. There are three main political parties in Great Britain: the Labour, the Conservative and the Liberal parties. The Liberal party is ruling the country nowadays.
The UK is a highly developed industrial country. It's known as one of the world's largest producers and exporters of machinery, electronics, textile, aircraft and navigation equipment. Agriculture is also developed in the country: there are a lot of crops grown there and a developed animal husbandry.
 The United States of America (or America) occupies most of the southern part of the continent of North America. It stretches from the Pacific Ocean in the west across to the Atlantic Ocean in the east, and down to the Gulf of Mexico in the south. The United States is the world's third largest country by land area. The total area of the country is over nine million square kilometers.
The United States of America (or America) occupies most of the southern part of the continent of North America. It stretches from the Pacific Ocean in the west across to the Atlantic Ocean in the east, and down to the Gulf of Mexico in the south. The United States is the world's third largest country by land area. The total area of the country is over nine million square kilometers.
The country is made up of fifty states. It is considered to be the oldest constitutional republic in the world, and has existed for over 200 years. The nation operates as a presidential system also known as a congressional system. There are three levels of government: federal, state, and local.
The USA is the world's wealthiest country. The value of the goods its factories produce, the crops its farms grow and the services it provides are larger than those from Russia, Japan and Germany combined. It also has a great wealth of natural resources, with many valuable minerals found below its ground.
The United States of America has vast economic, political and military influence on a global scale, which makes its foreign policy a subject of great interest and discussion around the world.
Notes:
to stretch - растягивать, простираться
influential - влиятельный
strengthening - укрепление, усиление
to reign - царствовать, господствовать
chamber - камера, зд. палата
animal husbandry - животноводство
to consider - считать, полагать, рассматривать
the wealthiest - самый богатый
valuable - ценный, значимый
value - значение, ценность, зд. величина
to influence - влиять, оказывать влияние
influence - влияние
Questions:
-
What country stretches over Europe and Asia?
-
What is the political system of Russia?
-
What natural resources is Russia rich in?
-
What countries is the United Kingdom made up of?
-
Who rules the UK?
-
What is Britain famous for?
-
Where is the United States of America situated?
-
How many states are there in the USA?
-
How many years has the country existed?
10. What kind of influence does the United States of America have in the world?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант.
1. A lot of countries … a lot of various problems at present.
a) is facing b) am facing c) are facing
2. The economy of Russia … the strengthening of its own internal market now.
a) is showing b) was showing c) will be showing
3. The Liberal party … the country nowadays.
a) was ruling b) is ruling c) shall be ruling
4. My friends … sightseeing when we met them near the museum.
a) are going b) was going c) were going
5. The country … a great number of hand-made things the whole decade last century.
a) was producing b) were producing c) is producing
6. This famous writer … in the USA for most of the 1990s.
a) am living b) was living c) is living
7. I … soon … my studies in King's College.
a) was … starting b) am … starting c) shall … be starting
8. The factories … lot of goods when they install up-to-date equipment.
a) will be producing b) were producing c) are producing
9. What … you … when we rang you up?
a) are … doing b) were … doing c) will … be doing
10. Russia … a new economic strategy all next year long.
a) will be developing b) is developing c) was developing
Задание 3.
Определите, соответствуют ли данные предложения тексту.
Верно - true (T), неверно - false (F).
1. Russia occupies about one-fifth of the earth's surface.
2. Russia is an influential member of the Commonwealth of Independent States since 1991.
3. There are a lot of opportunities for Russia to become one of the leading countries in the world.
4. The United Kingdom is made up of three countries: England, Scotland, Wales.
5. The Head of State is the Queen, the Queen reigns and rules the country.
6. There are three main political parties in Great Britain: the Labour, the Conservative and the Liberal parties.
7. The UK is a highly developed industrial and agricultural country.
8. The total area of the USA is less than nine million square kilometers.
9. The value of the goods is larger than those from Russia, Japan and Germany combined.
10. The United States of America has a little economic, political and military influence on a global scale.
Final Test 
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. Tom … Japanese is … all the languages he has studied.
a) think, the most difficult from b) thinks, the most difficult of c) thinks, more difficult in
2. There is a … going around the office that Mr. Blake … to leave at the end of the month.
a) rumour, is going b) report, going c) news, goes
3. … not … glass in the windows, that's why … so cold inside.
a) it is, no, it is b) there are, some, there is c) there is, any, it is
4. Hurry up! The ship … … New York soon.
a) leaves, to b) leaving, in c) is leaving, for
5. Ms. Jones, please, type … letters before noon. - Of course, sir. I … at the moment.
a) these, am doing b) this, do c) that, doing
6. Let's wait in this place … the wind … so strongly.
a) which, not blowing b) where, isn't blowing c) when, not blow
7. … is Gail? - I'm not sure, maybe she … the report at home.
a) where, is finishing b) who, finishing c) how, is finishing
8. Shhh! I … some men … in the distance. … you hear it too?
a) hear, is shouting, does b) am hearing, shouting, are c) hear, are shouting, do
9. The Chinese … strong traditions. Does your friend know … ?
a) has many, any b) have much, some c) have many, any
10. I have my English class … Monday morning. … you … to come?
a) on, are going b) in, is going c) at, do go
11. I was late. The students … a test when I … to class.
a) was writing, am getting b) were writing, got c) write, get
12. Tomorrow … this time, we … the lecture.
a) on, will attend b) at, will be attending c) in, will attending
13. You ... excuses … not … your homework on time.
a) are always making, for, doing b) always make, about, doing c) are always make, with, do
14. I'd like to ask you … questions. I need … more information.
a) few, little b) a few, a little c) few, a few
15. Last weekend when my parents … I with my girlfriend … a new film.
a) come, was enjoying b) came, were enjoying c) were coming, enjoy
16. Our band … new songs and … the best on Friday evening … next week.
a) will sing and play, on b) sing and play, in c) will be singing and playing, -
17. When Ms. White … the children …, the babysitter … on the sofa.
a) phoned, were fighting, was lying b) phones, was fighting, lying c) phone, fight, lies
18. It's Sunday afternoon. A mother … dinner for her children while they … their room.
a) is cooking, are cleaning b) cooks, clean c) cooking, cleaning
19. It … be raining outside. I … people with umbrellas.
a) can, am see b) must, see c) may, am seeing
20. … your business? - Not bad. We … on this interesting project.
a) how's, are still working b) what's, were still working c) who's, still work
21. I … for a walk at lunchtime. Who … to go with me?
a) go, wants b) going, wanting c) am going, wants
22. This time … last year my friends … in the South. Unfortunately, I … stay in the city.
a) in, were rest, have to b) -, were resting, had to c) at, rested, must
23. I have … work today. My family … when I … .
a) many, will sleep, come b) a lot of, will sleeping, came c) much, will be sleeping, come
24. My sister … to her boss at 8 p.m. tonight. They … in a café.
a) will talk, will meet b) talks, meet c) will be talking, will meet
25. Look! What a fine day! The sun …, birds … . I … it.
a) shines, sing, like b) is shining, are singing, like c) shining, singing, liking
26. I … that Ann … the truth now. This isn't in favour of her company.
a) not think, tells b) don't think, is telling c) am not thinking, telling
27. All last term our teacher … us hard. As a result we … English grammar well now.
a) was training, know b) trained, knew c) is training, are knowing
28. He … a new article this week. I'm sure it isn't difficult work … him.
a) is translating, for b) translates, with c) will translate, to
29. Sam … to understand what Mary … in his flat.
a) wants, seeking b) wanted, was seeking c) is wanting, is seeking
30. It's so romantic! We … in the night and … millions of stars … our heads.
a) stay, watch, on b) stayed, watched, before c) are staying, watching, above
Module IV
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
Ecology of Transport and Environmental Protection
Ecology is the study of the environment and the way plants, animals, and humans live together and affect each other. This word came from the Greek 'oikos' which means 'home'.
The problem of protecting nature is of primary importance today. Through their daily activities people pollute water, air, soil. If these activities aren't stopped the damage may become irreversible.
The Earth is suffering many ecological problems. One of them is air pollution. Air pollution destroys the ozone layer which protects the Earth from the dangerous light of the Sun.
The second important problem is water pollution. Plants and factories put trash into seas lakes and rivers. Many birds and fish die because of the polluted water.
Industries located along waterways downstream contribute a number of chemical pollutants, some of which are toxic. Another form of pollution that is characteristic of industrial societies is noise.
Waste is an enormous problem. One third of all waste is burnt which leads to contamination of air, water and soil. Waste recycling is of a great importance in most European countries.
Railway transport industry negatively impacts on nature by building railroads and industrial enterprises. Operation of railways and rolling stock lead to great fuel and energy consumption, and exhaust fumes from diesel locomotives contain a lot of harmful substances.
Construction and functioning of railways is connected with pollution of natural complexes by emissions, drains, waste which may break balance in ecological systems. In comparison with different means of transport, railways are environmentally friendly. Electric trains cause no pollution at all, while diesel-powered trains generate fifteen times less harmful substances than automobiles for the same traffic.
In recent years the pollution problems have received great publicity. Protection of natural resources and wildlife is becoming a political programme in every country.
Non-political environmental organisation Greenpeace has gained widespread trust and support. There are many serious actions in the list of Greenpeace activities. The national offices exist in 27 countries of the world. In Russia Greenpeace was formed in 1992. It works here in three directions: Wood Campaign, Antinuclear Campaign and Campaign for preservation of Lake Baikal. Greenpeace tries to attract public attention to different problems in the world and to find the way out.
To protect nature people should change their attitude to it. People must realize that they should keep air and water clean by establishing strict pollution control. Efforts are made to reduce pollution caused by automobile engines. Nowadays pollution-free engines are being developed which may eventually eliminate more serious air pollution problems. 
Notes:
to affect - оказывать влияние
to pollute - загрязнять
waterways downstream - вниз по течению
waste - отходы
contamination - загрязнение
rolling stock - подвижной состав
exhaust - выхлоп
drain - утечка
widespread trust - большое доверие
to eliminate - исключить
Questions:
-
What does the term "ecology" mean?
-
What ecological problems does the Earth suffer?
-
How does the railway transport industry impact on nature?
-
How is construction and functioning of railways connected with pollution of natural complexes?
-
Do electric trains cause any pollution?
-
Is Greenpeace a political or environmental organisation?
-
When was Greenpeace formed in Russia?
-
How does Greenpeace work in Russia?
-
What should people do to protect nature?
10. Have the pollution problems received great publicity nowadays?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант.
1. In recent years the pollution problems … great publicity.
a) has received b) will have received c) have received
2. Non-political environmental organisation Greenpeace … widespread trust and support.
a) has gained b) had gained c) have gained
3. Politicians … the problem of global warming until 2010.
a) have solved b) will not have solved c) will have not solved
4. In ten years' time, some wild animals … extinct.
a) will have become b) will have c) have become
5. By the year 2050, the temperature of the Earth … a few degrees.
a) will be rising b) will rise c) will have risen
6. Do you think people … up using cars in 50 years' time?
a) will give b) have given c) will have given
7. By the time the train finally arrived, we … for two hours already.
a) have waited b) had waited c) will have waited
8. In the 1960s people … on the streets, but not now.
a) had protested b) would protest c) have protested
9. Do you think we … a cure for AIDS by the year 2020?
a) will be finding b) will have found c) have found
10. My mother … by air.
a) has never travel b) have never travelled c) has never travelled
Задание 3.
Определите, соответствуют ли данные предложения тексту.
Верно - true (T), неверно - false (F).
-
The problem of protecting nature is of no importance today.
-
The second important problem is wastes.
-
Another form of pollution that is characteristic of industrial societies is noise.
-
Railway transport industry positively impacts on nature by building railroads and industrial enterprises.
-
Railways are environmentally harmful.
-
Electric trains cause much pollution.
-
In recent years the pollution problems have received great publicity.
-
Greenpeace tries to attract public attention to different problems in the world.
-
Greenpeace works in Russia in five directions.
10. Nowadays pollution-free engines are being developed.
Final Test 
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. There … a robbery of the bank on the High Street last night. … was stolen, … it ?
a) is, anything, was b) will be, something, wasn't c) was, nothing, was
2. We … some mice in the house lately. So we set some traps to get rid … them.
a) have seen, of b) saw, from c) see, against
3. Nick apologized … Kate … stepping on her dress.
a) before, about b) with, from c) to, for
4. Mr. Black, please, settle this question as soon as you … . - I … it, sir. Here's the report.
a) may, did b) can, have already done c) must, am doing
5. I can't find the book. Gail must … it with her when she went … .
a) take, from b) has taken, off c) have taken, out
6. … was early morning. The sun … just risen. A city … slowly.
a) there, has, is waking up b) it, have, wakes up c) it, had, was waking up
7. They … have … more strawberries. I want … to make jam.
a) can't, any, some b) mustn't, no, any c) can, any, any
8. Bob, … breakfast yet? - Yes, I … .
a) have you had, have b) did you have, did c) do you have, had
9. We … all the tasks since we … working on this test.
a) are answering, beginning b) have answered, began c) answer, begin
10. I … very busy before we … .
a) have been, met b) was, met c) was being, were meeting
11. Liza, … anything from Ted? Is he still in Rio? - He … be on his way home. I'm not sure.
a) did you hear, may b) had you heard, must c) have you heard, could
12. Ann, … tickets on your plane? What time … it take … ?
a) did you buy, did, out b) have you already bought, does, off c) do you buy, is, from
13. I remembered that Jack … his driving test. Finally he gave … trying to pass.
a) have failed, away b) had failed, up c) failed, off
14. It was … coffee that I had … cup.
a) so a good, else b) so good, other c) such good, another
15. How … will it … to learn the poem by heart?
a) much, need her b) long, take her c) many, she take
16. Mary has never been … London, … she?
a) to, has b) in, hasn't c) at, didn't
17. Why … your boots so … ? I … been playing football.
a) is, dirt, am b) have, dirtiest, has c) are, dirty, have
18. The door … closed. Jane … before we got there.
a) is, had left b) was, had leave c) has, has left
19. Improve your language … ! Practice more! You … Spanish fluently by the end of the year.
a) quality, speak b) skills, will have spoken c) ability, will speak
20. I … my car. Could you … me yours for a week?
a) have just sold, lend b) sell, borrow c) sold, give
21. We are finishing classes earlier than usually this year. Students … the exams … June.
a) pass, in b) will have passed, by c) will have, on
22. Please, … get … the bus. It's time … .
a) nobody, from, starting b) anybody, out, start c) everybody, on, to start
23. The production of milk … from year … year. By the time he comes back we … enough quantity for export.
a) is increasing, by, will have b) increases, to, will have had c) increased, with, have
24. My neighbours … the house … ten years, when they … to sell it.
a) had owned, for, decided b) owned, -, decided c) have owned, since, decide
25. Alice … the … before she … the letter.
a) will have learn, new, get b) will have learnt, news, gets c) will learn, new, will get
26. Den … his land many years ago. In 1953.
a) buys, ninety fifty third b) bought, ninety fifty three c) had bought, nineteen fifteen three
27. My friends … been waiting … me since I arrived at the town.
a) has, to b) is, of c) have, for
28. Sue … to me for nearly a month. I suppose that she's … a business trip.
a) hadn't written, from b) didn't write, on c) hasn't written, in
29. … you ever been … Turkey? Many Russian … spend their summer holidays there.
a) do, in, people b) are, on, peoples c) have, to, people
30. The longest day … .
a) must have an end b) you speak c) is a friend in need
Итоговый контроль (III-IV modules) 
Задание 1.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. Pierre … twenty cigarettes a day, but he … now because he's in class.
a) smokes, isn't smoking b) is smoke, not smoking c) smoking, not smoke
2. Alice and Peter … for a new house. They … living in London.
a) look, not like b) look, don't like c) are looking, don't like
3. I always … nice clothes for work. Today I … a bluejacket and skirt.
a) wearing, wear b) wear, am wearing c) wear, wear
4. Why you … to bed? It's only 10 p.m. - I always … to bed early.
a) do you go, go b) going, go c) are you going, go
5. He usually … in a bank, but today he … at home. He … reports.
a) works, is working, is writing b) work, working, write c) is working, works, writing
Задание 2.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. A teacher … me a lift to work tomorrow if I like.
a) will give b) gives c) gave
2. I … and see Venice as soon as I … Italy.
a) will go, will reach b) go, reach c) will go, reach
3. Where … for the next holiday?
a) do you go b) are you going c) will you go
4. I think he … when Jack … .
a) doesn't know, returns b) won't know, will return c) doesn't know, will return
5. She … if you ask her.
a) will come b) come c) are coming
6. I … glad if some of these hopes … realized.
a) will be, will be b) will be, are c) am, will be
7. I'm afraid I'm not quite ready. - Never mind. I … .
a) will wait b) wait c) am waiting
Задание 3.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
1. I … Anna ten years ago.
a) meet b) have met c) met
2. My sister … to France.
a) did never go b) has never been c) never go
3. I … a lot of ice-cream when I … a child.
a) have eaten, was b) ate, was c) eat, have been
4. They … Everest in 1953.
a) climbed b) have climbed c) climb
5. Star Wars is on TV tomorrow. … it?
a) did you see b) have you ever seen c) do you see
6. I like your watch. Where … it?
a) do you buy b) did you buy c) have you bought
7. … Chinese food before?
a) did you try b) do you try c) have you tried
Грамматический минимум к заданиям после текста 
Для того чтобы правильно выполнить задания, необходимо усвоить следующие разделы курса английского языка:
1. Простое распространенное предложение.
В повествовательном предложении (утвердительной и отрицательной формах) прямой порядок слов.
(обстоятельство) + подлежащее + сказуемое + дополнение + (обстоятельство)
2. Оборот there + be - быть, находиться, существовать.
Правила перевода:
а) если в предложении с оборотом there+be есть обстоятельства, перевод начинается с этого оборота.
There are many new industries in New-York. В Нью-Йорке много новых видов промышленности.
б) при отсутствии обстоятельства перевод начинается с самого оборота, т.е. с глагола.
There are different kinds of museums. Есть (существуют) различные виды музеев.
3. Множественное число имен существительных образуется путем прибавления окончания -s или -es.
a lecture лекция
lectures лекции
Исключения (мн.ч. образуется путем изменения корневой гласной):
a man - человек, мужчина men - люди, мужчины
a woman - женщина women - женщины
a foot - фут feet - футы
4. Грамматические функции окончания -s в предложении.
а) показатель 3 л. ед. ч. в Present Simple
б) показатель мн. ч. имени существительного
He works only five days a week. Он работает только пять дней в неделю.
works глагол - сказуемое в 3 л. ед. ч.
days мн. число имени существительного
в) окончание притяжательного падежа имени существительного в ед. и мн. числе.
Washington's street plan may seem very complicated to a visitor.
План улиц Вашингтона может показаться посетителю очень сложным.
5. Имя прилагательное - часть речи, которая употребляется для обозначения признака предмета -.financial year - финансовый год; direct taxes - прямые налоги.
Качественные прилагательные в английском языке имеют три степени сравнения: положительную, сравнительную и превосходную. Сравнительная степень одно-
сложных и некоторых двусложных прилагательных образуется путем прибавления к форме прилагательного в положительной степени суффикса -ег, а превосходная степень - путем прибавления суффикса -est.
Степени сравнения имен прилагательных.
Положительная (исходная) дается в словаре, сравнительная и превосходная образуется при помощи суффиксов.
Простые прилагательные
Положительная
Сравнительная
Превосходная
small
маленький
smaller
меньше
the smallest
самый маленький
Сложные прилагательные
difficult
трудный
more difficult
труднее
the most difficult
самый трудный
Исключения:
good, well
хороший, хорошо
bad, badly
плохой, плохо
much, many
много
little
маленький, мало
far
дальний, далекий далеко
better
лучше
worse
хуже
more
больше
less
меньше
farther, further
более дальний, дальше
the best
самый лучший,
лучше всего
the worst
самый плохой,
хуже всего
the most
самый большой,
больше всего
the least
самый маленький, меньше всего
the farthest, furthest
самый дальний, дальше всего
Конструкции типа:
the...the - чем...тем
as...as - такой же...как
not so...as - не такой...как
as + прилагательное + possible - как можно + прилагательное в сравнительной степени
The more exercises we do, the better we understand the grammar rules.
Чем больше упражнений мы делаем, тем лучше мы понимаем грамматические правила.
6. Числительные.
Количественные (отвечают на вопрос сколько)
От 1-12 - корневые
1 - one 7 - seven
2 - two 8 - eight
3 - three 9 - nine
4 - four 10 - ten
5 - five 11 - eleven
6 - six 12 - twelve
От 13-19 образуются при помощи суффикса -teen 13 - thirteen
Десятки образуются при помощи суффикса -ty
20 - twenty
30 - thirty
40 - forty
50 - fifty, etc.
100 - a (one) hundred
101 - one hundred and one
1000 - a (one) thousand
1250 - one thousand two hundred and fifty
1000000 - a (one) million
Чтение дат:
При чтении дат год произносится двумя цифрами:
1986 - nineteen eighty six
Порядковые (отвечают на вопрос который), образуются прибавлением суффикса -th к количественному числительному, употребляются с определенным артиклем, например:
4th - the fourth - четвертый
Исключения:
1-st the first - первый
2-nd the second - второй
3- d the third - третий
7. Местоимения.
Таблица личных и притяжательных местоимений.
Личные местоимения
Притяжательные местоимения
Имен. падеж
Объектный падеж
Простая форма
Независимая форма
Ед.ч.
я
ты, вы
он
она
он, она
оно
Мн.ч.
мы
вы
они
I
you
he
she
it
it
we
you
they
мне, меня
тебе, тебя
ему, его
ей, ее
ее, его, ему
нам, нас
вас, вам
их, им
me
you
him
her
it
it
us
you
them
мой, я,
твой, ваш
его
ее
его, ее
наш
ваш
их
my
your
his
her
its
its
our
your
their
mine
yours
his
hers
its
its
ours
yours
theirs
Притяжательные местоимения.
а) переводятся: свой, своя, свое, своих.
He gave all his life to the increase of human knowledge.
Он отдал всю свою жизнь увеличению человеческих знаний.
б) иногда не переводятся:
He raised his hand.
Он поднял руку.
Вопросительные местоимения.
who - кто
what - что, какой
whose - чей
which - который
Указательные местоимения.
Ед.ч.
Этот, эта, это - this
Тот, та, то - that
Это - it
Такой - such
Мн.ч.
Эти - these
Те - those
No - отрицательное местоимение - никакой, ни один
No student can translate this article without the help of a dictionary.
Ни один студент не может перевести эту статью без словаря.
Неопределенные местоимения и их производные местоимения.
В утвердительных
предложениях
some
несколько
некоторые
какой-то
примерно
около
any
любой
всякий
something
кое-что
что-то
что-нибудь
anything
все что угодно
somebody,
someone
кто-то
кто-нибудь
anybody,
anyone
любой
всякий
somewhere
где-то
куда-то
куда-нибудь
anywhere
везде
где угодно
В вопросительных
предложениях
any
какой-нибудь
сколько-нибудь
anything
что-нибудь
anyone,
anybody
кто-нибудь
anywhere
где-нибудь
куда-нибудь
В отрицательных
предложениях
not any
no
никакой
not anything
nothing
ничто
ничего
nobody
no one
none
not anybody
никто
никого
ничто
not...anywhere
nowhere
нигде
никуда
Во всех видах предложений
every
всякий
everything
всё
everybody
everyone
все
everywhere
везде
всюду
Местоимения many, much, few, little, a few, a little.
many - много
few - мало
a few - несколько
much - много
little - мало
a little - немного
a few methods - несколько методов
a little water - немного воды
употребляются с исчисляемыми, поддающимися счету во мн. ч. существительными
употребляются с неисчисляемыми существительными в ед.ч.
Module V
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
Taxes & Taxation Policy
 What are taxes?
What are taxes?
Taxes are defined as financial burdens borne by individuals and legal entities according to their ability to contribute towards the expenditures of public authority without a specific compensation. Taxes are compulsory levies that are regularly imposed and, as a rule, not destined for a special purpose; they are regarded as a contribution to the State Budget from which most government expenditures are financed in the common interest of the society.
Taxes represent a general obligation of taxpayers. In other words, there is no relationship between the tax paid by the person and the benefits received as a result of public expenditure. In modern economies taxes are the most important source of government's revenue.
Taxes are considered to have three functions:
a) fiscal or budgetary, to cover government expenditures, to provide the public authorities with the revenue required for meeting the cost of defense, social services, interest payments on the national debt, municipal services, etc.;
b) economic, to give effect to economic policy, to promote such general aims as full employment, monetary stability, to influence the stable satisfactory rate of economic growth of the nation, and also to influence the macroeconomic performance of the economy ( the government's strategy for doing this is called its fiscal policy. To achieve this aim tax exemptions are used.);
c) social or redistribute, to increase the welfare of the community, to lessen inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth by redistributing resources between individuals or classes of the population. Modern social security systems are intended to support the poor, the disabled or the retired by taxes on those who are still working.
Taxes are compulsory involuntary payments and every citizen of the country is legally bound to the tax imposed on him. Failure to pay taxes, or paying less than one owes, can lead to substantial penalties (besides just the tax owed). If the failure to pay or the payment of incorrectly low amount is intentional, not merely a mistake, it is a crime subject to more severe penalties, including large fines and imprisonment.
Progressive and regressive taxes describe the tax table, not a political opinion. In a progressive tax, the more you earn, the higher your tax rate. The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax. In this case, the less you earn, the higher your tax rate.
The classical progressive tax is income tax, where people with more income pay a higher percentage of it in taxes.
The classical regressive tax is income tax, where people with more income pay a less percentage of it in taxes. The classical regressive tax is sales tax (since lower income people spend a large portion of their income). Many taxes tend to be regressive in practice: social security taxes (because they exclude interest, rent, and other kinds of income common for the affluent), excise taxes and etc.
The main kinds of tax can be divided roughly into four groups:
-
direct taxes on incomes;
-
indirect spending taxes on individuals;
-
taxes on wealth;
-
company taxes.
Taxation Policy
There are many tax regimes in the world, with the rules for individuals and companies tailored to meet local conditions. Taxation is extremely complex.
The amount of money the government requires depends on its policy. Governments on the left tend to help the disadvantaged sections of society and generally need higher revenues than those on the right who deals with free market and little involved in the lives of individuals.
The tax burden on the individual in most Western countries appears to have fallen in the past decade, but some cuts are more apparent than real. In the UK, for instance, direct taxes on income have been cut substantially, but indirect taxes on spending (VAT) have risen to compensate it. Thus, the way in which the taxes are collected may have changed but the government's overall tax take has not been reduced.
Taxation policy may also reflect socially desirable and undesirable priorities in society. Interest on savings, contributions on charity may be tax-free to encourage thrift. Smoking and drinking may be discouraged by high level of tax imposed on them. Car ownership may be restricted by high sales taxes or duties on petrol. By transferring some resources to a central pool, communal projects for a common good can be paid for. Each country has its own priorities.
Notes:
burden - бремя
individual - личность, зд. физическое лицо
legal entity - юридическое лицо
to contribute - вносить вклад
charity - благотворительность
expenditure(s), spending - расходы, траты
public authority - органы государственной власти
revenue - годовой доход (государственный), валовой доход, доходные статьи бюджета
to impose a tax on (syn. to levy a tax) - облагать налогом
levy (n) - сбор, пошлина
benefit - польза, выгода
obligation - обязательство
to give effect - осуществлять, приводить в исполнение
exemption - законное освобождение от уплаты налога
welfare - благосостояние
inequality - неравенство
involuntary - недобровольный
bound - обязанный
failure - невыполнение
to owe - быть должным
severe penalty - строгое наказание
fine - штраф
tax rate - ставка налога
progressive tax - прогрессивный налог; налог, взимаемый по прогрессивной шкале
regressive tax - регрессивный налог
direct \ indirect - прямой \ косвенный
income - доход
wealth - богатство, зд. имущество
to meet local conditions - соответствовать местным условиям
disadvantaged - нуждающийся в помощи, обездоленный
Value Added Tax (VAT) - налог на добавленную стоимость (НДС)
overall tax take - общая сумма собранных налогов
desirable \ undesirable - желательный \ нежелательный
interest - ссудный процент
savings - накопления
to encourage - поощрять
thrift - развитие
sales tax - налог с продаж
ownership - право собственности
duty - пошлина
common good - общее благо
Questions:
-
What are taxes?
-
Who is obliged to pay taxes?
-
What is the most important source of government's revenue?
-
What can failure to pay taxes lead to?
5. Is there any relationship between the tax paid by the person and the benefits received by him?
6. What functions of taxes do you know?
7. What are the main kinds of tax?
8. What do a progressive tax and a regressive tax mean? Give examples.
8. What kind of governments usually requires more money?
9. What can taxation policy reflect?
10. How are things encouraged and discouraged by taxation policy?
11. Why are resources transferred to a central pool?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант, обращая внимание на формы пассивного залога и на построение вопросительных предложений.
1. Big tax cuts … by the government all this year.
a) are promised b) is promised c) are being promised
2. He … for tax evasion (for not paying his tax) last year.
a) was fined b) has fined c) has been fined
3. The payments … over a long period for tax purposes (in order to pay less tax on them).
a) were spreaded b) were spread c) was spread
4. The government … of money because of falling oil revenues this month.
a) are short b) was short c) is short
5. New taxes … .
a) have been introduced b) were introduced c) have introduced.
6. Commonly people on fixed incomes … by inflation.
a) are hurt b) is hurt c) were hurt
7. The government's overall tax take … since 1990.
a) wasn't reduced b) hasn't been reduced c) haven't been reduced
8. The taxes weren't popular but they …
a) must to be collected b)had to be collected c) had be collected
9. What … the source of the state revenue?
a) do b) are c) is
10. Are taxes involuntary … voluntary payments?
a) and b) but c) or
11. Who … financial burdens (taxes) according to their taxability?
a) does bear b) bear c) bears
12. When anyone … pay taxes or pays less than he (she) owes what can it lead to?
a) doesn't b) don't c) isn't
13. What … the amount of money the government requires depend on?
a) have b) does c) is
Задание 3.
Подберите к словосочетаниям из А соответствующие русские словосочетания из В.
1. ... standard of living …
a) налоговые сборы b) уровень жизни c) ставка налога
2. … tax burden …
a) подлежать налогообложению b) налоговое бремя c) уровень налога
3. … set against tax …
a) налог на расходы b) ставка налога c) делать налоговый вычет
4. … tax revenue …
a) налоговые сборы b) налоговое бремя c) налоговый режим
5. … tax rate …
a) уровень налога b) налоговый вычет c) ставка налога
6. … tax on spending …
a) подоходный налог b) налог на расходы c) налог с продаж
7. … subject to tax …
a) подлежать налогообложению b) предмет налога c) ставка налога
Final Test 
Выберите один правильный ответ.
Выполняя перевод с английского на русский язык, придерживайтесь контекста налоговой тематики.
1. … taxation is … .
a) налоговая политика b) налогообложение c) налог
2. … to meet the conditions …
a) встречать условия b) ознакомиться с условиями c) соответствовать условиям
3. … to rise the VAT …
a) собирать НДС b) поднимать НДС c) понижать НДС
4. … tax for individuals …
a) налог для физических лиц b) налог для индивидуальностей c) налог для личностей
5. … standard of living …
a) стандарт жизни b) условия жизни c) уровень жизни
6. … disadvantaged sections of society …
a) обездоленные секции общества b) преуспевающие группы общества
c) нуждающиеся в помощи слои населения
7. … customs duty …
a) таможенная пошлина b) таможенный долг c) таможенная обязанность
8. … communal project for a common good …
a) хороший коммунальный проект для общества b) общественный проект для общего блага c) общий хороший проект
9. … overall tax take …
a) общая сумма собранных налогов b) собирать налоги c) часть от собранных налогов
10. … interest …
a) интересный b) интерес c) ссудный процент
11. … fine to the government …
a) прекрасное государство b) штраф государству c) хорошее государство
12. … high revenues …
a) большие суммы налоговых сборов b) успешный реванш c) высокий авторитет
13. ... legal entity …
a) легальное лицо b) юридическое лицо c) законное мероприятие
14. … покрыть государственные расходы …
a) to give effect to economic policy b) to provide the public authorities
c) to cover government expenditures
15. … повлиять на удовлетворительный темп экономического роста …
a) to influence the stable satisfactory rate of economic growth b) to influence the macroeconomic performance of the economy c) to give effect to economic policy
16. … освобождение от уплаты налогов …
a) obligation b) compensation c) exemption
17. … увеличить благосостояние общества …
a) to make people rich b) to increase the welfare of the community
c) to rise the welfare of the government
18. … уменьшить неравенство в распределение доходов …
a) to enrich the income of the community b) to lessen inequalities in the distribution of income
c) to make the inequalities of the society less
19. … система социального страхования …
a) plan of the social insurance b) scheme of the support the poor c) social security system
20. … источник государственных доходов …
a) source of government's revenue b) result of public expenditure
c) contribution to the State Budget
21. … всеобщая обязанность налогоплательщиков …
a) financial burdens borne by individuals and legal entities b) compulsory levies imposed on tax agents c) general obligation of taxpayers
22. … прогрессивный и регрессивный налоги дают представление о налоговой таблице …
a) progressive and regressive taxes represent the tax scheme b) progressive and regressive taxes describe the tax table c) progressive and regressive taxes describe political opinion
23. … чем больше заработаешь, тем выше будет ставка налога …
a) the more you earn, the higher your tax rate b) the less you earn, the lower your tax rate
c) the most you earn, the high your tax rate
24. … исходя из практики, многие налоги можно отнести к регрессивным …
a) many taxes tend to be regressive in practice b) in practice many taxes are regressive
c) many regressive taxes in practice
25. … количество денег, необходимое правительству …
a) the quantity of money the government needs b) the amount of money the government requires
c) the sum of money the government wants
26. … общая сумма налоговых сборов не была снижена …
a) direct taxes on income have been cut b) indirect taxes on spending (VAT) have risen
c) the government's overall tax take has not been reduced
27. … не подлежать налогообложению …
a) not be subject to tax b) may be tax-free c) not be tax levied
28. … облагать высоким налогом …
a) high level of tax imposed b) to levy high taxes c) be liable to high tax
29. … быть ограниченным из-за высоких налогов …
a) be restricted by high sales taxes b) be limited because of high taxes c) be cut by high taxes on sale
30. … налоговое бремя на физическое лицо …
a) direct taxes on income b) indirect taxes on spending c) the tax burden on the individual
Module VI
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
A History of Taxation 
Ancient Times
Taxation has been around in various forms for a very long time, dating back to the Romans. It has a long and influential history in the shaping of civilization through the world.
In Egypt, during the various reins of the Egyptian Pharaohs tax collectors were known as scribes. During one period the scribes imposed a tax on cooking oil. They had to audit household to insure that appropriate amounts of cooking oil were consumed and that citizens were not using leavings generated by other cooking processes as a substitute for the taxed oil.
In Greece, in times of war the Athenians imposed a tax called eisphora. No one was exempt from the tax which was used to pay for special wartime expenditures.
Athenians imposed a monthly poll tax on foreigners, people who did not have both an Athenian Mother and Father, of one drachma for men and a half drachma for women. The tax called metoikion.
In Roman Empire, the earliest taxes were duties on imports and exports called portoria.
Ceasar Augustus was considered by many to be the most brilliant tax strategist of the Roman Empire. During his reign as "First Citizen" the publicani were virtually eliminated as tax collectors for the central government. Saint Mattew was a publican (tax collector) from Capernaum during Caesar Augustus reign.
Caesar Augustus instituted an inheritance tax to provide retirement funds for the military.
During the time of Julius Caesar 1 percent sales tax was imposed. During the time of Caesar Augustus the sales tax was 4 percent for slaves and 1 percent for everything else.
The Tax History of Great Britain
The first tax in England was introduced during occupation by the Roman Empire. When Rome fell, the Saxon kings imposed taxes, called Danegeld, on land and property. The kings also imposed substantial customs duties.
During 14th century taxes were very progressive. Under the earliest tax schemes an income tax was imposed on the wealthy office holders, and the clergy. A tax on movable property was imposed on merchants. The poor paid little or no taxes.
In 1800 the British invented a precursor to the modern income tax we know today to finance their engagement in the war with Napoleon. The tax was repealed in 1816.
To meet the costs of the 1939-45 war, the United States, Canada and the UK, all increased the rates of income tax.
In 1965 James Callaghan caused fiscal indigestion by introducing both capital gains tax and corporation tax.
In 1972 Edward Heath took Britain into the European Community and the value added tax replaced the much narrower purchase tax.
In 1974 Denis Healey increased the top rate of income tax to 95%, an even higher rate than during the 1939-1945 war. It has contrasted sharply with the top rate of 40% since 1988, which has brought in more revenue by attracting business to the UK and reducing avoidance and evasion.
The History of the Tax System in the United States of America
Colonial Times
England's need for revenue to pay for its wars against France led it to impose a series of taxes on the American colonies. In 1765 the English Parliament passed the Stamp Act, which was the first tax imposed directly on the American colonies, and then Parliament imposed a tax on tea.
The Post Revolutionary Era
To pay the debts of the Revolutionary War, Congress levied excise taxes on distilled spirits, tobacco and snuff, refined sugar, carriages, property sold at auctions, and various legal documents.
During the confrontation with France in the late 1790's, the Federal Government imposed the first direct tax on houses, land, slaves, and estates. The direct tax on estates was the first Federal estate tax.
To raise money for the War of 1812, Congress imposed excise taxes and raised money by issuing Treasury notes. Congress imposed an extra tax on imported rum to discourage its consumption. High customs duties and the sale of public land were the main source of revenue.
The Civil War
When the Civil War erupted, Congress passed the Revenue Act of 1861, which restored earlier excise taxes and imposed a tax on personal incomes. This tax on personal income was a new direction for a Federal tax system based mainly on excise taxes and custom duties.
On July 1, 1862 Congress passed new excise taxes on such items as playing cards, gunpowder, feathers, telegrams, iron, leather, pianos, yachts, billiard tables, drugs, patent medicines, and whisky. Many legal documents were also taxed. From 1868 to 1913, almost 90% of all revenue was collected from the remaining excises.
World War I and 1920's
The entry of the United States into World War I greatly increased the need for revenue. The 1916 Revenue Act imposed taxes on estates and excess business profits.
Another revenue act was passed in 1918, which codified all existing income tax laws and taxed incomes of more than $1 million at a rate of 77%. Still only 5% of the population had to pay income taxes.
During the 1920's business boomed and as the economy expanded, revenue from the income tax also grew. To collect more revenue, Congress passed the Tax Act of 1932, which raised the tax rates and lowered the exemption levels.
The social security tax
The state of the economy during the Great Depression led to passage of the Social Security Act in 1935. This law provided payments known as 'unemployment compensation' to workers who lost their jobs. Other sections of the Act gave public aid to the aged, the needy, the handicapped, and to certain minors. At first, these programs were financed by a 1% tax, paid by both employers and employees, on the first $3,000 of the employee's salary or wage.
World War II
The Federal income tax system was significantly affected by World War II. The need for high defense spending led to passage in 1940 of two tax laws that increased individual and corporate taxes.
In 1943, employers were required to withhold taxes from employees' paychecks, as was done during the Civil War.
Recent developments
After World War II Congress followed the usual pattern of reducing taxes.
Tax Reforms Act of 1969, which reduced income tax rates both for individuals and private foundations. The Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981 contained large reductions in income tax rates.
The Tax Reform Act of 1986 was designed to create a fairer tax system while reducing the overall level of the Federal individual income tax.
The taxpayer Relief Act of 1997 made additional changes to the tax code and provided some significant benefits for families with children through the Per Child Tax credit. The significant feature of this tax relief was that the credit was refundable for many lower-income families.
The Bush Tax Cut 
Under President George W. Bush's leadership the Congress halted the projected future increases in the tax burden by passing the Economic Growth and Tax Relief and Reconciliation Act of 2001. The centerpiece of the 2001 tax cut was to regain some of the ground lost in the 1990s in terms of lower ; line-height: 100%">The 2001 tax cut represented a resumption of a number of other trends in tax policy. For example, it expanded the Per Child Tax credit from $500 to $1000 per child. It also increased the Dependent Child Tax credit.
Notes:
scribe - писарь, переписчик
to audit - делать ревизию
leavings - остатки
substitute - замена
reign - правление
poll tax - подушный налог
publican - откупщик (в древнем Риме)
to eliminate - ликвидировать, упразднять, уничтожать
inheritance tax - налог на наследство
funds - средства
land - земля
property, movable property - имущество, движимое имущество
scheme - программа, схема
customs duties - таможенные пошлины
office holder - должностное лицо
clergy - духовенство
engagement - занятость, участие
indigestion - неприятие
capital gains tax - налог на доходы от капитала
corporation tax - налог на прибыль организации
purchase tax - налог на покупку (включался в цену товара)
avoidance - освобождение от налога
evasion - уклонение от налога
snuff - нюхательный табак, порошок
estate tax - налог на недвижимость
to issue - пускать в обращение (деньги и т.п.)
Treasury note - казначейский билет, облигация
rum - спиртной напиток
excise taxes - акцизный сбор
excess profit - сверхприбыль
exemption level - необлагаемый уровень
social security tax - налог на социальное страхование
salary or wage - заработная плата
war effort - военная экономика
withhold taxes - удерживать налоги из заработной платы
refundable - возмещаемый
; background: transparent"> to regain some of the ground lost - вернуть утраченные позиции
Questions:
1. What do you know about taxation in Egypt?
2. What can you say about taxation in Greece?
3. What are the earliest taxes in Rome?
4. Who was the most brilliant tax strategist of the Roman Empire? Why?
5. Who instituted an inheritance tax?
6. When was the first tax in England introduced?
7. Which taxes were under the earliest taxing schemes in England?
8. When were capital gains tax and corporation tax introduced?
9. What countries increased the rates of income tax during the 1939-45 war? Why?
10. What did England's need for revenue lead to?
11. When and on what was the first direct tax levied?
12. When were excise taxes imposed?
13. Why did Congress impose an extra tax on imported rum?
14. What were new excise taxes imposed on during the Civil War?
15. What happened to exemptions and taxes during World War I?
16. Why were tax rates raised in 1932?
17. What did the state of economy during the Great Depression lead to?
18. What did this law provide?
19. What happened to the Federal income tax system during World War II?
20. Describe the Tax Reforms Acts of the next years: 1969, 1981 and 1986.
21. What changes did the taxpayer Relief Act of 1997 make?
22. What was the centerpiece of the 2001 tax cut?
23. What taxes do know (according to the texts)?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант, обращая внимание на формы пассивного залога и на построение придаточных предложений времени и условия.
1. A government tax on imports … since ancient times.
a) have been introduced b) has been introduced c) was introduced
2. Car ownership … by duties on petrol.
a) may be restricted b) is be restricted c) may restricted
3. Please, wait a little! The capital for the program … .
a) was being transferred b) is being transferred c) is been transferred
4. New duties on tobacco … considered when the prime-minister … .
a) will be … arrives b) will … will arrive c) will be … will arrive
5. If high level of tax … on smoking and drinking people … to do them.
a) was imposed … will be discouraged b) will be imposed … are discouraged c) was imposed … would be discouraged
6. If government … direct taxes on income in this case indirect taxes on spending (VAT) … to compensate it.
a) cut … have been risen b) will cut … will have been risen c) cut … will have been risen
7. He said the tax burden on individuals … .
a) had been decreased b) have been decreased c) will have been decreased
8. This tax regime … about 5 years ago.
a) is introduced b) was introduced c) has been introduced
9. The British government is planning taxes … 5 per cent over the next year.
a) to be increased by b) increased by c) to increase by
10. The Inland Revenue is the office where national taxes … for all the time in Britain.
a) have been collect b) have been collected c) are collected
11. When the tax official came the money … .
a) is being counted b) were counted c) was being counted
Задание 3.
Составьте словосочетания, используя слова из А и В. Сделать таблицу
a) A B
1) influential a) expenditures
2) tax b) import and export
3) poll c) history
4) wartime d) collectors
5) duties on e) tax
b) A B
1) customs a) schemes
2) movable b) war
3) tax c) duties
4) top d) property
5) engagement in the e) rate
c) A B
1) legal a) income
2) to raise b) tax rate
3) extra c) level
4) source of d) documents
5) personal e) foundations
6) exemption f) revenue
7) unemployment g) tax
8) private h) money
9) ">
Final Test 
Выберите один правильный ответ.
Выполняя перевод с английского на русский язык, придерживайтесь контекста налоговой тематики.
1. … dating back to the Romans …
a) идти назад к римлянам b) датируясь периодом Римской Империи c) находиться в Римской Империи
2. … tax collectors …
a) сборники налогов b) налоговые сборы c) сборщики налогов
3. … to audit household …
a) аудит дома b) держать хозяйство в порядке c) делать ревизию ведения домашнего хозяйства
4. … special wartime expenditures …
a) особые временные военные траты b) специальные военные расходы
с) существенные военные потери
5. … monthly poll tax …
a) ежемесячный подушный налог b) налог на подушки c) ежегодный налог на души
6. … brilliant tax strategist …
a) блестящий стратег в налоговой сфере b) налог на бриллианты
c) успешная налоговая политика
7. … military …
a) охрана b) вооруженные силы c) военные
8. … retirement funds …
a) пенсионные фонды b) средства для выплаты пенсий c) фонды льгот и пособий
9. … during occupation by the Roman Empire …
a) находиться под властью Римской Империи b) во время захвата Римской Империи
c) римляне в оккупации
10. … land and property …
a) земельное имущество b) земля и имущество c) земля в собственности
11. … tax schemes …
a) налоговая программа b) налог на программу c) схемы налога
12. … wealthy office holders …
a) обеспеченные владельцы офисов b) богатые офисы c) богатые должностные лица
13. … poor …
a) бедняки b) слабые c) бездомные
14. … engagement in the war …
a) неучастие в войне b) участие в войне c) трудовая занятость в войне
15. … rate of income tax …
a) предел косвенного налога b) ставка подоходного налога c) сумма прямого налога
16. … the value added tax replaced purchase tax …
a) ввод НДС заменил более узкий налог на покупку b) отмена НДС из-за налога на покупку c) ввод налога на покупку вместо НДС
17. … avoidance and evasion …
a) уклонение и неуплата налогов b) ввод и отмена налогов c) освобождение и уклонение от налогов
18. … для того чтобы сражаться, Англия нуждалась в денежных доходах …
a) a) to finance their engagement in the war b) to meet the costs of the 1939-45 war
c) England's need for revenue to pay for its wars
19. … чтобы оплатить долги …
a) to raise money b) to pay the debts c) to give the debts
20. … выпуск облигаций …
a) issuing Treasury notes b) legal documents c) excess business profits.
21. … дополнительный налог…
a) excise taxes b) taxes on estates c) an extra tax
22. … в течение 1920-х бизнес бурно развивался …
a) during the 1920's business boomed b) the economy expanded in the 20-th c) during the 1920's business developed sharply
23. … понизил необлагаемый уровень …
a) passed the Tax Act of 1932 b) lowered the exemption levels c) raised the tax rates
24. … принятие закона об уплате налога на социальное страхование …
a) passage of the Social Security Act b) law provided payments known as 'unemployment compensation' c) passage in 1940 of two tax laws
25. … старики, нуждающиеся, инвалиды и несовершеннолетние …
a) the pensioners, the poor, the ill and the children b) old, need, invalid and young c) the aged, the needy, the handicapped, and certain minors
26. … как работодатели, так и работники …
a) work givers and workers b) as employees as workers c) both employers and employees
27. … удерживать налоги из заработной платы …
a) gave public aid b) to withhold taxes from employees' paychecks c) on the first $3,000 of the e employee's salary or wage
28. … дополнительные поправки в налоговом кодексе …
a) usual pattern of reducing taxes b) large reductions in income tax rates
c) additional changes to the tax code
29. … чтобы создать более справедливую налоговую систему …
a) to create a fairer tax system b) to regain some of the ground lost c) to collect more revenue
30. … предоставил значительные льготы …
a) represented a resumption of a number of other trends b) provided some significant benefits
c) halted the projected future increases
Текущий контроль (V-VI modules) 
Задание 1.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
Выберите верное определение данных словосочетаний.
1. Tax avoidance is … .
a) freedom from payment of taxes allowed by law b) legal ways of paying less taxes
2. Tax code is … .
a) legislation that provides rules of tax charges and tax payments b) collection of laws, rules and regulations relating to taxation
2. Tax collector is … .
a) responsibility to pay taxes b) person authorized to collect taxes
3. Tax rate is … .
a) a charge or payment of taxes fixed according to a standard scale b) amount of income, capital gain, goods on which one must pay taxes; taxable income, taxable goods, property etc.
4. Tax evasion is … .
a) illegal ways of paying less or no taxes b) legal ways of paying less taxes
5. Tax law is … .
a) a statement which each taxpayer must make once a year showing his/her income during the past year b) legislation that provides rules of tax charges and tax payments
6. Tax exemption is … .
a) freedom from payment of taxes allowed by law b) legal ways of paying less taxes
7. Tax revenue is … .
a) money paid as taxes b) the income received by the state from taxation
8. Tax payment is … .
a) money paid as taxes b) a stated period in a year when a new business is allowed not to pay taxes (in some countries)
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант.
1. The tax that people pay on their wages and salaries.
a) capital transfer tax b) income tax c) wealth tax
2. A tax on wages and salaries or on company profits.
a) direct tax b) indirect tax c) value-added tax
3. A tax levied at a higher rate on higher incomes.
a) progressive tax b) regressive tax c) wealth tax
4. A tax paid on property, sales transactions, imports, and so on.
a) direct tax b) indirect tax c) value-added tax
5. A tax collected at each stage of production, excluding the already-taxed costs from previous
stages.
a) added-value tax b) sales tax c) value-added tax
6. Profits made by selling assets are generally liable to a … .
a) capital gains tax b) capital transfer tax c) wealth tax
7. Gifts and inheritances over a certain value are often liable to a … .
a) capital gains tax b) capital transfer tax c) wealth tax
8. The annual tax imposed on people's fortunes (in some countries).
a) added-value tax b) capital gains tax c) wealth tax
9. Reducing the amount of tax you pay to a legal minimum.
a) creative accounting b) tax avoidance c) tax evasion
10. The tax on wages and salaries (and business profits in the USA). In Britain the tax on business profits is called corporation tax.
a) direct tax b) income tax c) wealth tax
11. Property taxes, sales taxes, customs duties on imports, and excise duties on tobacco, alcoholic drinks, petrol, etc. are … taxes.
a) direct b) indirect с) value-added
12. Most sales taxes are slightly … because poorer people need to spend a larger proportion of their income on consumption than the rich.
a) progressive b) regressive с) direct
13. Making false declarations is called … and is obviously illegal.
a) creative accounting b) tax avoidance с) tax evasion
14. The tax on income from earnings in most countries.
a) progressive b) regressive c) total
Module VII
Задание 1.
Прочитайте, переведите текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Text
 Taxation in the Russian Federation
Taxation in the Russian Federation
The History of Taxation in Russia
In the Soviet Union in practice there was no real taxation system. Practically speaking, all production property and assets were state-owned, and asset and profit allocation was done by the central planning organization.
In the planned economy the companies were not actually taxed, rather they transferred certain residual amounts of financing back to the center.
With the economic reforms of 1900s, there emerged a need to create a taxation system suitable for a market economy.
A tax system started to emerge from the beginning of the 1990s. During these early years of reforms the tax laws did not take shape within a unified system, but rather through the ad hoc adoption of laws and rules, regulating taxation, which kept changing frequently. There was a lack of clear rules for norm hierarchy (knowing which laws and rules would take preference over each other) and a lack of rules defining the authority of various governmental, federal and local bodies. The gradual adoption of the Russian Tax Code has brought order into the taxation system.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Tax Code Part I
The highest norm on taxes is set in the Russian Constitution article 57, which states, that "all are obliged to pay legally established taxes and duties."
The first part of the Tax Code was adopted in 1998 and came into force on 1 January 1999. This first part of the Tax Code regulates general taxation matters, setting out of the most important provisions of the Russian taxation system. It gives a closed list of possible taxes and charges (articles 13, 14 and 15).
It specifies the procedure of how taxes are introduced and recalled, and regulates all taxation matters: from the relations of the state, tax authorities, tax agents and taxpayers to the procedure of calculation and payment of all taxes.
All the various taxes that can be levied in Russia are listed in the Tax Code.
Tax Code Part I sets:
1. Types of taxes and fees that can be levied (articles 12, 13, 14, 15).
2. Circumstances giving rise to a tax liability and its fulfillment (chapter 8).
3. Principles of the introduction, enforcement and cancellation of taxes and dues, federal and local (article 12).
4. The general terms for setting taxes and duties (article 17).
5. Rights and obligations of the taxpayers and the taxation authorities (articles 21, 23, 31, 32).
6. Detailed description of administrative compliance rules and Tax Audits (chapter 14).
7. Liability for Tax Offences (Section VI).
8. The appeal procedures and dispute regulation (Section VII).
Tax Code part II sets:
In the second part of the Tax Code each individual tax is described separately and completely.
The first taxes under the Tax Code were the Value Added Tax, the Excise, the Personal Income Tax and the Social Tax in chapters 21-24 of the Tax Code. These taxes were adopted in 2000 and came into force in 2001. The list of taxes which were levied in 2005 is as follows:
Federal Taxes and Fees
1. Profit Tax
2. Value Added Tax
3. Excise Taxes
4. Personal Income Tax
5. Unified Social Tax
6. Mineral Extractions Charges
7. State Duty
8. Inheritance and Gift Tax
9. Duty on Usage of Water Resources
10. Charges for Use of Natural Resources
Regional Taxes and Fees
1. Property Tax (Corporate)
2. Tax on Gambling Industry (regional tax from 1 November 2003)
3. Transport Tax
Local Taxes and Fees
1. Land Tax
The Tax Authorities of the Russian Federation
The first part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that Tax Authorities (Tax Bodies) in the Russian Federation are the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation and its territorial divisions in the Russian Federation (article 30).
According to article 31 the Tax Bodies have the "background: transparent">1) To demand from a taxpayer or a tax agent documents in the forms established by state bodies and local self-government bodies to serve as grounds for the calculation and payment (deductions and transfers) of taxes.
2) To carry on tax inspections in the order prescribed by this Code.
3) To make a seizure of documents, during tax inspections of a taxpayer or a tax agent, testifying the tax offences to be committed.
4) To call in taxpayers, payers of dues or tax agents to tax bodies to give explanations by means of written notices in connection with the payment (deduction or transfer) of taxes by them or in connection with a tax inspection.
5) To suspend transactions in the accounts of taxpayers, payers of dues and tax agents in banks and to arrest the property of taxpayers, payers of dues and tax agents.
6) To examine (inspect) workrooms, depots, trading and other premises and areas used by taxpayers to derive income or connected with the maintenance of the objects of taxation, regardless of their place of location, to draw up an inventory of the property belonging to taxpayers. The procedure for drawing up an inventory of the taxpayer's property during a tax inspection shall be endorsed by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
7) To determine the sums of taxes to be paid by taxpayers to the budget or to the extra-budgetary funds and calculated on the basis of available information about a taxpayer.
8) To demand that taxpayers, tax agents and their representatives should remove the revealed breaches of the legislation on taxes and dues and to control the fulfillment of said requirements.
9) To recover tax and due arrears and also penalties in the order established by this Code.
10) To control the compliance of big expenses of individuals with their incomes.
11) To demand from banks documents confirming the execution of payment orders of taxpayers, payers of dues and tax agents.
12) To attract specialists, experts and interpreters for tax control.
13) To call in as witnesses persons who may know any circumstances of relevance to tax control.
14) To apply for the cancellation or suspension the validity of licenses issued for the engagement in certain activities to entities and individuals.
Notes:
assets - активы, фонды, капитал
allocation - размещение
residual - остаточный
ad hoc - (применяемый) к данному, конкретному случаю
the highest norm - норма высшей юридической силы
to set - устанавливать
article - статья
to be obliged - быть обязанным
legally - законно
matter - вопрос
provision - положение, статья
charge - сбор, налог
to specify - четко определять
to recall - отменять, отзывать
calculation - подсчет, исчисление
fee - сбор
circumstance - условие, обстоятельство
to give rise - приводить к
tax liability - налоговая обязанность, задолженность по налоговым платежам
fulfillment - выполнение
due - пошлина, сбор, налог
enforcement - установление
cancelation - отмена
term - условие
offence - правонарушение
rights and obligations - права и обязанности
appeal procedure - порядок обжалования
Tax Authorities (Tax Bodies) - налоговые власти (налоговые органы)
Local self-government bodies - органы местного самоуправления
deductions - удержание
transfers - перечисление
ground - основание
seizure - выемка, конфискация
notice - уведомление
to derive - извлекать
workroom - производственное помещение
deport - складское помещение
trading - торговый
premises - помещения
to endorse - утверждать
extra-budgetary - внебюджетный
to remove - устранять
revealed - выявленные
breaches - нарушения
to recover - взыскивать
arrears - недоимки
compliance - соответствие
penalties - пени
to apply for - ходатайствовать
cancellation - аннулирование
Questions:
1. What was the state of the tax system in Russia during the period of the Soviet Union? Why?
2. When did a need to create a taxation system suitable for a market economy emerge?
3. Why weren't the tax laws shaped into within a unified tax system?
4. Where is the highest norm on taxes set?
5. What does Tax Code Part I regulate?
6. What does Tax Code Part I set?
7. What is listed in the Tax Code?
8. What does Tax Code part II set?
9. What federal, regional, and local taxes do you know?
10. What are the Tax Bodies of the Russian Federation?
11. What do the Tax Bodies demand from a taxpayer or a tax agent?
12. Who determines the sum of taxes to be paid to the budget?
13. What state authorities endorse the procedure of drawing up an inventory on taxpayer's property?
14. Who do the Tax Bodies attract for tax control?
Задание 2.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант, обращая внимание на формы инфинитива.
1. … the breakup of business, governments offer special relief on business assets.
a) to avoid b) avoid c) to be avoid
2. Governments impose high duties on petrol … car ownership.
a) to restricted b) by restricting c) to restrict
3. VAT is convenient enough … a ready source of income for government.
a) to have been b) being c) to be
4. It was too difficult … the citizens to save money in national saving schemes.
a) to be persuaded b) to persuade c) persuade
5. … taxes is necessary.
a) to pay b) pay c) I pay
6. There has been a tendency in recent years … the tax burden.
a) to have reduce b) to be reduce c) to reduce
7. The work … by tax officials is very complex.
a) was done b) to be done c) to do
8. Taxation policy seems … social priorities.
a) to reflect b) to be reflect c) reflect
9. The tax regime in the country tends … .
a) to improving b) be improving c) to be improving
10. The old tax rate is said … .
a) to have been cut b) to have cut c) have been cut
Задание 3.
Выберите один правильный ответ.
Подберите синоним.
1. Inspection is … .
a) check b) fulfillment c) basis
2. Execution is … .
a) accommodation b) check c) fulfillment
3. Offence is … .
a) enough b) breach c) basis
4. Legislation is … .
a) a set of laws b) accommodation c) denial
5. Ground is … .
a) merchant b) premises c) basis
6. Trading is … .
a) check b) merchant c) sufficient
7. To carry on is … .
a) to continue b) to put c) to set up
8. To summon is … .
a) to set up b) to establish c) to order officially
Final Test 
Выберите один правильный ответ.
Выполняя перевод с английского на русский язык, придерживайтесь контекста налоговой тематики.
1. … production property and assets …
a) недвижимость и капитал b) имущество и акции c) собственность и вклады
2. … state-owned …
a) штатный b) государственный c) народный
3. … asset and profit allocation …
a) хранение вкладов и прибыли b) размещение капитала и прибыли
c) перевод акций и капитала
4. … residual amounts of financing …
a) сумма финансирования b) удвоенная прибыль c) остаточное количество
5. … market economy …
a) рыночная экономика b) экономические условия c) рынок труда
6. … adoption of laws and rules …
a) отмена норм и правил b) принятие законов и правил c) изменение законов и норм
7. … a lack of clear rules …
a) избыток бесполезных законов b) свод необходимых законов
c) недостаток четких законов
8. … federal and local bodies …
а) федеральные и местные органы b) государственная власть c) локальная служба
9. … has brought order into the taxation system …
а) изменил налоговую систему b) добавил несколько приказов в налогообложении
c) упорядочил систему налогообложения
10. … all are obliged to pay …
а) каждый должен оплачивать b) некоторые освобождены от уплаты
c) все обязаны платить
11. … came into force …
а) пришел в действие b) вступил в силу c) пришел с силой
12. … taxes are introduced and recalled …
а) вводить и взимать налоги b) ознакомиться с налогами
c) изменять и переименовывать налоги
13. … a closed list …
а) закрытый файл b) подробный список c) недоступный перечень
14. … tax authorities …
а) авторитет налоговика b) налоговая инспекция c) налоговые власти
15. … calculation, payment and fulfillment …
а) исчисление, уплата и выполнение b) вычет, неуплата и применение
c) подсчет, платеж и распределение
16. … fees, dues, charges …
а) сбор b) долг c) недоимки
17. … tax liability …
а) налоговая выплата b) задолженность по налоговым платежам c) начисление налога
18. … introduction, enforcement and cancellation …
а) принятие, применение и исчисление b) установление, изменение и ввод
c) ввод, установление и отмена
19. … tax offences …
а) налоговые органы b) налоговые правонарушения c) налоговые вычеты
20. … deductions and transfers …
a) удержание и перечисление b) подсчет и перевод c) исчисление и оплата
21. …проводить налоговые проверки …
a) to be tax inspector b) to carry on tax inspections c) to make tax searching
22. … seizure of documents …
a) подделка документов b) предоставление документов c) конфискация документов
23. … notice …
a) записка b) уведомление c) заметка
24. … the procedure for drawing up an inventory of the property …
a) порядок проведения инвентаризации имущества b) процедура изъятия инвентаря и имущества с) опись имеющегося имущества
25. … workrooms and deports …
a) раздевалки и душевые b) производственные и складские помещения
c) складские и торговые помещения
26. … extra-budgetary funds …
a) бюджетные фонды b) экстренные запасы c) внебюджетные средства
27. … to remove revealed breaches …
a) выявлять серьезные нарушения b) устранять выявленные нарушения
c) откладывать взыскание за нарушения
28. … to recover arrears and penalties …
a) взыскивать недоимки и пени b) покрыть расходы и штрафы c) охватить территории
заявлять ходатайства об аннулировании …
29. … compliance of big expenses of individuals with their incomes …
a) соответствие крупных расходов физ. лиц их доходам b) жалобы физ. лиц на большие расходы c) несоответствие расходов и доходов физ. лиц
30. … licenses issued for the engagement in certain activities …
a) право на участие в чем-либо b) участие в выдаче лицензий на деятельность
c) право на определенную деятельность
Итоговый контроль (V-VII modules) 
Задание 1.
Переведите предложения и выберите правильный вариант.
1. It is they … will bear the ultimate responsibility when financial markets … demand that deficit reduction … be once again the order of the day and tax increases … become mandatory.
a) which; will; should; -- b) that; will; should c) who; --; must;--
2. We … face the reality that taxes … rise a lot in coming years.
a) will; will b) may; are going to c) must; are going to
3. VAT is the … way … the hundreds of billions of dollars per year that …
a) least bad; of getting; will be needed b) least worse; to get; must need c) less worse; of getting; will be needed
4. The alternative is … tax rates that will … reduce the economic growth.
a) high; more b) higher; far more c) the highest; far more
5. The … we can hope to do is make incremental improvements to the existing tax system and hopefully prevent it … .
a) worst; to get better b) better; to getting worse c) best; from getting worse
6. Congress believe that … taxes are inevitable.
a) the highest b) lower c) higher
7. In particular, the enactment of a massive new Medicare drug benefit absolutely guarantees that the taxes … in the future even if Social Security … successfully.
a) will rise; will be reformed b) will be risen, is reformed c) will be raised; is reformed
8. … considerably different in their details, both bills had the same goal - to close tax loopholes and use the revenue to reduce rates.
a) owing to b) although c) according to
9. The point is that tax reform wasn't something that Reagan suddenly announced at the 1984 convention. It was already well in the work; detailed plans … under consideration in congress for some time. All he … do was to push the ball over the goal line for the final score.
a) had been; was to b) had been; had to c) was; had to
10. If Reagan … until his second term to begin the tax-reform process, there is a serious chance
that he … successful.
a) waited; would be b) had waited; would be c) had waited; would have been
11. Reagan had a clear tax philosophy - he wanted tax rates to be as low as possible. After cutting rates in 1981, however, the emergence of budget deficits made further tax cuts impossible and, in fact, led to tax increases. If he … this point, he likely … in 1992.
a) understood; would be reelected b) had understood; would have been reelected
12. They … supporters of tax reform … the time they … the article about it.
a) were; since; read b) have been; from; read c) have been; since; read
13. It is far more important to get the tax base straightened out. We … avoid double taxation, stop taxing things that … be taxed, start taxing things that … be taxed.
a) should; ought not to; should b) must; should; should c) need; shouldn't; must
14. … there are only two things that … be done with income - it … be saved or spent - eliminating the taxation of saving necessarily leaves a tax that falls only on consumption.
a) as; must; can b) for; can; must c) because; need; need
15. We … have a tax system that taxes only consumption. The objection to the national retail tax is that it would tax consumption in a way that just won't work administratively. One … as well replace the tax system with voluntary contributions to the government. It's a nice idea, but unworkable.
a) must; can b) should; might c) could; need
Грамматический минимум к заданиям после текста 
Для того чтобы правильно выполнить задания, необходимо усвоить следующие разделы курса английского языка:
-
Видо-временные формы глагола:
а) активный (действительный) залог - формы Simple (Present, Past, Future); формы Continuous (Present, Past, Future); формы Perfect (Present, Past, Future);
б) пассивный (страдательный) залог - формы Simple (Present, Past, Future), формы Continuous (Present, Past), формы Perfect (Present, Past, Future).
1. Действительный залог (The Active Voice)
Simple Tenses (неопределенные времена).
Существует 3 времени - настоящее, прошедшее, будущее.
Они употребляются для выражения обычно совершаемого действия в настоящем, прошедшем или будущем времени.
The Present Simple Tense - настоящее неопределенное время.
При спряжении во всех лицах глагол не имеет окончания, кроме 3 л. ед.ч., где прибавляется окончание -s или -es.
He works only five days a week. Он работает только пять дней в неделю.
Вопросительная и отрицательная формы образуются с помощью вспомогательного глагола «do» для всех лиц, кроме 3 л.ед.ч., где употребляется «does».
Do you work? Ты работаешь? Does he study? Он учится? He doesn't study. Он не учится.
The Past Simple Tense - прошедшее неопределенное время.
Прошедшее неопределенное время выражает действия в прошлом и переводится на русский язык глаголами как совершенного, так и несовершенного вида; отвечает на вопросы: Что делал? Что сделал?
Образование:
a) стандартные (правильные глаголы) - инфинитив без частицы «to» + оконч. «ed»
Boris and I played chess after dinner. Борис и я играли в шахматы после обеда.
b) нестандартные (неправильные) глаголы - путем изменения корневой гласной всей основы или окончания.
to be - was/were
to have - had
to give - gave
to see - saw
См.2 колонку в таблице (учебник, словарь).
My friend left Kiev for Moscow. Мой друг уехал из Киева в Москву.
Вопросительная и отрицательная формы «did» для всех лиц ед. и мн.числа. + инфинитив без частицы «to».
В вопросительной форме «did» ставится перед подлежащим.
В отрицательной форме «did not» ставится после подлежащего.
Past Simple употребляется обычно с обстоятельствами: yesterday (вчера), last month, week (в прошлом месяце, на прошлой неделе), а также с датами, относящимися к прошлому: 1960.
The Future Simple Tense - будущее неопределенное время.
Будущее неопределенное время выражает действие в будущем и переводится на русский язык глаголом как совершенного так и несовершенного вида; отвечает на вопросы: Что сделаю? Что буду делать?
Образование:
shall (для 1 л.ед.и мн.ч.) + инфинитив смыслового глагола без «to», will (для всех ост. лиц).
The students will solve this problem with their teacher's help.
Студенты будут решать эту проблему с помощью своего преподавателя.
Future Simple обычно употребляется с обстоятельствами: tomorrow (завтра), next month, week (в следующем месяце, на следующей неделе), а так же с датами, относящимися к будущему времени: in 2030.
При образовании отрицательной формы отрицание «not» ставится между вспомогательным и смысловым глаголами. In summer we shall not study. Летом мы не будем учиться.
При образовании вопросительной формы вспомогательный глагол становится перед подлежащим, а смысловой глагол после подлежащего.
Will he study in summer? Он будет учиться летом?
Таблица спряжения глагола to be:
Present Simple
Past Simple
I am
you are
he is
she is
it is
we are
you are
they are
I was
He was
She was
It was
You were
We were
They were
Таблица спряжения глагола to have:
Present Simple
Past Simple
I have
You have
He has
She has
It has
we have
you have
they have
had
had
had
had
had
had
Future Simple - will be, will have
Повелительное наклонение.
Выражает побуждение к действию: приказание, повеление, просьбу. Простая форма совпадает с формой инфинитива без частицы «to». Read the text! Читай (те) текст!
Отрицательная форма - do not + инфинитив без «to». Don't read the text, please!
Времена группы Continuous (продолженные времена) выражают длительное незаконченное действие и переводятся только глаголом несовершенного вида в настоящем, прошедшем или будущем времени, отвечают на вопрос: Что делаю? Что делал? Что буду делать?
Oбразованиe: to be + Participle I
The Present Continuous - am, is, are + Participle I
The importance of scientific research is growing with every day.
Важность научного исследования возрастает с каждым днем.
The Past Continuous - was, were + Participle I
In 1895 K.E.Tsiolkovsky was beginning to mention space flights in his papers.
В 1895 году К.Э.Циолковский в своих работах начал упоминать о космических полетах.
The Future Continuous - shall (will) + be + Participle I
The engineer will be preparing everything for his tests tomorrow.
Завтра инженер будет все готовить для своего опыта.
Времена группы Perfect (перфектные времена) выражают действие, законченное к определенному моменту в настоящем, прошедшем или будущем.
Образование: to have в соответствующем времени + Participle II
Present Perfect - have (has) + Participle II
Past Perfect - had + Participle II
Future Perfect - shall (will) + have + Participle II
Industry has developed various applications for the electromagnet.
Промышленность разработала различные применения электромагнита.
Scientists had solved many interesting problems by the end of the 19th century.
К концу 19 в. ученые решили много интересных проблем.
The mechanic will have installed the new equipment by the beginning of the new year.
Механик установит новое оборудование к началу нового года.
2. Страдательный залог (The Passive Voice)
В английском языке 2 залога: залог действительный (the Active Voice) и страдательный залог (the Passive Voice).
В пассивном залоге подлежащее пассивно, т.е. оно подвергается воздействию со стороны другого лица или предмета.
Образование: to be + Participle II
to be изменяется, Participle II - не изменяется
Present Simple Passive
am
is + Participle II
are
Past Simple Passive
was
were + Participle II
Future Simple Passive
shall
will + be + Participle II
Перевод:
Сказуемое в страдательном залоге может переводиться тремя способами:
- сочетанием глагола «быть» (в прошедшем или будущем времени) + краткая форма причастия страдательного залога.
Глагол-связка «быть» в настоящем времени при переводе на русский язык опускается:
The laboratory of our Institute was given a new task.
Лаборатории нашего института было дано новое задание.
- возвратным глаголом с окончанием -ся, -сь:
Today polymers are referred to as materials of vital importance.
На полимеры ссылаются сегодня как на материалы жизненной важности.
- неопределенно-личной формой глагола (3л.,мн.ч.) в действительном залоге:
The speaker was asked a number of difficult questions.
Оратору задали ряд трудных вопросов.
Примечание: если за сказуемым в страдательном залоге следует предлог, то перевод начинается с него.
The data of the latest research in this field of science are often referred to.
Часто ссылаются на данные самого последнего исследования в области науки.
3.Инфинитив (Infinitive)
Простые формы:
Active
Passive
Выражают действие, одновременное с действием сказуемого в предложении.
Simple
to ask
to go
to be asked
to be gone
Частица to перед глаголом является формальным признаком инфинитива.
После модальных глаголов can/could, may/might, must и вспомогательных глаголов shall/should, will/would, do/did Инфинитив употребляется без частицы to
The workers can get another qualification at the plant.
Рабочие могут получить другую квалификацию на заводе.
They will assemble the installation in some days.
Они будут собирать (монтировать) установку через несколько дней
Инфинитив может выполнять в предложении следующие функции:
- подлежащего:
To read is useful. - Читать - полезно. To solve this problem requires some experience.
Решение этой проблемы требует опыта.
- составной части сказуемого:
He began to work as an engineer last year. Он начал работать инженером в прошлом году.
The train was to arrive at midnight. Поезд должен был прибыть в полночь.
He used to come to see us every day. Раньше он навещал нас каждый день.
- дополнения:
I'd like to ask him what it all meant.
Я бы хотел спросить его, что это все значит.
He loved to drive and was always interested in cars.
Он любил водить машину и всегда интересовался автомобилями.
- определения:
Industrial systems to be built now perform many production tasks.
Промышленные системы, которые создаются сейчас, выполняют многие производственные задачи.
Another factor for any engineer to consider is the level of automation of the plant.
Другим фактором, который должен рассматривать любой инженер, является уровень автоматизации завода.
- обстоятельства:
He came to help us. Он пришел, чтобы помочь нам.
The car was too old to develop high speed. Автомобиль был слишком старый, чтобы развивать высокую скорость.
Перевод:
- существительным:
To design new machine-tools is the task of mechanical engineer.
Проектирование новых станков - задача инженера машиностроителя.
- неопределенной формой глагола:
The task is to raise the reliability of robots. Задача - поднять надежность роботов.
- придаточным предложением:
To be a good engineer one is to have technical knowledge.
Чтобы быть хорошим инженером, необходимо иметь технические знания.
The instructions to help to process data are developed by the qualified specialists.
Инструкции, которые могут помочь обработать данные, разработаны квалифицированными специалистами.
Список рекомендуемой литературы 
1. Английский язык.
Налоги и налогообложение. Tax & Taxation. Учебное пособие для специальности "Налоги и налогообложение". Осикова Л.Н. Москва: ГИС, 2006
2. Английский язык налоговой сферы. Учебное пособие для специальности "Налоги и налогообложение". Назарова Н.Б., Коробова Е.В. Москва: Университетская книга, 2011
 Базы данных, информационно-справочные и поисковые системы
Базы данных, информационно-справочные и поисковые системы
1. HM Customs and Excise - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia // en.wikipedia. org/wiki/HM_Customs_and_Excise
2. Назарова Н.Б., Коробова Е.В. An English Course in Practical Taxation // 93.94.223.197/c/document_library/get_file?p_l_id...pd
3. Federal Tax Police Service of the Russian Federation // en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_Tax_Police_Service_of_the_Russian_Federation
4. How to pay your fees // customs.govt.nz/features/charges
/feepayment/Pages/default.aspx
5. Tax Code of The Russian Federation // russian-tax-code.com/PartI/Section1/Chapter2.html
6. study-english.info - модули I - IV, грамматика и лексика.


