- Преподавателю
- Иностранные языки
- АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК для энергетических специальностей
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК для энергетических специальностей
| Раздел | Иностранные языки |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Другие методич. материалы |
| Автор | Сорокина Е.А. |
| Дата | 27.02.2016 |
| Формат | doc |
| Изображения | Есть |
ДЕПАРТАМЕНТ ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ ИВАНОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
ОБЛАСТНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ
«ИВАНОВСКИЙ ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ»
Сорокина Е.А.
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК
для энергетических специальностей
Иваново, ОГБПОУ «ИЭК», 2015
Unit 1
Ohm's Law. Electric circuit.
I. Decimal fractions.
-
Translate into Russian
decimal fractions
numeration
denominator
O [ ou ]
Ohm
ampere
volt
point
Decimal fractions.
0.002- zero point two zeros two
1.1- one point one
5.36- five point three six
65.57- sixty-five point five seven
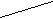 zero point seven
zero point seven
0
 .7 o point seven
.7 o point seven
point seven
-
Read these decimal fractions:
0.23 0.009 10.01 205.35 79.31 0.0003
II. Ohm's Law
-
Translate into Russian
current
resistance
voltage
law
times
to suppose
to equal
to divide
divided by
R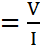 Resistance equals voltage divided by current.
Resistance equals voltage divided by current.
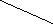
I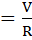 Current equals voltage divided by resistance.
Current equals voltage divided by resistance.
V = IR Voltage equals current times resistance.
-
Solve the following problems using the formulas of Ohm's Law.
Model: - Current equals 5 amp; resistance equals 10 ohms. How much is the voltage?
- Voltage equals current times resistance. 5 x 10 = 50 V
1) R = 80 ohms 2) R= 10.25 ohms 3) V = 50.05 V
V = 55 V I = 35 amp I = 120 amp
I = ? V = ? R = ?
4) 1= 10,500 amp 5) V = 20.05 V 6) I = 0.24 amp
V = 2,000 V R = 0.015 ohm R= 1.36 ohms
R = ? I = ? V = ?
III. Electric Circuit
-
Translate into Russian
circuit
conductor
function
difference
source
while
to reduce
to supply
to connect
to compare (with)
to pass through
to result in
to result from
to consist of
-
Translate the word - combinations:
Voltage source, to supply current, to reduce current, to connect the elements, to result from an open, to result in no current, trouble in a circuit.
-
Translate the sentence. Mind the word ,,while''
Current passes through circuit (a) while no current passes through circuit (b).
-
Translate into Russian
-
An open and a short are troubles in a circuit.
-
A trouble in a circuit results in no current in it.
-
What does an open in a circuit result in?
-
What does a short in a circuit result in?
-
What does a trouble in a circuit result from?
-
Read and translate the text
This is a circuit. Its elements are a voltage source, a resistor and a conductor. The circuit consists of a voltage source, a resistor and a conductor. A voltage source supplies current. A resistor reduces current. A conductor connects the elements of the circuit.
Compare circuit a with circuit b. What is the difference between them? Current passes through circuit a while no current passes through circuit b. Circuit b has an open. No current through circuit b results from an open. An open and a short are troubles in a circuit. A trouble in a circuit may result in no current in it.










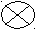
a ) b)
) b)













6. Complete these sentences, using the correct variant:
1.Circuit a consists of
a) resistors and conductors.
b) a voltage source and resistors.
c) a voltage source, a resistor and a conductor.
2. A voltage source
a) conducts current,
b) reduces current,
c) supplies current.
3. A conductor
a) connects the elements.
b) supplies voltage.
c) conducts current.
4. A resistor
a) connects the elements.
b) supplies current.
c) reduces current.
5. No current results from
a) an open.
b) a short.
7. Translate the words and distribute them into three columns. Mind the suffixes; the prefix:
Model: what? What kind of? What to do?
dependence dependent to depend on
difference, to differ, different, conductivity, to conduct, conductor, to resist, resistant, resistance, resistor, resistivity, independent, independence
8. Answer the following questions:
1. What elements does a circuit consist of?
2. What is the function of a voltage source?
3. What is the function of a conductor?
4. What is the function of a resistor?
5. When is there no current in a circuit?
6. What does an open or a short result in?
7. What does no current in a circuit result from?
Unit 2
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
-
Translate into Russian
branch
line
value
voltage drop
series
parallel
main
in order (to)
(the) same
(the) whole
to use
-
Translate the word - combinations:
main line, parallel branches, the same value of voltage, different values of current, the whole circuit.
-
Translate the sentences. Mind the word ,,while''.
1.Circuit (a) is a series circuit while circuit (b) is a parallel circuit.
2.The value of voltage is the same in all the elements of a parallel circuit while the value of current is different .
3.The value of current is the same in all the elements of a series circuit while the value of current is different .
4. Fill in the verbs : "to connect", "consist of", "to equal", "to compare":
1. Resistance ... voltage divided by current. 2. See Fig 1; ... circuit (a) with circuit (b); are they different? 3. Circuit (a) ... a voltage source and two resistors. 4. The elements in circuit (b) are ... in parallel. 5.How many elements does circuit (b) ... ?
5. Read and translate the text
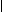
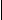
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
R

 1 R2 a) R1 b)
1 R2 a) R1 b)








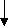









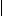
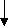


 R2
R2












 c) d) R1 R2 R1
c) d) R1 R2 R1

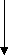
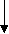







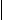







 R2
R2








Compare circuits a and b. Circuit a consists of a voltage source and two resistors. The resistors are connected in series. Circuit a is a series circuit. Circuit b consists of a voltage source and two resistors. The resistors are connected in parallel. Circuit b is a parallel circuit.
A parallel circuit has the main line and parallel branches.
In circuit b the value of voltage in R, equals the value of voltage in R2. The value of voltage is the same in all the elements of a parallel circuit while the value of current is different. A parallel circuit is used in order to have the same value of voltage.
In circuit a the value of current in R, equals the value of current in R2. The value of current is the same in all the elements of a series circuit while the value of voltage is different. A series circuit is used in order to have the same value of current. In R1 V1=IR1 is the voltage drop in R1. In R2 the voltage equals I*R2; IR2 is the voltage drop in R2. In circuit с a trouble in one element results in no current in the whole circuit. In circuit d a trouble in one branch results in no current in that branch only, a trouble in the main line results in no current in the whole circuit.
6 . Complete these sentences using the correct variant:
1. A parallel circuit has
a) parallel branches only.
b) the main line and parallel branches.
2. A parallel circuit is used in
a) to have the same value of current in order all the elements.
b) to have the same value of voltage in all the elements.
3. In a parallel circuit a trouble
a) results in no current in that branch in one branch only.
b) results in no trouble in the whole circuit.
4. No current in a parallel cir-
a) results from a trouble in one branch.
b) results from a trouble in\he main
line.
5. The sum of IR voltage drops
a) equals the value of voltage in the circuit.
b) is less than the smallest voltage drop.
c) is more than the value of voltage in the circuit.
7. Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model:
Model: Resistors connected in series have the same value of current...
Resistors connected in series have the same value of current while resistors connected in parallel have the same value of voltage.
-
Resistors connected in series have different values of voltage while ....
-
A trouble in one element of a series circuit results in no current in the whole circuit while ....
-
In order to have the same value of current in all the elements, a series circuit is used while ....
-
No current in a parallel circuit results from a trouble in the main line while ….
8. Translate the words, mind the suffixes and the prefixes.
to differ- indifferent
equal- to equal
main- mainly
ampere +meter- ampermeter
conductor- semiconductor
use-to use
to connect- interconnection
to compare- comparative
supply+ water - water-supply
open- to open
9. Answer the following questions:
1. What type of circuit has the main line and parallel branches?
2. What type of circuit is used in order to have the same value of current in all the elements?
3. What type of circuit is used in order to have the same value of voltage in all the elements?
4. What does a trouble in the main line result in?
5. What does a trouble in a branch result in?
6. What does no current in a series circuit result from?
7. How much does the sum of IR voltage drops equal?
8. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
Unit 3
Meters
-
Translate into Russian
meter
battery
scale
readings
terminal
positive
negative
in this way
among
common
to calibrate
to measure
to take into
consideration
Функции местоимения ONE
Значения one
Примеры
Перевод
…один из…
(one of)
Nuclear energy is one of the forms of energy.
Ядерная энергия- одна из форм энергии.
Заменитель ранее упомянутого существительного (ones-мн.число)
The old turbine was a water turbine and the new one is a steam turbine.
Старая турбина была водной турбиной, а новая - паровая турбина.
One + модальный глагол
One can, one may-
можно
One must, one should-
нужно, следует
One should control the chain reaction
Следует контролировать цепную реакцию.
Неопределенно-личное подлежащее
(one -вы , тот)
One knows that these installations do not operate on nuclear power.
Вы, знаете что эти установки не работают на ядерной энергии.
-
Translate the sentences. Mind one.
1. The second sputnik was launched about a month after the first one.
2. There are many insulating materials from which one may choose.
3. Some substances are efficient conductors, others, poor ones.
4. One uses special devices to measure current, voltage, and resistance.
5. One should take into consideration the difference between these circuits.
6. One should take into consideration that the ammeter is connected to the circuit in series.
7. What should one take into consideration using the ohmmeter?
8. One must choose only one of those variants.
-
Translate the sentence. Mind Complex Subject, one.
The new method proved to be much more efficient that the old one.
-
Translate the word -combinations.
the most common, the value of resistance, the measured value, in order to measure, to be connected in series.
-
Read and translate the text.
A mong the most common meters used there are the ohmmeter, the ammeter and the voltmeter. The ohmmeter is used to measure the value of resistance. It consists of a milliammeter calibrated to read in ohms, a battery and resistors. The meter is connected in parallel and the circuit is not opened when its resistance is measured. The readings on the scale show the measured value.
mong the most common meters used there are the ohmmeter, the ammeter and the voltmeter. The ohmmeter is used to measure the value of resistance. It consists of a milliammeter calibrated to read in ohms, a battery and resistors. The meter is connected in parallel and the circuit is not opened when its resistance is measured. The readings on the scale show the measured value.
The ammeter is used to measure the value of current. When the ammeter is used the circuit should be opened at one point and
t









 he terminals of the meter should be connected to it. One should take into consideration that the positive terminal of the meter is connected to the positive terminal of the source; the negative terminal - to the negative terminal of the source.
he terminals of the meter should be connected to it. One should take into consideration that the positive terminal of the meter is connected to the positive terminal of the source; the negative terminal - to the negative terminal of the source.
T he ammeter should be connected in series. The readings on the scale show the measured value.
he ammeter should be connected in series. The readings on the scale show the measured value.





 Wattmeter
Wattmeter
A wattmeter is used to measure the value of power. It is connected to the circuit directly. A wattmeter consists of coils: two fixed coils and a coil which moves in the magnetic field produced by the fixed coils. Wire used for the coils must have a high resistance; the fixed coils are in series with the load, the moving coil is connected across the line in series with a resistance. When a wattmeter is used, the readings on its scale show the value of power being used
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
1. The ammeter is
a) a common meter.
b) an uncommon meter.
2. In order to measure the value of current
a) the ohmmeter is used.
b) the voltmeter is used.
c) the ammeter is used.
3. A meter has
a) positive terminals only.
b) negative terminals only.
c) positive and negative terminals.
4. When the ammeter is used
a) the circuit should be opened.
b) the circuit should not be opened.
5. The ammeter should be connected
a) in series,
b) in parallel.
6. One should take into consideration that
a) the positive terminal should be connected to the negative terminal.
b) the positive terminal should be connected to the positive terminal of
the source.
-
Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model.
Model: The ammeter is used to measure the value of current....
The ammeter is used to measure the value of current while the ohmmeter is used to measure the value of resistance.
1. The ohmmeter is used to measure the value of resistance……..
2. The ammeter is connected in series………
3. When the ammeter is used to measure the value of current the circuit
should be opened……..
4. A wattmeter consist of two fixed coils a coil which moves…
-
Translate the text in writing.
Meters
One of the important things that an engineer should take into consideration is "how much?" How much current is this circuit carrying? What is the value of voltage in the circuit? What is the value of resistance? In fact, to measure the current and the voltage is not difficult at all. One should connect an ammeter or a voltmeter to the circuit and read off the amperes and the volts.
Common ammeters for d. c. measurements are the ammeters of the magneto-electric system. In an ammeter of this type an armature coil rotates between the poles of a permanent magnet; but the coil turns only through a small angle. The greater the current in the coil, the greater the force, and, therefore, the greater the angle of rotation of the armature. The deflection is measured by means of a pointer connected to the armature and the scale of the meter reads directly in amperes.
When the currents to be measured are very small, one should use a galvanometer. Some galvanometers detect and measure currents as small as 10of an ampere per 1 mm of the scale.
A voltmeter is a device to be used for measuring the potential difference between any two points in a circuit. A voltmeter has armatures that move when an electric current is sent through their coils. The deflection, like that of an ammeter, is proportional to the current flowing through the armature coil.
A voltmeter must have a very high resistance since it passes only very small currents which will not disturb the rest of the circuit. An , ammeter, on the other hand, must have a low resistance, since all the current must pass through it. In actual use the ammeter is placed in series with the circuit, while the voltmeter is placed in parallel with that part of the circuit where the voltage is to be measured.
In addition to instruments for measuring current and voltage, there are also devices for measuring electric power and energy.
-
Answer the questions.
-
What is the ammeter used for?
-
What is the voltmeter used for?
-
What is the ohmmeter used for?
-
What terminals does a meter have?
-
Should the measured circuit be opened when the voltmeter is used?
-
Should the measured circuit be opened when the ammeter is used?
-
In what way should the voltmeter be connected to the circuit?
-
In what way should the ammeter be connected to the circuit?
-
What is the difference between a voltmeter and an ammeter?
-
What common meters are used to measure the values in a circuit?
-
What is the wattmeter used for?
-
What does it consist of?
-
In what way are the elements connected?
-
What do the readings on the scale show?
-
 Describe these circuits
Describe these circuits



a
 ) R1 R2 b) R1 R2
) R1 R2 b) R1 R2












 + -
+ -




 + -
+ -
R1









 R1
R1





 c) d) R2
c) d) R2
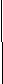

 R2 R2
R2 R2









 + - + -
+ - + -




Unit 4
Resistors.
-
Translate into Russian
capacity
power
heat
rate
low
high
fixed
in case
any
charge
pressure
protection in case
since
variable
the (more)
the (more)
to rise
to rate
to move
to left
to produce
to change
to vary
-
Translate the word- combinations:
Constant value, fixed resistors, high conductivity, free electrons, variable resistor, current- caring, capacity.
-
Translate into Russian using чем ... тем:
-
The more one studies nature, the better one knows its laws.
-
The longer one learns, the more one knows.
-
The higher the atmosphere, the less is its pressure.
-
The heavier the object, the more work one has to do in order to lift it.
-
The greater the number of free electrons in any metal, the higher is its conductivity.
-
Translate into Russian. Mind no.
1.There is no energy in this machine.
2. No charges move through an open circuit.
3. No material is a perfect conductor of electricity.
4. No electric machinery is used without protection.
5. No special material is needed in this case.
-
Read and translate the text.
Resistors
A resistor is one of the most common elements of any circuit. Resistors are used:
1. to reduce the value of current in the circuit;
2. to produce IR voltage drop and in this way to change the value of the voltage.
When current is passing through a resistor its temperature rises high. The higher the value of current the higher is the temperature of a resistor. Each resistor has a maximum temperature to which it may be heated without a trouble. If the temperature rises higher the resistor gets open and opens the circuit.
Resistors are rated in watts. The watt is the rate at which electric energy is supplied when a current of one ampere is passing at a potential difference of one volt. A resistor is rated as a 1-W resistor if its resistance equals 1,000,000 ohms and its current-carrying capacity equals 1/1,000,000 amp, since P = E x I = IR x I = I2R where P - power is given in watts, R - resistance is given in ohms and I - current is given in amperes.
If a resistor has a resistance of only 2 ohms but its current-carrying capacity equals 2,000 amp, it is rated as a 8,000,000-W resistor.
Some resistors have a constant value - these are fixed resistors, the value of other resistors may be varied - these are variable resistors.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
1. A resistor is used a) to measure the resistance.
b) to reduce the current.
c) to change the resistance.
d) to produce IR voltage drop.
2. When current passes through a resistor a) its temperature drops.
b) its temperature rises.
3. Resistors are rated a) in ohms.
b) in volts.
c) in watts.
4. Power is given a) in amperes,
b) in watts.
5. Fixed resistors have a) a constant value.
b) a variable value.
6. The value of a variable resistor a) is fixed.
b) is varied.
7. A two-ohm resistor rated as a a) has a current-carrying capacity 8,000,000- W resistor equal to 2,000 amp.
b) has a current-carrying capacity equal to 200 amp.
-
Complete the sentences using while.
1. The value of a fixed resistor is constant..........
2. Current-carrying capacity is given in amperes..........
3. The lower the value of current, the lower is the temperature of a resistor ..........
4. An electric source produces energy..........
-
Translate the words. Mind the suffixed .
Activity, active, act, active by, additional, add, addition, additionally,
Equalize, equally, equality, equal, differ, different, difference, common,
commonly, use, usefully, useful, user.
-
Answer the questions:
-
What is a resistor used for?
-
When does the temperature of a resistor rise?
-
What element is used to change the value of voltage?
-
How are resistors rated?
-
What types of resistors do you know?
-
When does a resistor get open?
-
What does an open resistor result in?
-
What is the difference between a fixed resistor and a variable resistor?
-
How much is the current-carrying capacity of a two-ohm resistor?
-
What resistors have a variable value?
-
Translate the text in writing
Rheostat
A rheostat is a resistor whose resistance value may be varied. Thus,
a rheostat is a variable resistor.
It is used to change the resistance of circuits, and in this way to vary
the value of current.
A rheostat consists of a coil and a switch. Take into consideration
that wire used for the coil must have a very high resistance. When a
rheostat is used its terminals are connected in series with the load. The
switch is used to change the length of the wire through which the measured
current passes. The resistance may be changed to any value from
zero to maximum.
The longer the rheostat wire used in the circuit, the greater is the resistance.
1. What type of resistor is a rheostat?
2. What is a rheostat used for?
3. In what way does a rheostat vary the value of current?
4. What elements does a rheostat consist of ?
5. In what way are the terminals connected with the load?
6. What is the function of the switch?
Unit 5
Electric Cells
-
Translate into Russian.
cell
output
bulb
to light
to increase
to substitute
and so on=et cetera(etc)
-
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
electrode
electrolyte
to start
to operate
to isolate
-
Translate the word - combinations . in writing.
current capacity
resistor temperature
voltage output
current value
to operate well
to operate badly
to increase the voltage output
to substitute the resistor
-
Translate into Russian. Say-ing forms are Participle I, Gerund or Verbal Noun
to start supplying energy
to stop operating
to start lightening
to stop lightening the bulbs
-
Read and translate into Russian. Mind one:
-
The element has a trouble. It operates badly. It should be substituted by a new one.
-
The element with a trouble was substituted with a new one and the cell started operating.
-
Read and translate the text.
Electric Cells
-An electric cell is used to produce and supply electric energy. It consists of an electrolyte and two electrodes. Electrodes are used as terminals, they connect the cell to the circuit - current passes through the terminals and the bulb lights.
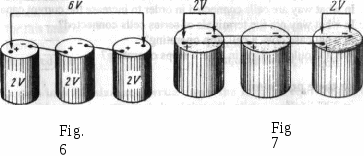
Cells can be connected in series, in parallel and in series-parallel. In order to increase the current capacity cells should be connected in parallel. In order to increase the voltage output cells should be connected in series. In case a battery has a large current capacity and a large voltage output, its cells are connected in series-
parallel.
When cells are connected in series the positive terminal of one cell
is connected to the negative terminal of the second cell, the positive terminal of the second cell - to the negative terminal of the third ... and so on.
When cells are connected in parallel their negative terminals are connected together and their positive terminals are also connected.
In case a cell has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. This cell should be substituted by another one.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
-
A cell is used
a) to increase the voltage output.
b) to reduce the current capacity.
c) to supply electric energy.
-
The terminals of a cell are used
a) to conduct current.
b) to increase voltage.
c) to connect the battery to a circuit
-
When cells are connected in series
a) all the positive terminals are
connected together.
b) all the negative terminals are
connected together.
c) the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative
terminal of the second.
-
Cells are connected in series in order
a) to increase the current capacity.
b) to increase the voltage output.
-
In order to increase the current capacity
-
cells are connected in series,
-
cells are connected in parallel.
-
Destitute the words into columns. Mind the suffixes and the prefixes.
Model: what? What kind of? What to do? How?
Failure, fail, faulty, overestimate, consumer, act, impossibility, carelessly, noisy, easily, numerous, possible, power, powerful, clockwise, superconductor, output, operate.
-
Answer the following questions :
-
What is a cell used for?
-
What does a cell consist of?
-
What is the function of the terminals?
-
In what way are cells connected in order to increase the voltage output?
-
In what way are cells connected in order to increase the current capacity?
-
In what way are the terminals of series cells connected?
-
In what case does a cell stop operating?
-
What should be done in case it stops operating?
Unit 6
Capacitors
-
Translate into Russian.
сapacitor
insulator
frequency
distance
advantage
disadvantage
plate
part
reason
besides
provided that
for this reason
c-centigrade
to store
to apply
to move
to prevent
-
Translate the word- combinations
paper insulators
air insulators
electrolyte capacitors
advantages of electrolyte capacitors
disadvantages of air insulators
cells under test
capacitors in common use nowadays
radio sets under test
PC in common use nowadays
a radioman
radio work
radio parts
telephone and radio work
-
Translate into Russian. Mind provided that.
1. A circuit operates well provided that it does not have any trouble.
2. The bulb lights provided that the circuit is connected to the cell.
3. A cell supplies energy provided that its electrodes are of different materials.
-
Read and translate the text
Capacitors.
A capacitor is one of the main elements of a circuit. It is used to store electric energy. A capacitor stores electric energy provided that a voltage source is applied to it.
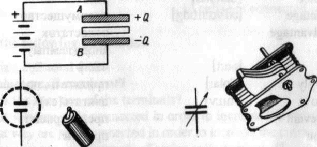
The main parts of a capacitor are metal plates and insulators. The
function of insulators is to isolate the metal plates and in this way to
prevent a short.
In the diagram one can see two common types of capacitors in use
nowadays: a fixed capacitor and a variable one. The plates of a fixed
capacitor cannot be moved; for this reason its capacity does not change.
The plates of a variable capacitor move; its capacity changes. The
greater the distance between the plates, the less is the capacity of a capacitor.
Variable capacitors are commonly used by radiomen; their
function is to vary the frequency in the circuit. Fixed capacitors are
used in telephone and radio work.
Fixed capacitors have insulators produced of paper, ceramics and
other materials; variable capacitors have air insulators. Paper capacitors
are commonly used in radio and electronics; their advantage is their
high capacity: it may be higher than 1,000 picofarad.
Besides, electrolyte capacitors are highly in use. They also have a
very high capacity: it varies from 0.5 to 2,000 microfarad. Their disadvantage is that they change their capacity when the temperature
changes. They can operate without a change only at temperatures not
lower than -40° C. ,
Common troubles in capacitors are an open and a short. A capacitor
stops operating and does not store energy in case it has a trouble. A capacitor
with a trouble should be substituted by a new one.
-
Complete these sentences using the correct variant
1. A capacitor is used
a) to supply voltage.
b) to increase the voltage output.
c) to store energy.
2. The main parts of a capacitor are
a) insulators only.
b) metal plates only.
c) metal plates and insulators between
them.
3. The function of insulators is
a) to store energy.
b) to isolate the metal plates.
c) to prevent a short between the
metal plates
4. The capacity of a capacitor depends
on
a) the size of the plates.
b) the distance between the plates.
c) the material of the insulators.
5. The capacity of a fixed capacitor
a) is constant,
b) is varied.
6. The plates of a variable capaci
tor
a) can be moved,
b) cannot be moved.
7. In order to charge a capacitor a
voltage source is applied
a) to the metal plates.
b) to the insulators.
8. The greater the distance between
the plates,
a) the greater is the capacity of a
capacitor.
b) the less is the capacity.
9. Variable capacitors have
a) air insulators.
b) paper insulators.
c) ceramic insulators.
10. Electrolyte capacitors have
a) a very low capacity.
b) a very high capacity.
11. In case a capacitor has a trouble a) it operates.
b) it stops operating.
-
Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13:
1. The plates of a fixed capacitor cannot be moved to vary the capacity ...
2. The capacity of a variable capacitor is varied.......
3. Electrolyte capacitors change their capacity when the temperature changes.......
4. The less the distance between the plates, the greater is the capacity ...
5. When a capacitor has no trouble it stores energy.......
-
How many parts does each word consist of? What are the stems? Translate the words and their stems.
Model: un-doubt-ed-ly
failure, indifferent, uncommonly, unequality, numerously, uselessly, noiseless, advantageous.
-
Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and ask him/her to answer them.
1. What is a capacitor used for?
2. What are the main parts of a capacitor?
3. What is the function of insulators?
4. What does the capacity of a capacitor depend on?
5. What is the difference between a fixed capacitor and a variable one?
6. What should be done in order to change a capacitor?
7. What is the relation between the value of capacity and the distance of plates?
8. What type of insulators have variable capacitors?
9. What should be done in case a capacitor has a trouble?
Unit 7
Conductors and Insulators
-
Translate into Russian.
carbon
enough
plastics
wise
cheap
copper
decrease
load
make smb (smth)
do smth
thus
difficulty
rubber
since
increase
to decrease
-
Translate the word- combinations
diagram
coefficient
function
transformer
to transfer
-
Translate into Russian. Mind provided that.
-
Copper conductors are widely used since they are much cheaper than silver ones.
-
A minimum voltage drop is produced in copper wire conductors since they have a low resistance.
-
A bulb connected to an open circuit does not light since an open circuit has no current.
-
Read and translate the text
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials having a low resistance so that current easily passes through them. The lower the resistance of the material, the more current can pass through it.
The most common conductors are metals. Silver and copper are the best of them. The advantage of copper is that it is much cheaper than silver. Thus copper is widely used to produce wire conductors. One of
the common functions of wire conductors is to connect a voltage source to a load resistance. Since copper wire conductors have a very low resistance a minimum voltage drop is produced in them. Thus, all of the applied voltage can produce current in the load resistance.
It should be taken into consideration that most materials change the value of resistance when their temperature changes.
Metals increase their resistance when the temperature increases while carbon decreases its resistance when the temperature increases. Thus metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance while carbon has a negative temperature coefficient. The smaller is the temperature coefficient or the less the change of resistance with the change of temperature, the more perfect is the resistance material.
Materials having a very high resistance are called insulators. Current passes through insulators with great difficulty.
The most common insulators are air, paper, rubber, plastics. Any insulator can conduct current when a high enough voltage is applied to it. Currents of great value must be applied to insulators in order to make them conduct. The higher the resistance of an insulator, the greater the applied voltage must be.
When an insulator is connected to a voltage source, it stores electric charge and a potential is produced on the insulator. Thus, insulators have the two main functions:
-
to isolate conducting wires and thus to prevent a short between them and
-
to store electric charge when a voltage source is applied.
-
Complete these sentences using the correct variant
Insulators are materials having
a) low resistance.
b) high resistance.
Current passes through conductors
a)easily.
b) with great difficulty.
Copper and silver are
a) common conductors.
b) common insulators.
Air, paper and plastics are
a) common insulators.
b) common conductors.
In case a high voltage is applied to an insulator
a) it does not conduct current.
b) it conducts current.
Insulators are used
a) to store electric charge.
b) to reduce voltage.
c) to prevent a short between conducting wires.
Metals increase their resistance
a)when the temperature decreases.
b)when the temperature increases.
Carbon decreases its resistance
a)when the temperature increases.
b) when the temperature decreases.
Metals have
a) a positive temperature coefficient of resistance.
b) a negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
-
Complete the sentences using while.
-
Conductors have a low resistance……
-
Current passes through insulators with great difficulty….
-
Metals are common conductors…..
-
To make insulators conduct, currents of great value must be applied….
-
Carbon decreases its resistance when the temperature increases ....
-
Metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistance ....
7. Which of the words are adjectives? adverbs? Why?
easily, equal, noisy, numerous, faulty, anticlockwise, eastwards well carelessly, powerful, traceable, good, simply, comfortable, useful, northward, dangerous, businesslike, naturally, inferior, bad
8. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate , and ask him/her to answer them.
1) What is the difference between conductors and insulators?
2)How does current pass through insulators?
3)What materials are commonly used to produce insulators?
4)What materials are commonly used to produce conductors?
5)In what case do insulators conduct current?
6)How does resistance change when the temperature decreases?
Unit 8
Transformers
-
Translate into Russian
iron
primary
frequency
due to
coil
time
device= instrument
core
winding
turn
to step up
to step down
to receive
-
Put down the Russian for:
iron core
closed core
input voltage
output voltage
primary winding
secondary winding
step-up transformer
step-down transformer
-
Read and translate the text.
Transformers
A transformer is used to transfer energy. Due to the transformer electric power may be transferred at a high voltage and reduced at the point where it must be used to any value. Besides, a transformer is used to change the voltage and current value in a circuit. 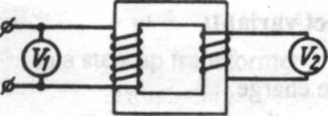
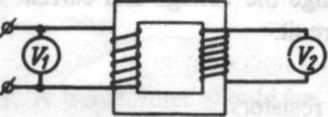 A two-winding transformer consists of a closed core and two coils (windings). The primary winding is connected to the voltage source. It receives energy. The secondary winding is connected to the load resistance and supplies energy to the load.
A two-winding transformer consists of a closed core and two coils (windings). The primary winding is connected to the voltage source. It receives energy. The secondary winding is connected to the load resistance and supplies energy to the load.
The value of voltage across the secondary terminal depends on the number of turns in it. In case it is equal to the number of turns in the primary winding the voltage in the secondary winding is the same as in the primary. In case the secondary has more turns than the primary the output voltage is greater than the input voltage. The voltage in the secondary is greater than the voltage in the primary by as many times as the number of turns in the secondary is greater than the number of turns in the primary. A transformer of this type increases or steps up the voltage and is called a step-up transformer. In case the secondary has fewer turns than the primary the output voltage is lower than the input. Such a transformer decreases or steps down the voltage, it is called a step-down transformer.
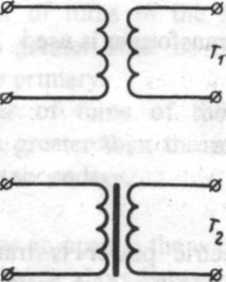
Compare T1 and T2 in the diagram. T1 has an iron core. For this reason it is used for low-frequency currents. T2 has an air core and is used for high frequencies.
Common troubles in transformers are an open in the winding, a short between the primary and the secondary, and a short between turns. In case a transformer has a trouble it stops operating or operates badly. A transformer with a trouble should be substituted.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
A transformer is used
-
to store charge.
-
to prevent the change of energy.
-
to transfer energy.
-
to change the voltage and current value in a circuit.
Electric power is transferred at a
high voltage and reduced to any value
-
due to resistors.
-
due to capacitors.
-
due to transformers.
A transformer consists of
-
cores only.
-
the primary and the secondary windings.
-
a core and the primary and the secondary windings.
The function of the primary is
a. to prevent the change of voltage.
b. to supply energy .
c. to receive energy.
The function of the secondary is
a. to receive energy
b. to supply energy
c. to transfer energy.
A step-up transformer is used
a) to step down or decrease the secondary voltage.
b) to step up or increase the primary voltage.
A step-down transformer is used
a) to step down the secondary voltage
b) to step down the primary voltage.
A transformer with an iron core
a) is used for high-frequency currents
b) is used for low-frequency currents.
A transformer with an air core is used
a) for high-frequency currents and for low frequency currents.
b) for high-frequency currents only.
In a step-up transformer
a) the number of turns of the secondary
winding is greater than the number of turns of the primary. b)the number of turns of the primary winding is greater than the number of turns of the secondary.
A transformer should be substituted
a) in case it has an open in the winding.
b) in case it has a short between the primary and the secondary.
c) in case it has a short between turns.
-
Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The secondary winding of a transformer is connected to the load resistance ....
2. The primary winding receives energy ....
3. A step-down transformer decreases the primary voltage ....
4. An air core transformer is used for high-frequency currents.......
5. In a step-up transformer the number of turns of the secondary winding is greater than the number of turns of the primary winding...... Look up the meanings of these words in a dictionary, if necessary. How are they translated in the sentences below? Mind the word order. place, iron, lift, house, light, heat, use, form, change, wire
1. The conductor wires are placed high up.
2. Electromagnets lift iron weights.
3. The plastic box houses the conducting and the insulating elements of the apparatus.
4. The house is lighted and heated by solar energy.
5. The light went out. Light the candle, please.
6. After the metal was heated it changed its colour to a red heat.
7. Numerous changes are taking place in the uses of atomic energy.
8. Electric power is used universally.
9. The newly made invention has a great number of uses.
10. The wire and the source form a circuit.
7. Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and ask him/her to answer them.
1. What is a transformer used for?
2. What does a transformer consist of?
3. What is the function of the primary winding?
4. What is the function of the secondary winding?
5. What type of transformer is called a step-up transformer?
6. What type of transformer is used for high-frequency currents?
7. What type of transformer is called a step-down transformer?
8. What type of transformer is used for low-frequency currents?
9. What is the relation between the number of turns in the windings and the value of current?
10. What are common troubles in a transformer?
11. What should be done in case a transformer has a trouble?
Unit 9
Types of Current
-
Translate into Russian
seldom
alternating
direct
direction
flow
necessary
to consider
use
-
Read the words and write down their Russian equivalents:
cycle
type
per second
-
Put down the Russian for:
one time
five times
sixty times
-
Read and translate the text
Types of Current
Current is a flow of electricity through a circuit. Let us consider two main types of current: direct and alternating. A direct current (d.c.) flows through a conducting circuit in one direction only. It flows provided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit.
An alternating current (a.c.) is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating voltage source is applied to the circuit. Alternating current flows in cycles. The number of cycles per second is called the frequency of the current. In a 60-cycle alternating current circuit the current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
It is easy to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another by a transformer. Transformers are also used to step down the voltage at the receiving point of the line to the low values that are necessary for use.
When necessary a.c. can be changed into d.c. but this is seldom necessary.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
D.c. is a current that
a) changes its direction of flow.
b) flows in one direction.
A.c. flows provided
a) a direct voltage source is applied.
b) an alternating voltage source is applied.
In an alternating cur-circuit second.
a) current flows in one direction 60 times per rent
b) current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
A.c.
a) can be changed into d.c.
b) cannot be changed into d.c.
-
Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
-
An alternating current changes its direction of flow….
-
A direct current flows provided a direct voltage source is applied…
-
Look up the meanings of these words in a dictionary, if necessary. How are they translated in the sentences below? Mind the word order.
balance, amount, water, fuel, control, measure, cause, increase
-
The fuel-and-energy balance is important for industry.
-
Conductivity increases with heating.
-
The machine should be re-fuelled.
-
The amount of power used in the world in a year amounts to 12,000 million tons of equivalent fuel.
-
Water barriers are crossed by submarine cables.
-
The instrument is foot-controlled by a pedal.
-
Force and motion go together; one is a cause, the other, a result.
-
An electromotive force causes the electrons to move.
-
Control of the apparatus is placed on the panel.
10. The volt is a measure of electromotive force.
-
Answer the following questions:
-
What is current?
-
What types of current do you know?
-
When does a direct current flow?
-
What type of current is called an alternating current?
-
What type of current is called a direct current?
-
What is called the frequency of current?
-
What device is used to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another?
-
Is it often necessary to change a.c. into d.c?
Unit 10
Inductance and Mutual Inductance
-
Translate into Russian
inductance
close
coil
though
size
unit
fast
mutual
definite
that is
to induce
to provide
to touch
to bring
-
Translate into Russian and put down the Russian equivalents. Then translate them back into English (orally).
a. definite value
primary coil
wire coil
mutual inductance
varying current
one ampere per second
b. 1. Coils of wire are called inductors.
-
Two coils are brought close together.
-
A source of current is applied to one of the coils.
-
Mutual inductance is measured in henries.
-
Which of the words are nouns and which are verbs?
resistor, resist, resistance; induce, induction, inductor, inductance; conductor, conduct, conductance; compute, computer
-
Read and translate the text
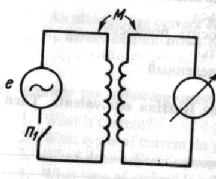
Inductance and Mutual Inductance
Any conductor has some definite value of inductance. The inductance of a conductor shows how well it can provide induced voltage.
Elements of a circuit with a definite value of inductance are coils of wire called inductors. The inductance of a coil depends upon its size and material. The greater the number of turns of a coil, the higher is its inductance. An iron core also increases the value of inductance. Coils of this type are used for low-frequency currents while coils with an air core are used for high-frequency currents. Two coils A and В are brought close together and a source of varying current is applied to coil A. If a measuring device is connected across the terminals of coil В it will be found that a voltage is induced in this coil though the two coils do not touch. The secondary voltage, that is the voltage in coil B, is called induced voltage and energy from one coil to the other transfers by induction. The coil across which the current is applied is called the primary; that in which voltage is induced is called the secondary. The primary and the secondary coils have mutual inductance. Mutual inductance is measured in the same units as inductance, that is in henries.
Thus, when a rate of change of one ampere per second in the primary coil will produce one volt in the secondary coil, the two coils have one henry of mutual inductance. It should be taken into consideration that induction by a varying current results from the change in current not in the current value. The faster the current changes, the higher the induced voltage.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant
Any conductor has
-
Some definite value of resistance.
-
Some definite value of inductance.
Any conductor can provide
-
Electric power
-
Induced voltage
Elements with a definite value of inductance
a) are called inductors.
b) are called coils.
c) are called sources.
The inductance of a coil depends upon
a) its size.
b) its core.
c) its material.
d) its number of turns.
An iron core
a) increases the value of inductance.
b) decreases the value of inductance.
The value of mutual inductance is measured
a) in watts.
b) in henries.
Induction by a varying current
a) results from the change in current.
b) results from the change in the current value.
The faster the current changes
a) the lower is the induced voltage.
b) the higher is the induced voltage.
-
Complete these sentences using while.
1. An air core decreases the value of inductance.......
2. An iron core is used for low-frequency currents.......
3. The coil in which voltage is induced is called the secondary......
7. Read the following words. What are their prefixes? stems? suffixes?
Translate the words into Russian:
generate, inefficient, abnormally, underproduction, anticlockwise, counteraction, demagnetize, superconductor, unequality, misunderstand, unequally, equality, interrelation, non-conductor, input, simplify, waterless, irregularity, redden, enlargement, unreadable, southward, clockwise, fully, noisy, typically, impossible, superconductor
8. Answer the following questions:
1. What value of inductance do conductors have?
2. What is the function of inductors?
3. What are elements with a definite value of inductance called?
4. What does the inductance of a coil depend upon?
5. How does the inductance of a coil depend upon the material of its core?
6. In what units is the value of mutual inductance measured?
7. What does induction by a varying current result from?
8. What is the relation between the current changes and the value of induced voltage?
9. What is the unit of resistance?
10. What is the unit of potential difference?
11. For what type of current is an air core used?
12. What is the relation between the number of turns of a coil and its inductance value?
Unit 11
Components of Electric Circuits
Translate into Russian
-
Incandescence
-
incandescent lamp
-
switch
-
fuse
-
relay
-
copper
-
steel
-
according to
-
etc.= et cetera
-
to convert
-
to utilize
-
to deliver
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
-
aluminium
-
chemical
-
generator
-
material
-
mechanical
-
thermal
-
motor
3. Translate into Russian:
a. convertible values, protected power source, various fuses, variable resistors, chemical cells
b. cells delivering electric power generator converting mechanical energy circuits utilizing common fuses
c. Primary cells deliver electric power.
Different kinds of energy can be converted into electric energy. Protection devices are utilized in any circuit.
-
Read and translate the text.
Components of Electric Circuits
The main components of any circuit are devices that produce and utilize electric energy. They are: 1. power sources, 2. utilizing loads, 3. connecting conductors.
The most common power sources are electric generators and primary cells. Electric generators convert chemical energy into electric energy.
Loads include electric heaters, electric motors, incandescent lamps, etc. Motors convert electric energy into mechanical, incandescent lamps and heaters convert electric energy into light and heat. Utilizing devices or loads convert electric energy into thermal, mechanical or chemical energy.
Electric power is delivered from power sources to loads by electric wires. According to their material, wires can be aluminium, copper, steel, etc.
Besides, electric circuits use different types of switches, protection devices (relays and fuses), and meters (ammeters, voltmeters, wattmeters, etc.).
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
1. The main components of electric circuits are
a) loads and wires.
b) power sources, load and wires.
2. Power sources are used
a) to produce electric energy.
b) to deliver it to the loads.
-
Electric conductors are used
a) to connect the circuit elements.
b) to deliver electric power.
-
Protection devices are utilized
a) in some circuits.
b) in any circuit.
5. A switch is utilized
a) in some circuits.
b) in any circuit.
6. Answer these questions:
1. What are the main components of an electric circuit?
2. What is the function of an electric source?
-
What is the function of a load?
-
What is the function of wire conductors?
-
What other devices are utilized in a circuit?
Unit 12
Power transmission
-
Translate into Russian
efficiency
ignorance
dependence
cost
installation
cross-section
loss
length
long
exceedingly per cent
to transmit
to offer
to ignore
to depend (on)
to exceed
-
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
line
station
engineer
engineering
-
Translate into Russian:
a. line efficiency
voltage loss
power station
b. interdependent values
interconnected sources
changing power efficiency
c. exceedingly high power losses _
exceedingly inefficient energy sources _
d. One can ignore these exceedingly low power losses.
One should take into consideration the interdependence of these values.
One should not ignore the high cost of these installations.
-
Read and translate the text
Electric Lines and Their Efficiency
Wires are used to deliver electric power and to interconnect different components of electrical installations. Conductors used for electric wiring are commonly produced of copper and aluminium. Aluminium is widely used nowadays due to its low cost. Copper is also widely used in electrical engineering but its cost is much higher.
Wires connecting the components of various installations may be insulated. They may also be used without insulation. Since in short lengths of wire power loss is exceedingly low one can ignore it. In long wires (longer than 10 m), power loss cannot be ignored since it is rather high. Power loss in a line should not exceed a definite value. If this value is exceeded the line becomes inefficient.
One should know that the efficiency of a line is not constant - it may change. The value of the line efficiency depends on the load: the greater the load the lower is the line efficiency. At voltage losses of 2 to 5 per cent the efficiency of a line is 98-95 per cent. Protecting devices, fuses and relays are used to protect the circuit against overcurrents and short-circuits.
5. Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
1. Aluminium is used due to its
a) high cost.
b) low cost and high efficiency.
-
Cross-section of different conductors
a) varies.
b) is the same.
3. Power loss can be ignored
a) in short wires.
b) in long wires.
4. A definite value of loss
a) can be exceeded.
b) should not be exceeded.
5. Electric lines nowadays are
a) efficient.
b) inefficient.
6. Installations are protected
a) by switches.
b) by fuses.
6. Complete these sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13:
1. The cost of aluminium is comparatively low while ....
2. In a short length of wire power loss is extremely low while ....
3. The greater the load the lower is the efficiency of the line ....
-
Answer these questions:
1. Why is aluminium widely used nowadays?
2. Is its cost very low or comparatively low?
3. What is the cross-section of copper conductors?
4. May one ignore power loss in short wire? Why?
5. What does the efficiency of a line depend on?
6. What are fuses used for?
7. When does a line become inefficient?
8. Think of three questions about this extract and put them to your groupmate.
con'sumer - потребитель; relation - отношение
When electric energy is produced at the power station, it is to be transmitted over electric wires to the consumer. Wire conductors offer resistance to the current flow; the longer the wire, the greater is its resistance to the current flow. Accordingly, the higher the offered resistance, the greater are the heating losses in the wire.
Unit 12(продолжение)
Transmission Lines
-
Translate into Russian
area
network
support
cord
bus
enterprise
accordingly
as to
by means of
indoor
overhead
to serve
to baze
to term
to support
to distribute
-
Put down the Russian for:
long distance
length of transmission lines
power consumption
distribution centre
city area
interdependent city areas
interacting underground lines
interconnected overhead lines
transmitting power lines
transmission and distribution lines
overhead lines
step-down transformer
indoor lines
underground lines
-
Read and translate the text
Transmission Lines
A power system is an interconnection of electric power stations by high voltage power transmission lines. Nowadays the electricity is transmitted over long distances and the length of transmitting power lines varies from area to area.
A wire system is termed a power line in case it has no parallel branches and a power network in case it has parallel branches.^
According to their functions, power lines and networks are subdivided into transmission and distribution lines.
Transmission lines serve to deliver power from a station to distribution centres. Distribution lines deliver power from distribution centres to the loads.
Lines are also classed into: 1) overhead; 2) indoor; 3) cable (underground).
Overhead lines include line conductors, insulators, and supports. The conductors are connected to the insulators, and these are connected to the supports. The greater the resistance, the higher are the heating losses in the conducting wires. In order to reduce the losses, a step-down transformer can be used.
Indoor lines include conductors, cords, and buses. The conductor may include one wire or a combination of wires not insulated from one another. They deliver electric current to the consumers.
As to underground lines, they are used in city areas. Accordingly, they are used in cities and towns, and in the areas of industrial enterprises.
-
Complete these sentences using the correct variant.
1. Electric power is transmitted
a) by electric lines.
b) by power networks.
2. Lines are divided into
a) overhead and underground.
b) overhead, indoor and underground.
3. An overhead line includes
a) conductors and supports.
b) conductors, insulators and supports.
4. The insulators are connected
a) to the buses.
b) to the supports.
5. Conductors consist of
a) bare wire.
b) insulated wire.
6. Underground lines are used
a) in cities.
b) in areas of enterprises.
c) in agricultural areas.
5. Complete the sentences using while or as to. Follow the model on page 13.
1. The system is termed a power line in case it has no parallel branches
2. Transmission lines deliver power from a station to distribution centres ....
3. Low current results in decreased heating losses ....
4. Overhead lines are used in open areas ....
6. Answer these questions:
1. By what means is electric power system transmitted?
2. Which system has no parallel branches?
3. Into what groups are all the transmitting lines classed?
4. What components does an overhead line have?
5. What elements do conductors consist of?
6. In what areas are overhead (underground) lines used?
7. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
HV Power Transmission
A high-capacity hydrogenerator produces an a.c. current at 22,000 V. The current with the potential difference of 220,000 V is produced by means of the transformers at a step-up station and then transmitted over the power lines.
The current potential difference is lowered to medium 6,600 V at the main step-down substation at the end of the line. From here the power is transmitted to the next substations. Transformers stepping the voltage down from 6,600 V are installed at those substations.
Due to voltage conversion, alternating current is used widely in industry. Direct current for battery charging for trams, trolleybuses and electric locomotives is changed from alternating current by means of rectifiers.
1. Where is the current potential difference lowered?
2. Where is the main step-down substation installed?
-
Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Compressed-gas-insulated Transmission
Transmission lines in which compressed gas is used as insulator have a number of advantages. The main advantages are simplicity of construction and low cost.
What is the construction of compressed-gas-insulated transmission lines? It is rather simple. They comprise a number of phase conductors; each phase conductor is placed inside a tube and centered by means of circular spacers. The tube space is filled with compressed gas - usually sulphur hexofluoride. Each tube in a 345-kV line has a diameter about 50 cm.
The system including compressed-gas-insulated transmission has the following advantages: its losses are rather low, they are considerably lower than those of cable transmission. Unlike cables, compressed-gas-insulated transmission system can be designed for ultra high frequencies. No external electric field appears in the system. The shunt capacitance is considerably less for a gas-insulated line than for a cable. A gas-insulated line can thus transmit power over larger distances than cable lines.
The system should be protected against metallic particles. In case metallic particles get into the system, they cause a fault - a dielectric breakdown.
1. Does the system described have any advantages? What are they?
2. What gas is the space filled with?
3. Why should the system be protected?
-
Read and translate the text
POWER TRANSMISSION
A transformer is an electrical device by which the electromotive force of a source of alternating current may be increased or decreased. They are widespread in long-distance power transmission as well as in telephones, radio transmitters and receivers, television and etc. Nearly all transformers come under one of the two following classes: step-up, and step-down transformers. In the transmission of electrical energy over wires for long distance, transformers are practically indispensable. At the power house in the distant mountains, for example, electric current is generated by huge alternating current generators, at the relatively low voltage-of several thousand volts. Jf an attempt were made to transmit this electrical energy, at a voltage of say 2,200 volts, over many miles of wire cable to a distant city, the current would be so large that nearly all of the energy would be consumed in heating the power line. The heat generated (it should be remembered) is proportional to the square of the current (heat=0.24/2 Rt).
To avoid large heat losses, transformers at the power house step the voltage up to some 220,000 volts before switching the current onto the power line. Since the voltage in the case cited is increased one-hundred fold, the current drops by the same proportion to one-hundredth. Since the square of 1/100 is 1/10*000the heat loss along the transmission line is only one ten thousandth of what it would have been had the transformer not been used.
At the city end of , a transformer substation steps the voltage down to. Its original value, of 2,200 volts. From there branch lines distribute the power to various sections of the city where smaller transformers, one near each group of several houses, step it down again to the relatively safe voltage of 110 to 220 volts.
Unit 13
Safety Earthing System. Electric shock
-
Translate into Russian.
safe
safety
danger
strength
earth
ground
dead
dangerous
strong
live
dry
wet
to save
to disappear
to appear
-
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents. Then translate them back into English (orally).
atmosphere
personnel
contact
regular
control
detect
-
Read and translate the text
Safety Earthing System. Electric Shock
The strength of current depends on both the voltage and the resistance in a circuit. A current of 50 mA is dangerous for a man and a current of 100 mA and higher is lethal.
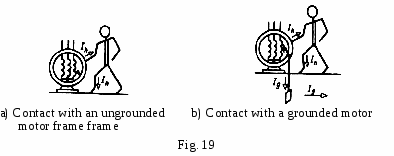
Earthing system serves to protect attending personnel from electric shocks when voltage appears on parts that are normally dead. The risk of an electric shock decreases with decreasing voltage. In wet and hot atmosphere the risk of electric shock increases. Safe voltage for circuits used in dry atmosphere is under 36 V. When the power is on, contacts with live conductors are dangerous for life. Thus, measures are taken to protect attending personnel from contacts with live parts of installations under voltage.
The danger of an electric shock disappears provided the metal parts of installations under voltage are connected with ground by means of safety earthing.
Connecting to ground is made by means of earthing electrodes which are connected directly with ground.
The insulation resistance of any installation should be regularly controlled by means of measuring devices. The faulty parts should be detected, eliminated, and replaced by new ones.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
-
Earthing system serves
a) as protection from an electric shock.
b) as connection with ground.
-
Voltage appears on
a) dead parts.
b) live parts.
-
Contact with live conductors is
a) dangerous.
b) safe.
-
Connection to ground is made
a) dangerous.
b) safe.
-
Danger of an electric shock disappears if the frame
a) is earthed.
b) is unearthed.
-
Complete the sentences using while. Follow the model on page 13.
-
The insulation resistance of a faulty unearthed frame is extremely …..
-
Danger of an electric shock disappears when the faulty parts earthed ....
-
One should work on the circuit when the power is off. One should work on the circuit when the power is ....
-
Contact with dead conductors is safe ... .
-
In dry air the risk of an electric shock decreases ....
-
Answer these questions:
1. What does an earthing system serve for?
2. What parts are termed dead (live)?
3. In what air does the risk of an electric shock decrease?
4. By what means is connection to ground made?
5. What does an electric shock result from?
6. Is a current of 50 mA dangerous for a man?
7. Is wet and hot atmosphere dangerous for the attending personnel?
8. Does the risk of an electric shock decrease with increasing current?
7 Read the text and write four questions about it. Ask your groupmates to answer them.
A man can get an electric shock when he comes into contact with the electric fish. One of this kind is found in the tropical waters of South America: it is the electric eel. Small electric eels, one inch long, give a small shock. When the fish is 6 inches long its internal battery gives as much as 200 volts. A very big fish can generate 600 volts! When it is short-circuited, a current of one ampere can be obtained. A two-meter long eel can light a dozen 50 watt lamps. The eel's head is positively charged and the opposite end is negatively charged.
Unit 14
Electric Motors
-
Translate into Russian
condition
plant
pole
torque
poor
nameplate
-
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents. Then translate them back into English.
industry
service
transport
motor
practical
potential
-
Read and translate the text
Electric Motors
Motors are used for converting different forms of energy into mechanical energy.
The main part of a motor is a coil or armature. The armature is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet. When a motor is put into operation current starts flowing through the coil (armature) and the armature starts rotating.
Electric motors are used practically in every branch of industry, transport, and agriculture. Naturally, they are produced in many different designs. They are used in industrial plants, and operate under different conditions.
Each motor is supplied with a nameplate which bears machine ratings: output power, voltage, the rated current, the starting current, the power factor, the efficiency, and the rated torque.
These motor ratings should be taken into consideration since they are necessary for the users. On them depends the length of motors' service life, which is normally equal to about 10 years, provided that the operating conditions are normal. Naturally, under abnormal conditions the service life becomes much shorter: motors operate poorly and may have different faults.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
-
Motors are used
a) for transmitting energy.
b) for converting energy.
-
Motor's main part is
a) the frame.
b) the armature.
c) the stator.
-
The armature is placed
a) between the poles of the magnet.
b) about the poles of the magnet.
-
Motors' service life becomes shorter
a) under normal conditions,
b) under abnormal conditions
-
Faulty motors operate
a) normally.
b) poorly.
5 Answer these questions. Use them in a talk with your groupmate:
1. What are motors used for?
2. What is the motor's main part?
3. Where is the armature placed?
4. What ratings does the nameplate of a motor bear?
5. Under what conditions does a motor operate normally (poorly)?
Unit 15
Faults of Motors and Ways of Their Repair
-
Translate into Russian
brush
gap
spark
speed
noise
slow
excessive
check
to repair
to adjust
-
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents:
commutator
stator
rotor
contact
to contact
process
-
Put down the verbs corresponding to the given nouns and translate them:
check to check проверять
spark
brush
repair
slow
-
Put down the Russian equivalents of these word combinations. Trans late them back into English (orally).
air gap
brush sparks
slow speed
excessive speed
safety devices
5. Answer these questions:
1. What do motors' faults result from?
2. Are there any faults that can be ignored?
3. What makes motors' service life shorter?
4. What does voltage supply stop result in?
5. What processes show the (dis)advantages of devices?
-
Are the words: spark, short, slow, brush, fault, load, test nouns? Are they verbs? Translate the sentences into Russian:
1. New motors are given a no-load and under a load tests.
2. When the motor is tested it should produce no abnormal noise.
3. In case this noise appears the motor must be disconnected.
4. This generator must be checked; one should give it a test.
5. The motor's brushes seem to be sparking. Can you see the sparks?
6. The windings of the coil are shorted. I have detected a short in the windings.
7. The armature rotates slowly; let's check it up!
8. The speed of rotation is too excessive; it must be slowed down.
9. In case the rotor brushes against the stator, the motor operates slowly. The faulty brushes should be replaced.
-
Read and translate the text
Faults of Motors and Ways of Their Repair
Motors may have different faults. A faulty motor does not start, or, when it is started, it operates at an excessive speed.
Its brushes may spark and its windings and the commutator may be overheated and burnt. Besides, a motor may produce an abnormal noise, etc. All these and other faults should be detected and repaired.
In case the motor does not start it may have different faults (see the table):
-
Possible causes of faults
Ways of repair
1. Fuses are faulty.
1. Replace the fuses.
2. Motor is overloaded.
2. Reduce motor load.
3. Circuit in armature winding has an open.
3. Repair the armature winding.
In case the motor, when started, stops:
1. Rheostat is shorted.
1. Check the rheostat and repair it.
2. Rheostat switches from one position to another.
2. Slow down operation of rheostat handle.
Brushes may spark in case:
1. Motor is overloaded.
1. Reduce the load and remove overload.
2 Brushes are in poor condition.
2. Replace the brushes.
3. Pressure is low.
3. Adjust the pressure.
4. Pressure is excessive.
4. Adjust the pressure.
In case the armature winding is overheated:
1. Motor is overloaded.
1. Remove the overload.
2. Ventilation fails to operate properly.
2. Check for slowing down the speed of the motor.
In case of abnormal motor speed:
1. Motor is overloaded.
1. Reduce the load.
2. Rotor circuit has poor contact.
2. Repair the shorting mechanism.
In case rotor brushes against stator:
Rotor brushes against stator.
Adjust air gap.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
A motor with a fault a) operates normally.
b) operates poorly.
Motor brushes spark in case a) they are in normal conditions.
b) they are in poor conditions.
Burnt commutator should be a) replaced.
b) repaired.
Brushes may spark in case a) pressure is low.
b) pressure is excessive.
Air gap is adjusted in case a) the rotor brushes against the stator.
b) the stator brushes against the rotor.
-
Answer these questions:
1. When does a motor operate poorly?
2. What should be done in case the motor is overloaded?
3. What should be done in case the fuses are faulty?
4. What should be done in case the rheostat is shorted?
5. What should be done in case the brushes spark?
6. What should be done in case the pressure is low?
7. What should be done in case the ventilation does not operate?
8. What should be done in case the rotor brushes against stator?
Unit 16
Electric Power Consumers and Power Systems
-
Translate into Russian
predominant
graph
national economy
to achieve
to belong (to)
to feed
to determine
to relate
-
Read the words and put down their Russian equivalents. Then translate them back into English (orally).
characteristic-
municipal -
to electrify -
hydro -
period -
-
Distribute the words below into three columns:
action process doer
utilizer, protect, distribution, utilize, protection, distributor, consumption, consume, utilization, consumer
-
Put down the Russian equivalents of these word combinations. Translate them back into English (orally).
-
load graph
-
lighting load
power load
-
-
power utilizing devices
-
parallelly operating plants
enterprises utilizing power
-
Complete the sentences translating the words in brackets:
1. Water-turbine (заводы) are called hydroturbines.
2. Load graph (определяет) the operating load (условия).
3. Economical (потребление) of electric power (достигается) by interconnected operation of power plants.
-
Read and translate the text
Electric Power Consumers and Power Systems
An electric power consumer is an enterprise utilizing electric power. Its operating characteristics vary during the hours of day, days and nights, days of week and seasons.
All electric power consumers are divided into groups with common load characteristics. To the first group belong municipal consumers with a predominant lighting load: dwelling houses, hospitals, theatres, street lighting systems, mines, etc.
To the second group belong industrial consumers with a predominant power load (electric motors): industrial plants, mines, etc.
To the third group belongs transport, for example, electrified railways. The fourth consists of agricultural consumers, for example, elec-trotractors.
The operating load conditions of each group are determined by the load graph. The load graph shows the consumption of power during different periods of day, month, and year. On the load graph the time of the maximum loads and minimum loads is given.
Large industrial areas with cities are supplied from electric networks fed by electric power plants. These plants are interconnected for operation in parallel and located in different parts of the given area. They may include some large thermal and hydroelectric power plants.
The sum total of the electric power plants, the networks that interconnect them and the power utilizing devices of the consumers, is called a power system. All the components of a power system are interrelated by the common processes of protection, distribution, and consumption of both electric and heat power.
In a power system, all the parallelly operating plants carry the total load of all the consumers supplied by the given system.
The building up of a power system is of great importance for the national economy. An economical utilization of the power plant installations and of the sources of power is achieved by interconnected operation of a series of power plants in a common power distribution system.
-
Answer these questions:
1. What enterprises are called electric power consumers?
2. When do their operating characteristics vary?
3. What consumers belong to the four different groups?
4. What conditions does the load graph determine?
5. What type of system is called a power system?
6. What processes interconnect the components of a power system?
7. In what way is an economical utilization of power installations achieved?
Unit 17
Substantions
-
Translate into Russian
auxiliary
breaker
busbar
feeder
flexible
to comprise
to distribute
as ... to
as well as
-
Put down the Russian equivalents of these word combinations Translate them back into English (orally).
circuit breaker
auxiliary units
distribution centre
flexible construction
reliable operation
switch gear bus
hydraulic as well as solar sources of energy
as to phase-word motors
-
Read and translate the text
Substations
A substation is designed to receive energy from a power system, convert it and distribute it to the feeders. Thus a substation serves as a distribution centre. Substations feed (supply) various consumers provided that their basic load characteristics are similar. Therefore the energy is distributed without transformation of the voltage supplied.
Common substations comprise isolators, switchgear buses, oil circuit breakers, fuses, power and instrument transformers and reactors.
Substations are classed into step up and step down ones. The step up substation includes transformers that increase the voltage. Connected to the busbars of the substation are the power transmission lines of power plants of the system.
As to step down substations, they reduce the voltage to 10 or 6 kV. At this voltage the power is supplied to the distribution centres and to the transformer substations of power consumers.
A transformer substation serves for transmitting and distributing electric power. It comprises a storage battery, control devices and auxiliary structures.
Transformer substations are classed into indoor and outdoor; both types are used for feeding industrial enterprises. Compared to other types of substations, transformer substations have certain advantages. They have flexible construction and easy and reliable operation. In case of a fault in the left-hand section, the main circuit breaker opens while the normally open section circuit breaker closes and puts the voltage of the section to normal. Power from a substation is delivered to distribution centres.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
-
A substation serves
a) to consume energy.
b) to distribute energy.
c) to convert energy.
2. A substation feeds consumers
a) with various load characteristics.
b) with similar load characteristics.
3. The lines of power plants are connected
a) to the busbars.
b) to the switchgear.
4. A substation comprises
a) the main elements.
b) the main and auxiliary elements.
5. Flexible construction is
a) an advantage.
b) a disadvantage.
-
Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate, and ask him/her to answer them.
1. What does a substation serve for?
2. What type of consumers does a substation feed?
3. What parts are the power transmission lines connected to?
4. What components does a substation comprise?
5. What types are substations classed into?
6. What are advantages of a transformer substation?
Unit 18
Hydroelectric power plants
-
Translate into Russian
blade
level
magnitude
head
plant
runner
shaft
to rotate
to influence
to fluctuate
-
Put down the Russian equivalents of these word combinations. Then translate them back into English (orally).
runner blade
turbine runner
turbine shaft
water level
water head
large capacity power plant
magnitude of the water head
daily inflow of water
turbine runner shaft
-
Read and translate the text
Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectric power plants are built on rivers. Large-capacity hydroelectric power plants are commonly located at considerable distances from the consumers of electric power.
The production process at these plants is rather simple: the water flows into the hydroturbine runner, acts upon the runner blades and rotates the runner and the turbine shaft.
The generator shaft is connected to the turbine runner shaft. The difference in the water level influences the power capacity of a plant, i.e. the magnitude of the water head and the daily inflow of water fluctuates considerably according to the season.
The production process is different at power plants of different constructions and of different kinds. In atomic power plants, for example, it is not so simple as in hydroelectric plants.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
1. Hydroelectric power plants are built
a) on rivers, b) on waterfalls,
2. Large-capacity power plants located power.
a) at a short distance from consumers of power,
b) at a considerable distance from consumers of are
3. The production
a) is very complex, process at the
b) is rather simple, plants
4. The power capacity of a plant
a) remains constant.
b) changes considerably.
c) is influenced by the difference in the water level.
5. The daily inflow of water
a) fluctuates according to the consumption.
b) fluctuates according to the season.
6. The production process
a) depends upon the construction of the plant.
b) is the same at power plants of different constructions.
5. Pair work. Put these questions to your group mate and ask him/her to answer them:
1. On what sites are hydroelectric power plants built?
2. Are large-capacity plants located far from consumers of power?
3. Is the production process at the plants simple or is it complex? What influences the power capacity of a plant? According to what factors does the daily inflow of water fluctuate? Does the production process at the plant depend on its construction? Do you know that a thermal power plant seldom has an efficiency more than 40%?
Unit 19
Atomic Power Plant
1.Translate into Russian
exchanger
steam
tube
dust
attending personnel
to deliver
to pollute
to shield
-
Put down the Russian equivalents of these word combinations. Then translate them back into English (orally).
-
-
auxiliary units
-
steam generator
heat exchanger
fuel consumption
-
-
water to be heated in the reactor
-
water to be converted into steam
steam to be fed into the turbogenerator
-
-
the polluted atmosphere
-
utilized nuclear fuel
shielded concrete walls
-
Read and translate the text
Ato Atomic power plants.
mic Power Plant
Atomic power plants are modern installations. They consist of several main units and a great number of auxiliary ones.
In a nuclear reactor uranium is utilized as a fuel. During operation process powerful heat and radioactive radiation are produced. The nuclear reactor is cooled by water circulation. Cooling water circulates through a system of tubes, in which the water is heated to a temperature of 250-300°C. In order to prevent boiling of water, it passes into the reactor at a pressure up to 150 atmospheres.
A steam generator includes a series of heat exchangers comprising tubes. The water heated in the reactor is delivered into the heat exchanger tubes. The water to be converted into steam flows outside these tubes. The steam produced is fed into the turbogenerator.
Besides, an atomic power plant comprises a common turbogenerator, a steam condenser with circulating water and a switchboard.
Atomic power plants have their advantages as well as disadvantages. The reactors and steam generators operate in them noiselessly; the atmosphere is not polluted by dust and smoke. As to the fuel consumption, it is of no special importance and there is no problem of fuel transportation.
The disadvantage of power plants utilizing nuclear fuel is their radiation. Radioactive radiation produced in the reactors is dangerous for attending personnel. Therefore, the reactors and steam generators are installed underground. They are also shielded by thick (up to 1.5 m) concrete walls. All their controls are operated by means of automatic devices. These measures serve to protect people from radioactive radiation.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant
1.A nuclear reactor is used in
a) wind-power plants.
b) atomic power plants.
2. A nuclear reactor is cooled by
a) water circulating in tubes.
b) oil circulating in tubes.
3. Water is passed into the reactor
a) at a low pressure.
b) at a high pressure.
-
High pressure
a) activates boiling of water.
b) prevents boiling of water.
-
Atomic power plants
a) pollute the air with dust and smoke.
b) do not pollute the air with dust and smoke.
-
Circulating water flows
a) inside the heat exchangers.
b) outside the heat exchangers.
-
Attending personnel is shielded by
a) thick concrete walls.
b) thick metal walls.
-
Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and let him/her answer them:
1. What are the main units of an atomic power plant?
2. By what means is the nuclear reactor cooled?
3. At what pressure does the water pass into the reactor?
4. What types of power plants pollute the air with dust and smoke?
5. Why is it necessary to protect attending personnel?
6. By what means is it done?
Unit 20
Protection Against Environmental Pollution
-
Translate into Russian
concrete
environment
fission
(stainless) steel
vessel
waste
to confine
to release
to withstand
to dispose
-
Put down the Russian equivalents of these word combinations. Then translate them back into English (orally):
nuclear fuel
nuclear fission
steel vessel
reactor vessel
fission release
sealed tubes
concrete housing
waste products
nuclear waste
shielded cylinders
-
Read and translate the text
Protection Against Environmental Pollution
Any operating nuclear power plant releases fission products into the environment, which causes environmental pollution.
To prevent the harmful effects of nuclear power release, the nuclear power plants are supplied with protective installations that serve as barriers to the pollution.
First, the nuclear fuel and the fission products are confined within sealed tubes made of stainless steel or zirconium. Then the assembly of tubes is placed in a steel reactor vessel. And finally the steel reactor vessel is placed in a large steel and concrete housing.
As to the hot radioactive waste products they are disposed in heavily shielded cylinders. The cylinders are buried 305 to 610 metres underground.
-
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
1. A nuclear power plant
a) liquid products, releases
-
fission products.
-
Operating nuclear power plants
a) pollute the environment.
b) prevent the pollution.
3. The protective power plant installations
a) produce the release of fission products.
b) prevent the release of fission products.
4. The sealed tubes are made of
a) bronze.
b) stainless steel.
5. The fission products are confined
a) within sealed tubes.
b) within open tubes.
6. The steel reactor vessel is placed
a) in a concrete housing.
b) in a zirconium housing.
7. The waste products are disposed
a) in an open vessel.
b) in shielded cylinders.
-
Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmate and let him/her answer them:
1. What kind of products does the operating nuclear power plant release?
2. What installations are used to prevent the harmful effects of a nuclear power plant operation?
3. What material are the tubes made of?
4. Where are the fission products confined?
5. In what part of the installation is the reactor vessel placed?
6. In what way are the hot radioactive waste products disposed?
66


