- Преподавателю
- Химия
- Атом на англисском
Атом на англисском
| Раздел | Химия |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Конспекты |
| Автор | Ниязбаев Т.О. |
| Дата | 23.03.2014 |
| Формат | docx |
| Изображения | Есть |
Contents
1 Characteristics
2.Properties of the electron
3. History of discovery
4.Mendeleev
5.Structure of the periodic system
6.Groups
7.Periods
8.Blocks
9.Other periodic patterns
10.Literature
Atom (from the Greek atomos - indivisible) - mononuclear, chemically indivisible particle of a chemical element, the carrier material properties. Substances consist of atoms. The atom itself consists of a positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electron cloud. In general, the atom is electrically neutral. Size of the atom is completely determined by the size of its electron cloud, since the size of the nucleus is negligible compared to the size of the electron cloud. The core consists of positively charged protons Z (proton charge corresponds to 1 in arbitrary units) and N neutrons, which do not carry a charge (protons and neutrons are called nucleons). Thus the nuclear charge determined only by the number of protons and atomic number is equal to the periodic table. Positive charge of the nucleus is compensated by negatively charged electrons (electron charge -1 in arbitrary units) that form the electron cloud. Thus the number of electrons equal to the number of protons. The mass of protons and neutrons are (respectively 1 and 1 amu). Determine the mass of the atomic mass of its nucleus, because the electron mass is about 1850 times smaller than the mass of the proton and neutron, and rarely taken into account in the calculations. The number of neutrons can be found from the difference between the mass of the atom number of protons (N = AZ). Kind of atoms of a chemical element with a nucleus consisting of a well-defined number of protons (Z) and neutrons (N) is called a nuclide
Since the nucleus of an atom is concentrated almost all mass, but its size is negligible compared with the total volume of the atom, the nucleus is conventionally assumed a material point at rest in the center of the atom, and the atom is regarded as a system of electrons. Chemical reaction nucleus of an atom is not affected (except nuclear reactions) as the internal electronic levels, and involves only the outer electron shell electrons. For this reason it is necessary to know the properties of the electron and the rules for the formation of the electron shells.
Properties of the electron
Before examining the properties of the electron and the rules of formation of the electronic levels, it is necessary to address the history of the formation of ideas about the structure of the atom. We will not consider the complete history of the formation of atomic structure, and focus only on the most urgent and the most "faithful" representations that can most clearly show how electrons are arranged in an atom. The first presence of atoms as elementary constituents of matter, suggested another ancient Greek philosophers. After that, the story structure of the atom was a difficult path and different ideas, such as the indivisibility of the atom, the Thomson model of the atom, and others. The closest model of the atom was proposed by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. He compared the atom to the solar system where the sun acted as an atom's nucleus and electrons moving around him like planets. Placing electrons in fixed orbits was a very important step in the understanding of atomic structure. However, such a planetary model of the atom was in contradiction with classical mechanics. The fact that the motion of an electron in orbit he had to lose potential energy and eventually "fall" into the nucleus and the atom was to cease to exist. This paradox was eliminated by the introduction of Niels Bohr postulates. According to these postulates an electron moving on stationary orbits around the nucleus under normal conditions is not absorbed and emitted energy. Postulates show that to describe the atom laws of classical mechanics do not fit. This model is called the Bohr model of the atom, Rutherford. Continuation of the planetary structure of the atom is a quantum-mechanical model of the atom, according to which we shall consider an electron.
Electron is showing quasiparticle wave-particle duality. He is both a particle (corpuscle) and a wave. By properties include particle mass of the electron and its charge, and to the wave properties - the ability for the diffraction and interference. Communication between the wave and particle properties of the electron is reflected in the de Broglie equation:
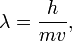
where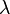 - wavelength
- wavelength 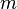 - mass of the particle
- mass of the particle 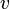 - particle
- particle 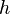 - Planck's constant = 6,63 • 10-34 J • s.
- Planck's constant = 6,63 • 10-34 J • s.
For an electron can not calculate its trajectory, we can only talk about the probability of finding an electron in a particular place around the nucleus. For this reason, do not speak about the orbits of the electron around the nucleus, and on the orbitals - the space around the nucleus in which the probability of finding an electron is greater than 95%. For an electron is impossible to accurately measure both the position and velocity (Heisenberg uncertainty principle). The more precisely we measure the electron coordinate, the greater the error in the measurement of its velocity, and vice versa: the more precisely we know the electron velocity, the greater the uncertainty in its coordinate. The presence of the wave properties of the electron allows us to apply it to the Schrödinger wave equation.
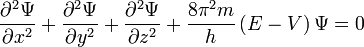
where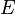 - the total electron energy,
- the total electron energy, 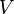 potential energy, the physical meaning of the function
potential energy, the physical meaning of the function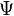 - the square root of the probability of finding an electron in a space with coordinates x, y and z (the kernel is considered the origin).
- the square root of the probability of finding an electron in a space with coordinates x, y and z (the kernel is considered the origin).
Represented by the equation written for the one-electron system. For systems with more than one electron description principle remains the same, but the equation takes a more complicated form. Graphic solution of the Schrödinger equation is the geometry of the atomic orbitals. Since s-orbital is spherical, p-orbital - a figure eight "knot" at the origin (at the nucleus), where the probability of finding an electron tends to zero.
In the framework of modern quantum mechanical theory of the electron is described by a set of quantum numbers: n, l, ml, s and ms. According to the Pauli principle in one atom can not be two electrons with completely identical set of quantum numbers.
Principal quantum number n determines the energy level of the electron, that is what the electronic level is given electron. The principal quantum number can take only integer values greater than 0: n = 1, 2, 3 ... n The maximum value for a particular atom of an element corresponds to the period in which the item is located in the periodic table of Mendeleev.
Electrons in the levels and orbitals are not placed randomly but according to the rule Klechkovskii whereby electrons are filling on the principle of minimum energy, ie in order of increasing amounts of principal and orbital quantum numbers n + l. In case the programming code for the two variants of filling the same, originally filled lowest energy level (for example, when n = 3 and l = 2 and n = 4 and l = 1 is initially filled will be level 3). The magnetic quantum number ml determines the location of the orbitals in space, and can be an integer value from-l to + l including 0. For the s-orbitals is only one value of ml = 0. For p-orbitals for three values -1, 0 and 1, that is p-orbital can be placed in three axes x, y and z.
Electron has intrinsic angular momentum - spin quantum number is denoted s. Electron spin - constant and equal to 1/2. The phenomenon of spin can be conventionally represented as a movement around its own axis. Initially, the electron spin equated to the movement of the planet around its own axis, but such a comparison is misleading. Spin - a purely quantum phenomenon, which has no analogues in classical mechanics.
Periodic Table of Elements ( Mendeleev's table ) - classification of chemical elements , which establishes the dependence of various properties of the elements of the charge of the atomic nucleus. The system is a graphic expression of the periodic law , established by the Russian chemist Mendeleev in 1869. Its original version was developed by Mendeleev in the 1869-1871 years , and established the dependence of properties of elements to their atomic weight (in the modern , from the atomic mass ) . Total proposed several hundred [1 ] the image of the periodic system options ( analytical curves , tables, geometric shapes , etc.) . In the modern version of the system is assumed mixing elements in the two-dimensional table in which each column (group ) defines the basic physical and chemical properties , and the rows represent periods to a certain extent similar to each other.
History of discovery
By the middle of the XIX century were discovered 63 chemical elements , and try to find patterns in this set have been made repeatedly . In 1829 Dobereiner published found them "law triads " : atomic weight of many elements close to the arithmetic mean of the other two elements close to the original chemical properties (strontium , calcium and barium , chlorine, bromine and iodine , etc.). The first attempt to arrange elements in order of increasing atomic weights taken Chancourtois Emil Alexander (1862 ), which placed the elements along the helix and noted frequent cyclic repetition of chemical properties of vertically. Both of these models do not attract the attention of the scientific community.
In 1866, his version of the periodic system proposed chemist and musician John Alexander Newlands , the model of which ( the "law of octaves ") looks a bit like Mendeleev , but was compromised by persistent attempts to find a table 's mystical musical harmony . In the same decade, appeared a few attempts to systematize chemical elements closest to the final version came Julius Lothar Meyer (1864 ) . Mendeleev published his periodic table of the first scheme in 1869 in the article " Value of properties with an atomic weight of elements" ( in the Journal of the Russian Chemical Society ) , even before ( February 1869 ) a notice of scientific discovery was sent to them the world 's leading chemists . The opening day of the periodic law is considered to March 1 ( February 17 , Old Style ), 1869 , which Mendeleev finished work on "experience of the elements, based on their atomic weight and chemical similarity .
Mendeleev
According to legend , the idea of chemical elements came to Mendeleev in a dream , but we know that once the question of how he discovered the periodic system , the scientist said, " I'm working on it, maybe twenty years of thought , and you think, and suddenly sat ready ... ".
Writing on cards the basic properties of each element ( them while 63 were known , one of which - Didim Di - helpful in further mixture of two newly discovered elements praseodymium and neodymium ) , begins Mendeleev repeatedly rearrange these cards , make one series of similar properties elements match series with one another . The work was sent in 1869 in the scientific institutions of Russia and other countries, the first version of the system ( "Experience system elements based on their atomic weight and chemical similarity "), in which the elements were arranged by nineteen horizontal rows ( rows of similar items, which became the prototype groups of modern systems) and six vertical columns ( the prototype for future periods). In 1870 Mendeleev " Fundamentals of Chemistry " published the second version of the system (" The natural system of elements "), having a more familiar to us form horizontal columns elements peers turned into eight groups of vertically arranged , six vertical columns of the first version turned into periods beginning alkaline metal and ending with halogen. Each period was divided into two rows of different elements included in a group of rows formed subgroups.
The essence of Mendeleev's discovery was the fact that with increasing atomic mass of chemical elements their properties do not change monotonically , and periodically . After a certain number of different properties of the elements in order of increasing atomic weight , the properties begin to repeat . For example , similar to potassium , sodium , similar to fluoro chloro and the like gold silver and copper. Naturally , the properties do not repeat exactly added thereto and changes. Honors the work of Mendeleev's work of his predecessors was that the basis for classification of the elements Mendeleev was not one, but two - the atomic mass and chemical similarity . In order to fully comply with the periodicity , Mendeleev had taken very bold steps he corrected the atomic masses of some elements (eg , beryllium, indium , uranium, thorium , cerium , titanium, yttrium ) , multiple items posted in their system , contrary to accepted while representations about their similarity to others (eg , thallium , which was considered an alkali metal, he placed third in the group according to its actual maximum valence) , leave empty cells in a table , where they were to stay until the open elements . In 1871, on the basis of these studies formulated Mendeleev 's periodic law , the form of which eventually was somewhat improved.
Scientific credibility of the periodic law was confirmed very soon : in the years 1875-1886 were discovered gallium ( ekaalyuminy ) , scandium ( ekabor ) and germanium ( ekasilitsy ) for which Mendeleev , using a periodic system , predicted not only the possibility of their existence , but also with amazing accuracy , described a number of physical and chemical properties.
At the beginning of XX century with the discovery of the structure of atoms , it was found that the frequency of changes in the properties of elements is not determined by atomic weight and nuclear charge equal to the atomic number and the number of electrons , which are distributed as electron shells of atoms of element determines its chemical properties.Further development of the periodic system involves filling empty cells of the table , which were placed in more and more new elements: noble gases , natural and artificially produced radioactive elements . In 2010 , with the synthesis of element 117 , the seventh period of the periodic system was completed , the problem of the lower boundary of the periodic table is one of the most important in modern theoretical chemistry.
Structure of the periodic system
The most common are three forms of the periodic table : "short" ( short-period ) , "long" ( long-period ) and " Extra long ." In " Ultra Long " version of each period takes exactly one line . In the "long" version of the lanthanides and actinides are removed from the common table , making it more compact . In the "short" form of the recording , in addition to this , the fourth and subsequent periods occupied by two lines , characters and the main elements of sub-group aligned with the edges of the various cells.The short form of the table , with eight groups of elements , was officially abolished by IUPAC in 1989. Despite the recommendation to use the long form , short form continues to be driven in a large number of Russian handbooks and manuals , and after this time. Of modern foreign literature , short form is completely excluded , used instead the long form . Such a situation , some researchers have linked including apparent rational compactness of the short form of the table , as well as inertia, stereotyped thinking and modern non-perception (international) information.
In 1970, Theodore Seaborg proposed extended periodic table of elements . Niels Bohr developed staircase ( pyramidal ) shape of the periodic system . There are many others , rarely or not used , but highly original , graphical way to display the Periodic Law . Today, there are hundreds of options table, the scientists propose new variants .
Groups
Group or family , - one of the columns of the periodic table. For groups tend to have significantly more pronounced periodic trends than to the frames or blocks. Modern quantum mechanical theories of atomic structure explain group commonality that elements within the same group usually have the same electron configurations in their valence shells . Accordingly , the elements that belong to the same group traditionally have similar chemical characteristics , and exhibit a clear pattern of change in properties with increasing atomic number . However, in some fields of the table , for example - in the d- block and f- block horizontal similarity may be just as important or even more markedly pronounced than vertical .
In accordance with the international system of naming groups are numbered from 1 to 18 from left to right - from the alkali metals to the noble gases . Previously used to identify them Roman numerals . In American practice after Roman numerals also posed letter A ( if the group is located in the s- block or p- block ) or B ( if the group was in the d- block) . Then applied identifiers correspond to the last digit of modern numerical indicators - for example, elements of the group 4 corresponds to the name of IVB, but to those who are now known as a group of 14 - IVA. A similar system has been used in Europe, except that the letter A refers to the group prior to the tenth , and B - to the groups after the tenth inclusive. Groups 8, 9 and 10 , moreover, is often regarded as one triple group identifier VIII. In 1988 came into effect new IUPAC notation system , and former names of groups out of use.
Some of these groups have been assigned the trivial , non-systematic name (such as " alkaline metals ", " halogen ", etc. ), but some of them are rarely used. Groups three through fourteenth inclusive, do not have the same names and their identified either by number or by name representative of the first (" titanium ", " cobalt " and so forth ), since they exhibit a lesser degree of similarity between a vertical line or minimal laws ] .
Elements belonging to the same group tend to show certain trends in atomic radius, ionization energy and electronegativity . From top to bottom within a group the atomic radius increases ( the more he filled energy levels , the farther from the nucleus are arranged valence electrons ), and the ionization energy decreases ( due to weaker atom , and therefore it becomes easier to remove an electron ) , as well as and electronegativity (which, in turn, caused an increase in the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus ) . Happen , however, are exceptions to these laws - for example, in a group of 11 from top to bottom electronegativity increases and does not decrease .
Periods
Period - row of the periodic table . Although groups , as mentioned above , is characterized by more significant trends and patterns , there are also areas where the horizontal direction is more significant and indicative rather than vertical - eg regarding f- block , where the lanthanides and actinides form two important horizontal sequence of elements
Within the period of the elements exhibit a definite pattern in the three aspects mentioned above ( the atomic radius and electronegativity of the ionization energy ) , and in electron affinity . From left to right the atomic radius usually decreases ( due to the fact that each subsequent element increases the number of charged particles and electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus and parallel with increasing ionization energy (the stronger bond in the atom , the more energy is required to withdraw electron). increases accordingly and elektrootritsatelnostChto regard the electron affinity , the metal on the left side of the table are characterized by a lower value of this index , and non-metals on the right , respectively , great - except for the noble gases
Blocks
In view of the importance of the outer electron shell of the atom different areas of the periodic table are sometimes described as units called in accordance with those on which the shell is the last electron. S- block includes the first two groups , that is, alkali and alkaline earth metals , as well as hydrogen and helium ; p- block consists of the last six groups ( 13 to 18 according to standard IUPAC naming , or IIIA to VIIIA by American system ), and includes among other elements , all of metalloids . D- block - this group of 3 to 12 ( IUPAC ) , they - with stage IIIB to IIB -American , which includes vseperehodnye metals . F- block vynosimy typically beyond the table consists of lanthanides and actinides
Other periodic patterns
Electronic configuration . Organization electrons demonstrates certain periodic repeating pattern. Electrons occupy a sequence of shells which are identified by numbers (sheath 1 , the sheath 2, etc. ) , and those in turn are composed of sub-levels defined letters s, p, d, f and g. Increasing atomic number of electrons gradually fill these shells , and each time the electron takes a new shell for the first time , a new period in the table. Similarities in the electron configuration determine the similarity properties of the elements ( watching them , in fact, led to otkrytiyuperiodicheskogo law).
Metallicity / nemetallichnost . The lowering of the ionization energy indicators , electronegativity and electron affinity elements acquire features typical of metals, and as they increase - on the contrary, for non-metals ] . In accordance with the laws for the aforementioned characteristics , the most pronounced metals are located at the beginning of the period, and non-metals - at its end. In groups , in contrast, as one moves from top to bottom metal properties are intensified , albeit with some exceptions to the general rule . The combination of horizontal and vertical patterns gives conditional dividing line between metals and nonmetals stepped form , along this line elements are sometimes defined as metalloids .
Value of the periodic system
Periodic system of Mendeleev was a milestone in the development of the atomic- molecular theory . Thanks to her, had the modern concept of the chemical elements have been refined notions of simple substances and compounds.
The predictive role of the periodic system , shown by another Mendeleev in the XX century was manifested in the evaluation of chemical properties of transuranic elements .
Developed in the XIX century . within the science of chemistry , the periodic table was finished ordering of types of atoms for new areas of physics , which have developed in the early XX century. - Atomic physics and nuclear physics . Studies atom physics methods , it was found that the serial number of the element in the periodic table (atomic number ) is a measure of the electric charge of the atomic core of this element , the horizontal row number ( period) in the table determines the number of electron shells of atoms , and the number of vertical rows - quantum structure upper shell , what elements of the series and similarity of chemical properties are required .
The appearance of the periodic system has opened a new , genuinely scientific era in the history of chemistry and related sciences series - instead of disparate information about the elements and compounds appeared orderly system on which it became possible to generalize, draw conclusions , predict.
Literature
D.I Mendeleev - periodic law of chemical elements / / Encyclopedic Dictionary Brockhaus and Efron : In 86 volumes ( 82 tons and 4 extra. ) . - St. Petersburg. , 1890-1907 .
Agafoshina NP periodic law and the periodic system of elements Mendeleev . - M.: Education , 1973 . - 208 .
Evdokimov Yu , Ph.D. Chem . Sciences . On the history of the periodic law . Science and Life , № 5 (2009), pp. 12-15 .
Makarenya AA Rysev YV Mendeleev . - M.: Education , 1983 . - 128 p.
Makarenya AA Trifonov DN periodic law of Mendeleev . - M.: Education , 1969 . - 160 .
Eric R. Scerri. The Periodic Table: Its Story and Its Significance. - New York : Oxford University Press, 2007 . - 368 .


