- Преподавателю
- Химия
- Chemical Reactions
Chemical Reactions
| Раздел | Химия |
| Класс | - |
| Тип | Тесты |
| Автор | Арынова К.Ш. |
| Дата | 11.05.2014 |
| Формат | doc |
| Изображения | Есть |
CHEMISTRY - CHAPTER 3: EQUATIONS
BALANCING EQUATIONS: FORMULAS GIVEN Practice Sheet #1
Balance the following equations:
1. Al + N2 → AlN
2. Fe + O2 → Fe3O4
3. CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
4. NH4NO3 → N2O + H2O
5. KI + Cl2 → KCl + I2
6. Pb(NO3)2 + HCl → PbCl2 + HNO3
7. BaO2 → BaO + O2
8. Al + H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + H2
9. CH4 + Cl2 → CHCl3 + HCl
10. MgCl2 + NaOH → Mg(OH)2 + NaCl
11. AgNO3 + CuCl2 → AgCl + Cu(NO3)2
12. ZnS + O2 → ZnO + SO2
13. Na + H2O → H2 + NaOH
14. BaCl2 + (NH4)2CO3 → BaCO3 + NH4Cl
15. C6H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
16. Na + H2O → NaOH + H2
17. Fe + FeCl3 -→ FeCl2
18. Ba(OH)2 + AlCl3 → Al(OH)3 + BaCl2
19. H2C2O4 + KOH → K2C2O4 + H2O
20. C2H2Cl4 + Ca(OH)2 → C2HCl3 + CaCl2 + H2O
21. (NH4)2Cr2O7 → N2 + Cr2O3 + H2O
22. Zn3Sb2 + H2O -→ Zn(OH)2 + SbH3
23. HClO4 + P4O10 → H3PO4 + Cl2O7
24. C6H5Cl + SiCl4 + Na → (C6H5)4Si + NaCl
25. Sb2S3 + HCl → H3SbCl6 + H2S
26. IBr + NH3 → NI3 + NH4Br
27. KrF2 + H2O → Kr + O2 + HF
28. Na2CO3 + C + N2 → NaCN + CO
29. K4Fe(CN)6 + H2SO4 + H2O → K2SO4 + FeSO4 + (NH4)2SO4 + CO
BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS - NAMES GIVEN Practice Sheet #2
1. Potassium reacts with water yielding potassium hydroxide and hydrogen
2. Chlorine reacts with potassium bromide yielding potassium chloride and bromine
3. Zinc + hydrogen chloride yields zinc chloride and hydrogen
4. iron + water → Fe3O4 + hydrogen
5. zinc sulfide + oxygen → . zinc oxide + sulfur dioxide
6. C10H16 + Cl2→ C + HCl
7. Aluminum + sodium hydroxide → Na3AlO3+ hydrogen
8. C2H2 + O2→ CO2 + H2O
9. Ammonia + oxygen → nitrogen monoxide + water
10. Phosphorus + iron(III) oxide → tetra-phosphorus decoxide + iron
11. Cupric sulfide + oxygen → copper(I) oxide + sulfur dioxide
12. sodium bicarbonate + hydrogen sulfate → sodium sulfate + water + carbon dioxide
13. Sodium carbonate + silver nitrate → sodium nitrate + silver carbonate
14. Calcium + oxygen → calcium oxide
15. Zinc + ferric oxide → zinc oxide + iron
16. Magnesium bromide + chlorine → magnesium chloride + bromine
17. Sodium + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
18. Potassium nitrate → potassium nitrite + oxygen
19. Calcium oxide + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water
20. Magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
21. Iron + oxygen → iron(II) oxide
22. Water + dinitrogen trioxide → nitrous acid
23. Sodium oxide + water → sodium hydroxide
24. Iron(III) oxide + carbon monoxide → iron + carbon dioxide
25. Methane (CH4) + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
EQUATIONS - PREDICTING BY TYPE OF REACTION
Part I: Complete the word equation and write the balanced chemical equation. Give the reason for the product(s) in each case. Consult the activity series and the solubility tables.
Composition reactions:
1. sodium + iodine →
2. calcium + oxygen →
3. hydrogen + chlorine →
4. calcium oxide + water →
5. dinitrogen pentoxide + water →
Decomposition reactions:
6. nickel(II) chlorate →
7. barium carbonate →
8. zince hydroxide →
9. mercury(II) oxide →
10. copper (II) carbonate →
Replacement reactions:
11. aluminum + sulfuric acid →
12. potassium iodide + chlorine→
13. iron + copper (II) nitrate →
14. zinc + hydrochloric acid →
15. magnesium + silver nitrate →
Double Replacement (ionic reactions)
16. silver nitrate + zinc chloride →
17. copper(II) hydroxide + acetic acid →
18. iron(II) sulfate + ammonium sulfide →
19. ammonium chloride + sodium hydroxide →
20. hydrochloric acid + potassium hydroxide →
TYPES OF CHEMICAL EQUATIONS (IDENTIFICATION)
State whether each of the following equations represents a synthesis (s) , decomposition(d), single replacement (sr), double replacement (dr), or combustion reaction (c).
_____________ 1. CO2→ C + O2
_____________ 2. NaCl + AgNO3→ NaNO3 + AgCl
_____________ 3. S + Cl2→ SCl2
_____________ 4. BaCl2 + 2NaOH -→ 2NaCl + Ba(OH)2
_____________ 5. 2C2H2 + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2 H2O
_____________ 6. Zn + CuSO4→ ZnSO4 + Cu
_____________ 7. CH4→ C + 2H2
_____________ 8. Pb(NO3)2 + Mg → Pb + Mg(NO3)2
_____________ 9. Mg + 2 HCl → MgCl2 + H2
____________ 10. H2SO4→ H2 + S + 2O2
_____________ 11. 2O2 + N2→ N2O4
_____________ 12. 3CaBr2 + 2Na3P → Ca3P2 + 6NaBr
_____________ 13. 2KI + Br2→ 2KBr + I2
_____________ 14. C6H12O6→ 6C + 6H2O
_____________ 15. 2NaF → 2Na + F2
_____________ 16. Si + O2→ SiO2
_____________ 17. 2NaI + Pb(NO3)2→2NaNO3 + PbI2
_____________ 18. H2 + CO + O2→ H2CO3
_____________ 19. C3H8 + 5O2→ 3CO2 + 4H2O
_____________ 20. Li3PO4→ 3Li + P +2O2
_____________ 21. CS2 + 2F2→ CF4 + 2S
_____________ 22. NaI + Cs → CsI + Na
REACTION PREDICTION (Set #1)
If the word equation is complete, write and balance the chemical equation. If the word equation is incomplete, complete it and write the balanced chemical equation. Tell the type of reaction. Give reason(s) for the product(s)
1. barium chloride + sodium sulfate →
2. calcium + hydrochloric acid →
3. iron(II) sulfide + hydrochloric acid → hydrogen sulfide (g) +
4. zinc chloride + ammonium sulfide →
5. ammonia + oxygen → nitric acid + water
6. magnesium + nitric acid →
7. potassium + water →
8. sodium iodide + bromine →
9. silver + sulfur→
10. sodium chlorate →
11. carbon + steam (H2O) → carbon monoxide(g) + hydrogen (g)
12. zinc + lead(II) acetate →
13. iron (II) hydroxide →
14. iron(II) oxide + carbon monoxide → iron + carbon dioxide (g)
15. lead (II) acetate + hydrogen sulfide →
16. aluminum bromide + chlorine →
17. magnesium carbonate →
18. iron(II) chloride + sodium hydroxide →
19. calcium oxide + diphophorus pentoxide →
20. chromium + oxygen →
21. sodium + water →
22. calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid →
23. calcim hydroxide + phophoric acid →
24. sodium carbonate + nitirc acid →
25. aluminum hydroxide + sulfuric acid →
26. sodium sulfite + sulfuric acid →
27. copper + sulfuric acid → copper (II) sulfate + water + sulfur dioxide (g)
28. calcium hydroxide + ammonium sulfate → calcium sulfate + water + ammonia
REACTION PREDICTION (Set #2)
In each of the following examples:
a. State what type of reaction is expected.
b. Write the balanced equation for those reaction that do take place.
1. aluminum plus hydrochloric acid
2. calcium hydroxide plus nitric acid
3. magnesium plus zinc nitrate
4. mercury plus oxygen
5. zinc chloride plus hydrogen sulfide
6. dinitrogen pentoxide plus water
7. sodium chlorate heated to high temperature
8. barium nitrate plus sodium chromate
9. sodium bromide plus silver nitrate
10. zinc carbonate strongly heated
11. potassium plus fluorine
12. potassium nitrate plus zinc phosphate
13. lithium oxide plus water
14. sodium chloride molten electrolyzed
15. iron(iii) hydroxide plus phosphoric acid
16. sodium plus nitric acid
17. sulfur dioxide plus water
18. oxygen plus sulfur
19. sodium sulfate plus barium chloride
20. hydrogen plus oxygen
21. sodium oxide plus water
22. mercury(I) nitrate plus sodium carbonate
23. magnesium plus hydrochloric acid
24. lead(II) nitrate and sodium iodide
25. chromium(II) perchlorate and sodium sulfide
REACTION PREDICTION (Set #3)
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reacions. Classify the reation type.
-
iron(III) oxide + hydrogen
-
bismuth(V) oxide
-
Manganeese (II) chlorate + potassium phosphate
-
Lead (II) acetate + sodium chromate
-
potassium + iodine
-
ammonium sulfate + barium nitrate
-
zinc oxide
-
gold(III) chloride + sodium sulfide
-
magnesium + hydrochloric acid
-
calcium hydroxide + iron (II) nitrate
-
C4H10 + O2
-
tin(IV) sulfide
-
silver nitrate + zinc
-
potassium carbonate + lead (II) nitrate
-
ammonium chloride + mercury(II) acetate
-
iron + hydrochloric acid
-
sodium iodide + chlorine
-
aluminum + oxygen
-
barium chloride + lithium sulfate
-
sulfuric acid + calcium hydroxide
-
iron (II) nitrate + sodium sulfite
-
C5H12 + O2
REACTION PREDICTION (Set #4)
Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reacions. Classify the reation type.
-
zinc chloride + ammonium sulfide
-
zinc + copper (II) sulfate
-
magnesium bromide + chlorine
-
aluminum oxide
-
silver nitrate + sodium chloride
-
magnesium + copper (II) nitrate
-
sodium hydroxide + sulfuric acid
-
lead (II) nitrate + potassium bromide
-
copper + tin (IV) chloride
-
C10H22 + O2
-
potassium sulfide + iron (III) nitrate
-
zinc + silver nitrate
-
silver + oxygen
-
tin(IV) chloride
-
calcium hydroxide + phophoric acid
-
magnesium iodide + chlorine
-
barium nitrate + sodium phophate
-
manganeese(IV) oxide
-
nitrogen + hydrogen ammonia
-
C11H22 + O2
-
aluminum chloride + potassium sulfide
22. sodium sulfite + hydrochloric acid
REVIEW OF WRITING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
For each of the following equations write a formula equation.
YOU DO NOT HAVE TO BALANCE IT.
When applicable, write a net ionic equation.
1. Solutions of sodium fluoride and dilute hydrochloric acid are mixed.
2. A saturated solution of barium hydroxide is mixed with a solution of iron(III) sulfate.
3. A solution of ammonium sulfate is added to a potassium hydroxide solution.
4. Carbon dioxide gas is bubbled through a concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide.
5. Solid copper is added to a dilute nitric acid solution.
6. Magnesium metal is burned in nitrogen gas.
7. Sulfur dioxide gas is passed over solid calcium oxide.
8. Lead foil is immersed in silver nitrate solution.
9. A solution of ammonium sulfate is added to a saturated solution of barium hydroxide.
10. Acetic acid solution is added to a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
11. Hydrogen gas is passed over hot iron(III) oxide.
12. Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a dilute solution of mercury (I) nitrate.
13. Sodium metal is added to water.
14. Dilute sulfuric acid is added to a solution of lithium hydrogen carbonate.
15. A piece of lithium metal is dropped into a container of nitrogen gas.
16. Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of potassium sulfite.
17. Solid sodium oxide is added to water.
18. A solution of sodium sulfide is added to a solution of zinc nitrate.
19. A solution of ammonia is added to a dilute solution of acetic acid.
20. Solid calcium is added to warm water.
21. Powdered magnesium oxide is added to a container of carbon dioxide gas.
22. Gaseous hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of nickel(II) nitrate.
23. A strip of magnesium is added to a solution of silver nitrate.
24. Solid potassium chlorate is heated in the presence of manganese dioxide as a catalyst.
25. Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of potassium carbonate.
26. Sulfur trioxide gas is added to excess water.
27. Dilute sulfuric acid is added to a solution of barium chloride.
28. Solutions of zinc sulfate and sodium phosphate are mixed.
29. Solutions of silver nitrate and lithium bromide are mixed.
30. Excess hydrochloric acid solution is added to a solution of potassium carbonate.
31. Ethanol (C2H5OH) is burned in excess oxygen gas.
OXIDATION /REDUCTION REACTIONS
1. Assign oxidation number to each element in the following compounds:
a. PbSO4 b. H2O2 c. K2Cr2O7 d. K2SiO3
2. Which of the following are oxidation-reduction reactions?
a. 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
b. C + O2 → CO2
c. 2H2O ↔ 2H2 + O2
d. NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
e. NH3 + HCl → NH4+1 + Cl-1
f. 2KClO3 → 2KCl + O2
g. H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
h. 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
i. H2SO4 + 2KOH →K2SO4 + 2H2O
j. Zn + CuSO4 →ZnSO4 + Cu
3. For each oxidation-reduction in Question 2 identify the:
a. substance oxidized
b. substance reduced
c. the oxidizing agent
d. the reducing agent
e. write the oxidation and reduction half-reactions
OXIDATION REDUCTION REACTIONS - BALANCING: Set #1
Balance the following equations using the ion-electron method.
1. H2S + O2 SO2 + H2O
2. MnO2 + HCl H2O + MnCl2 + Cl2
3. zinc + hydrochloric acid zinc chloride + hydrogen
4. iron + copper(II) sulfate iron (II) sulfate + copper
5. copper + sulfuric acid copper (II) sulfate + hydrogen
6. potassium dichromate + sulfur + water sulfur dioxide + potassium hydroxide + chromium (III) oxide
7. bromine + water hydrobromic acid + hypobromous acid
8. HCl + KMnO4 H2O + KCl + MnCl2 + Cl2
9. K2Cr2O7 + HCl KCl + CrCl3 + H2O + Cl2
10. Cu2O + SO2 CuS + O2
11. CS2 + SCl2 CCl4 + S
12. NaAu(CN)2 + Zn Na2Zn(CN)4 + Au
13. FeSO4 + O2 + H2O FeOHSO4
14. HBr + Ca(BrO)2 CaBr2 + Br2 + H2O
15. Ca3(PO4)2 + SiO2 P4O10 + CaSiO3
16. The oxidation-reduction reaction between copper and concentrated nitric acid yields the following products: copper(II) nitrate, water and nitrogen dioxide. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
17. The reaction between copper and dilute nitric acid yields the following products: copper (II) nitrate, water and nitrogen monoxide. Write the balanced equation.
Balancing REDOX Reactions: Set #2
Balancing Equations: Formulas Given, Page 1
1) 2, 1, 2
2) 3, 2, 1
3) 1, 1, 1
4) 1, 1, 2
5) 2, 1, 2, 1
6) 1, 2, 1, 2
7) 2, 2, 1
8) 2, 3, 1, 3
9) 1, 3, 1, 3
10) 1, 2, 1, 2
11) 2, 1 ,2 , 1
12) 2, 3 ,2, 2
13) 2, 2, 1, 2
14) 1, 1, 1, 2
15) 2, 15, 12, 6
16) 2, 2, 2, 1
17) 1, 2, 3
18) 3, 2, 2, 3
19) 1, 2, 1, 2
20.) 2, 1, 2, 1, 2
21) 1, 1, 1, 4
22) 1, 6, 3, 2
23) 12, 1, 4, 6
24) 4, 1, 8, 1, 8
25) 1, 12, 2, 3
26) 3, 4, 1, 3
27) 2, 2, 2, 1, 4
28) 1, 4, 1, 2, 3
29) 1, 6, 6, 2, 1, 3, 6
Balancing Equations - Names Given (pages 2/3)
1. 2K + 2H2O 2KOH + H2
2. Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2
3. Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2
4. 3Fe + 4H2O Fe3O4 + 4H2
5. 2ZnS + 3O2 2ZnO + 2SO2
6. C10 H16 + 8Cl2 10C + 16 HCl
7. 2Al + 6NaOH 2Na3AlO3 + 3H2
8. 2C2H2 + 5O2 4CO2 + 2H2O
9. 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O
10. 12P + 10Fe2O3 3P4O10 + 20 Fe
11. 4CuS + 5O2 2Cu2O + 4SO2
12. 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2
13. Na2CO3 + 2AgNO3 2NaNO3 + Ag2CO3
14. 2Ca + O2 2CaO
15. 3Zn + Fe2O3 3ZnO + 2Fe
16. HgBr2 + Cl2 MgCl2 + Br2
17. 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2
18. 2KNO3 2KNO2 + O2
19. CaO + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O
20. 2 MgO + O2 2MgO
21. 2Fe + O2 2FeO
22. H2O + N2O3 2HNO2
23. Na2O + H2O 2NaOH
24. Fe2O3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO2
25. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O
EQUATIONS - Predicting by type of reaction, page 4
1. 2Na + I2 → 2NaI
2. 2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
3. H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
4. CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
5. N2O5 + H2O → 2HNO3
6. Ni(ClO3)2 → NiCl2 + 3O2
7. BaCO3 → BaO + CO2
8. Zn(OH)2 → ZnO + H2O
9. 2HgO → 2Hg + O2
10. CuCO3 → CaO + CO2
11. 2Al + 3 H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2O
12. 2KI + Cl2→ 2KCl + I2
13. 2 Fe + 3Cu(NO3)2 →2 Fe(NO3)3 + 3Cu
14. Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
15. Mg + 2AgNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + 2Ag
16. 2AgNO3 + ZnCl2 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2AgCl(s)
17. Cu(OH)2 + 2 CH3COOH → Cu(CH3COO) 2 + 2H2O
18. FeSO4 + (NH4)2S → FeS + (NH4)2SO4
19. NH4Cl + NaOH → NH3 + H2O + NaCl
20. HCl + KOH → KCl + H2O
Types of Chemical Equations (Page # 5)
1. d 2. dr 3. s 4. dr 5. c 6. sr 7. d
8. sr 10. d 11. s 12. s 13. dr 14. d 15. d
16. s 17. dr 18. s 19. c 20. d 21. sr 22. sr
Reaction Prediction (Set #1) Page 6
1. BaCl2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl
2. Ca + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2
3. FeS + 2HCl → H2S + FeCl2
4. ZnCl2 + (NH4)2S → ZnS(s) + 2NH4Cl
5. NH3 + 2O2 → HNO3 + H2O
6. Mg + 2HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + H2
7. 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
8. 2NaI + Br2 → 2NaBr + I2
9. 2Ag + S → Ag2S
10. 2NaClO3 → 2NaCl + 3O2
11. C + H2O → CO + H2
12. Zn + Pb(C2H3O2)2 → H2 + Zn (C2H2O3)2
13. Fe(OH)2 → FeO + H2O
14. FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
15. Pb(C2H3O2)2 + H2S → PbS + 2HC2H3O2
16. 2AlBr3 + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3 Br2
17. MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
18. FeCl2 + 2NaOH → Fe(OH)2(s) + NaCl
19. 6CaO + 2P2O5 → 2Ca3(PO4)2
20. 4Cr + 3O2 → 2Cr2O3
21. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
22. CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
23. 3Ca(OH)2 + 2 H3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2(s) + 6H2O
24. Na2CO3 + 2HNO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
25. 2Al(OH)3 + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 6H2O
26. Na2SO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + SO2 + H2O
27. Cu + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2
28. Ca(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2NH3 + 2H2O
Reaction Prediction (Set #2): (Page 7).
In each of the following examples:
a. State what type of reaction is expected.
c. Write the balanced equation for those reaction that do take place.
1. aluminum plus hydrochloric acid 2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
2. calcium hydroxide plus nitric acid Ca(OH)2 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O(l)
3. magnesium plus zinc nitrate Mg + Zn(NO3)2 → Mg(NO3)2 + Zn
4. mercury plus oxygen 2Hg + O2 → 2HgO
5. zinc chloride plus hydrogen sulfide ZnCl2 + H2S → ZnS(s) + 2HCl
6. dinitrogen pentoxide plus water N2O5 + H2O → 2HNO3
7. sodium chlorate heated to high temperature 2NaClO3 →2NaCl + 3O2
8. barium nitrate plus sodium chromate Ba(NO3)2 + Na2CrO4 → BaCrO4(s) + 2NaNO3
9. sodium bromide plus silver nitrate NaBr + AgNO3 → NaNO3 + AgBr(s)
10. calcium phosphate plus aluminum sulfate Ca3(PO4)2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 3CaSO4(s) + 2AlPO4(s)
11. zinc carbonate strongly heated ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
12. potassium plus fluorine 2K + F2 → 2KF
13. lithium oxide plus water Li2O + H2O → 2LiOH
14. sodium chloride molten electrolyzed 2NaCl ---electrolysis → 2Na + Cl2
15. iron(iii) hydroxide plus phosphoric acid Fe(OH)3 + H3PO4 → FePO4 + 3H2O(l)
16. sodium plus nitric acid 2Na + 2HNO3 → 2 NaNO3 + H2
17. sulfur dioxide plus water SO2 + H2O →H2SO3
18. oxygen plus sulfur O2 + S → SO2
19. sodium sulfate plus barium chloride Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl
20. hydrogen plus oxygen 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
21. sodium plus water 2Na + 2H2O → 2 NaOH + H2
22. mercury(I) nitrate plus sodium carbonate Hg2(NO3)2 + Na2CO3 →Hg2CO3(s) + NaNO3
23. magnesium plus hydrochloric acid Mg + 2 HCl → MgCl2 + H2
24. lead(II) nitrate and sodium iodide Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaI → PbI2(s) + 2NaNO3
25. chromium(III) perchlorate and sodium sulfide 2Cr(ClO4)3 + 3Na2S → 2Cr2S3(s) + 6NaClO4
Reaction Prediction (Set #3): (Page 8).
-
Fe2O3 +3H2 3H2O + 5Fe
-
Bi2O5 4Bi + 5O2
-
3Mn(ClO3)2 + 2K3PO4 6KClO3 + Mn3(PO4)2 (s)
-
Pb(CH3COO)2 + Na2CrO4 PbCrO4(s) + 2NaCH3COO
-
2K + I2 2KI
-
(NH4)2SO4 + Ba(NO3)2 BaSO4(s) + 2NH4NO3
-
2ZnO 2Zn + O2
-
2AuCl3 + 3Na2S 6NaCl + Au2S3(s)
-
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
-
Ca(OH)2 + Fe(NO3)2 Fe(OH)2 (s) + Ca(NO3)2
-
2C4H10 + 13 O2 8CO2 + 10 H2O
-
SnS2 Sn + 2S
-
2AgNO3 + Zn Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
-
K2CO3 + Pb(NO3)2 2KNO3 + PbCO3(s)
-
2NH4Cl + Hg(C3H3O2)2 2NH4C2H3O2 + HgCl2(s)
-
Fe + 2HCl FeCl2 + H2 or 2Fe + 6HCl 2FeCl3 + 3H2
-
2NaI + Cl2 2NaCl + I2
-
4Al + 3O2 2Al2O3
-
BaCl2 + Li2SO4 BaSO4(s) + 2 LiCl
-
H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 CaSO4 + 2H2O
-
Fe(NO3)2 + Na2S FeS + 2NaNO3
-
C5H11 + 8O2 5CO2 + 6H2O
Reaction Prediction (Set #4): (Page 9).
1. ZnCl2 + (NH4)2S → 2NH4Cl + ZnS(s)
2. Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
3. MgBr2 + Cl2 → MgCl2 + Br2
4. 2Al2O3 → 2Al + 3O=
5. AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl(s) + NaNO=
6. Mg + Cu(NO3)2 → Mg(NO3)2 + Cu
7. 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
8. Pb(NO3)2 + 2KBr → PbBr2(s) + 2KNO3
9. 2Cu + SnCl4 → 2CaCl2 + Sn
10. 2C10H22 + 31O2 → 20CO2 + 22H2O
11. 3K2S + 2Fe(NO3)3 → 6KNO3 + Fe2S3(s)
12. Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
13. 4Ag + O2 → 2Ag2O
14. SnCl4 → Sn + 2Cl2
15. 3Ca(OH)2 + 2H3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2(s) + 6H2O
16. MgI2 + Cl2 → MgCl2 + I2
17. 3Ba(NO3)2 + 2Na3PO4 → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaNO3
18. MnO2 → Mn + O2
19. N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
20. 2C11H22 + 33O2 → 22CO2 + 22H2O
21. 2AlCl3 + 3K2S → 6KCl + Al2S3
22. Na2SO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + SO2(g) + H2O
REVIEW OF WRITING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS: PAGE 10
Formula Equation Ionic Equation
1. NaF(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl + HF(g) H+ + F- → HF(g)
2. Ba(OH)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 → BaSO4 + Fe(OH)3
Ba+2 + OH- + Fe+3 + SO4-2 →BaSO4(s) + Fe(OH)3(s)
3. (NH4)2SO4 + KOH→ K2SO4 + NH3(g) + H2O NH4+ + OH- → NH3 + H2O
4. CO2(g) + NaOH(aq) → Na2CO3 + H2O CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
H2CO3 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O H+ + OH- → H2O
5. Cu + HNO3 → H2 + Cu(NO3)2 NO REACTION
6. Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
7. SO2(g) + CaO → CaSO3
8. Pb(s) + AgNO3 (aq) → Ag + Pb(NO3)2 Pb(s) + Ag+ → Pb+2 + Ag(s)
9. (NH4)2SO4 + Ba(OH) 2 → BaSO4(s) + NH4OH Ba+2 + SO4-2 → BaSO4(s)
10. HC2H3O2 + NaHCO3 → NaC2H3O2 + H2O + CO2 H+ +HCO3-→ H2O + CO2
11. H2 + Fe2O3 → Fe + H2O H2 + Fe+3→ H+ + Fe
12. HCl + Hg2(NO3)2 → HNO3 + Hg2Cl2(s) Hg2+2 + Cl- → Hg2Cl2(s)
13. Na + H2O → NaOH + H2 Na + H+ → H2 + Na+
14. H2 SO4 + LiHCO3 → Li2SO4 + H2O + CO2 H+ +HCO3-→ H2O + CO2
15. Li + N2 → Li3N
16. HCl + K2SO3 → KCl + H2O + SO2 H+ + SO3-2 → H2O + SO2
17. Na2O + H2O → NaOH
18. Na2S + Zn(NO3)2 → ZnS(s) + NaNO3 Zn+2 + S-2 → ZnS(s)
19. NH4OH + HC2H3O2 → NH4C2H3O2 + H2O H+ + OH- → H2O
20. Ca + H2O → Ca(OH)2
21. MgO + CO2 → MgCO3
22. H2S(g) + Ni(NO3)2 → NiS(s) + HNO3 Ni+2 + S-2 → NiS(S)
23. Mg + AgNO3 → Ag + Mg(NO3)2 Mg + Ag+1 → Mg+2 + Ag
24. KClO3 → KCl + O2
25. HCl + K2CO3 → KCl + H2O + CO2 H+ CO3-2 → H2O + CO2
26. SO3(g) + H2O → H2SO3
27. H2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + HCl Ba+2 + SO4-2 → BaSO4(s)
28. ZnSO4 + Na3PO4 → Zn3(PO4)2(s) + Na2SO4 Zn +2 + PO4-3 → Zn3(PO4)2(s)
29. AgNO3 + LiBr → LiNO3 + AgBr Ag+ + Br- → AgBr
30. HCl + K2CO3 → KCl + H2O + CO2 H+ CO3-2 → H2O + CO2
31. C2H5OH + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Oxidation/Reduction Reactions: page 11
1. (a) +2, +6, -2 2. +1, -1 3. +1, +6, -2
2. (a), (b), (c), (f), (g) (h), (j) are oxidation/reduction reactions
3.
Question #
Substance oxidized
Substance reduced
Oxidizing agent
Reducing agent
Equation
(a)
Na0
Cl2
Cl2
Na
Na0 → Na+1 + 1e; Cl2 + 2e → 2Cl-
(b)
C0
O2
O2
C0
C0 → C+4 + 4e; O2 +4e → 2c
(c)
O-2
H+1
H+1
O-2
2O-2→ 3O2 +4e; 4e + 4 H+1 → H20
(f)
O-2
Cl+5
Cl+5
O-2
6 O-2→ 3O2 +12e; 2Cl+5 + 12 e → 2Cl-1
(g)
H20
Cl20
Cl20
H20
H20 → 2H+1 + 2e; Cl20 + 2e → 2Cl-1
(h)
H20
O2
O2
H20
O2 +4e O-2→ 2O-2 ; 2 H20 → 4H+1 + 4e
(j)
Zn0
Cu+2
Cu+2
Zn0
Zn0→ Zn+2 + 2e; Cu+2 + 2e → Cu0
Oxidation/Reduction Reactions - Balancing: page 12
-
2, 2, 2
-
1, 4, 2, 1, 1
-
1, 2, 1, 2
-
1, 1, 1, 1
-
1, 2, 1, 1
-
1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2
-
1, 1, 1, 1
-
16, 2, 8, 2, 2, 5
-
1, 14, 2, 2, 7,3
-
2, 4, 4, 1
-
1, 2, 1, 4
-
2, 1, 1, 2
-
4, 1, 2, 4
-
4, 1, 1, 2, 2
-
2, 6, 1, 6
-
1, 4, 1, 2, 2
-
3, 8, 3 ,4, 2
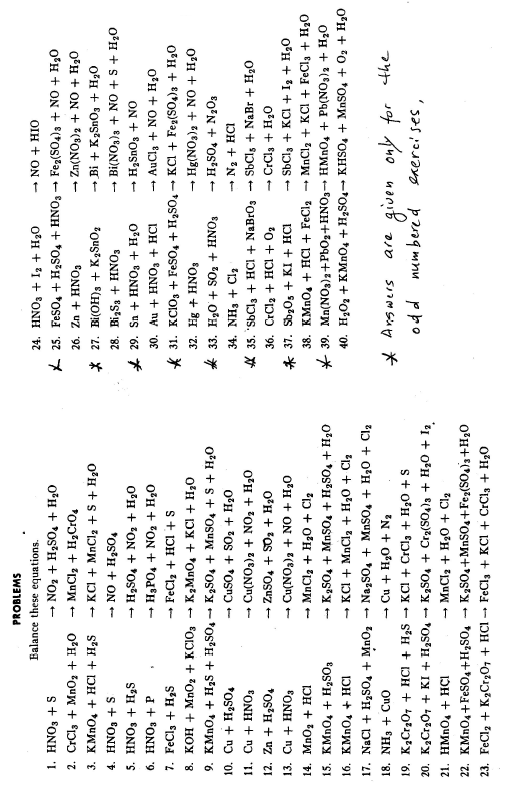
Answers to Odd Numbered Exercises: page 13

19ch3 chemical reactions
3/19/2015


